This document covers several key topics in geography related to populations and rivers/coasts:
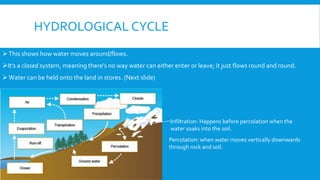
1) It discusses the hydrological cycle and how water is stored and moves through different processes like percolation and infiltration.
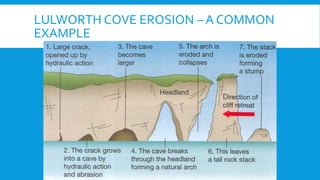
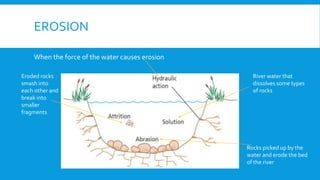
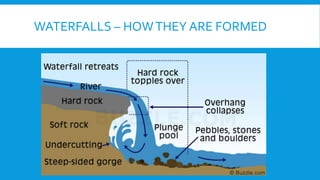
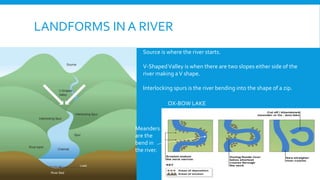
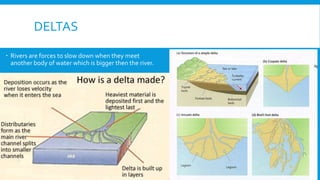
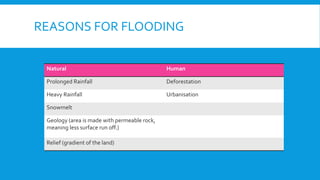
2) It examines different landforms created by rivers like meanders and ox-bow lakes. It also looks at reasons for flooding and a case study of Boscastle.
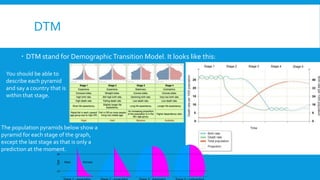
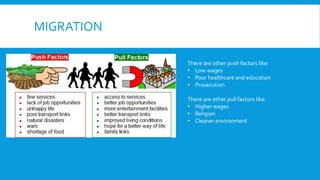
3) Population topics include the demographic transition model, overpopulation issues, aging populations, and case studies on policies like China's one child policy and urbanization trends.