Embed presentation
Downloaded 92 times






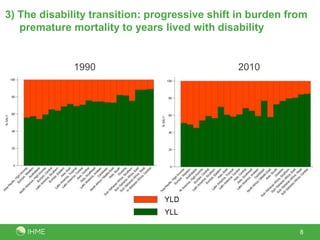
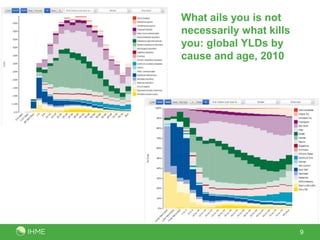
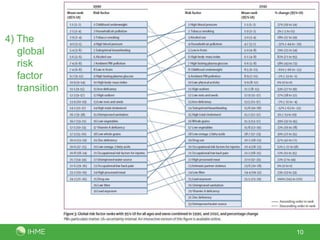
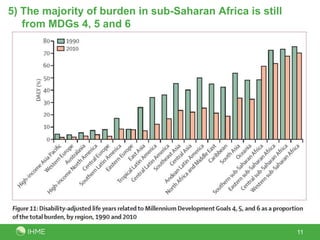
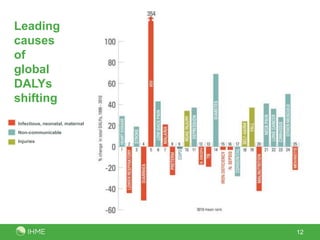

The document summarizes the findings of the Global Burden of Diseases, Injuries, and Risk Factors 2010 study conducted by 486 authors from 302 institutions in 50 countries. The study analyzed 291 diseases and injuries, 1,160 disabling sequelae, 67 risk factors, and provided 650 million findings for 187 countries from 1990-2010. Key observations included rapid demographic changes outside sub-Saharan Africa, a progressive disease transition from communicable to non-communicable causes, a disability transition resulting in more years lived with disability, a global risk factor transition, and sub-Saharan Africa still facing a large burden from MDGs 4, 5 and 6.












