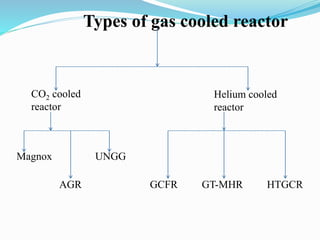
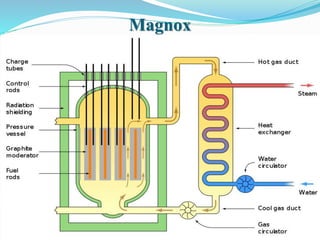
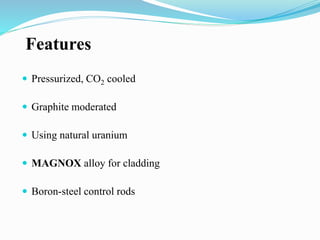
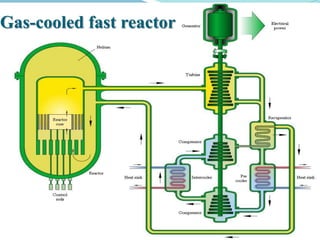
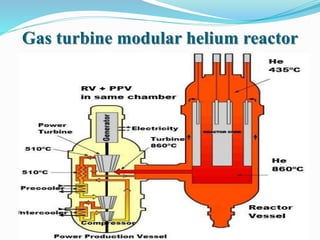
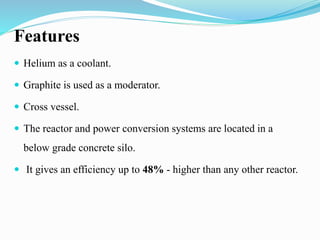
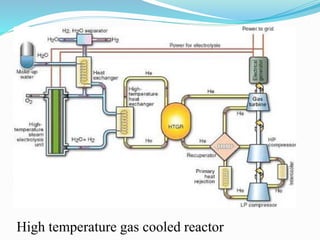
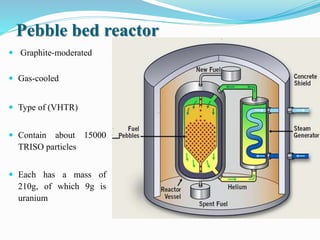
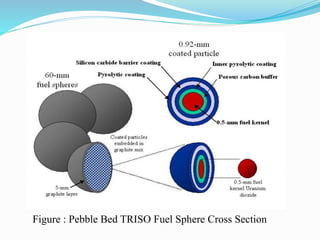
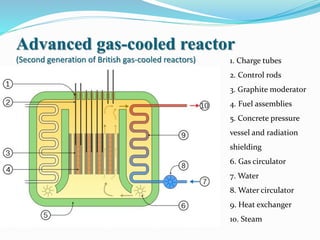
Gas-cooled reactors use gas like CO2 or helium as a coolant and graphite as a moderator. There are several types of gas-cooled reactors including Magnox reactors, UNGG reactors, Advanced Gas-cooled Reactors (AGR), Gas-cooled Fast Reactors (GCFR), Gas Turbine Modular Helium Reactors (GT-MHR), Very High Temperature Reactors (VHTR), High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactors (HTGCR), Pebble Bed Reactors (PBR), and Prismatic Block Reactors (PMR). Each type has distinct features related to the coolant, moderator, fuel type, and design configuration.