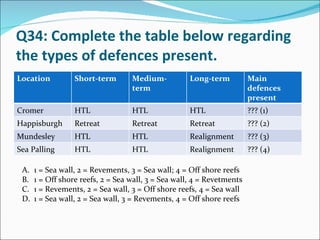
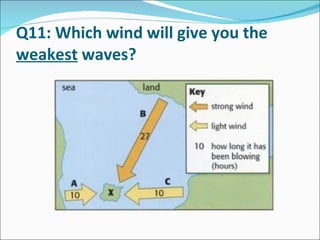
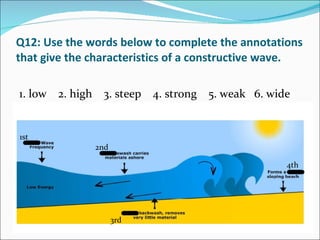
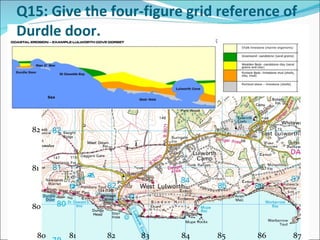
This document contains a quiz about coastal landforms and processes. It includes multiple choice and true/false questions about coastal geology, weathering and erosion processes like hydraulic action, and coastal features like headlands, stacks and spits. Coastal management strategies and Shoreline Management Plans (SMPs) for different areas of the UK coast are also discussed.


















![Q19: Fill in the missing gaps that will give you a possible 6 mark answer to the question below. Using an example, describe and explain the coastal formations found on a headland. [6] The Foreland, a chalk headland on the _____Coast has all of the features of an eroded headland (caves, arches, stacks and stumps). Old Harry, is a particularly famous example of a _____ and Old Harry's Wife is an example of a stump. These features are formed when a headland is eroded by the waves - by _______________ and solution, particularly along lines of weakness in the rock. The erosion of a headland begins as erosion exploits a weakness in a rock forming a ____. If the weakness runs through the headland, two caves may form back to back, eventually forming an ____, an opening which passes right through the headland. Wave attack continues at the base of the arch, whilst weathering processes such as _________ attack the roof of the arch until it eventually collapses leaving a stack (an isolated column of rock). Again this is attacked by weathering and erosion processes until it collapses leaving the base, which forms a ______. 1. arch 2. cave 3. Dorset 4. freeze-thaw 5. hydraulic action 6. Norfolk 7. stump 8. stack](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lesson13-theme1coastsreview-110202120029-phpapp02/85/GCSE-Geog-OCR-B-Theme-1-Coasts-review-23-320.jpg)