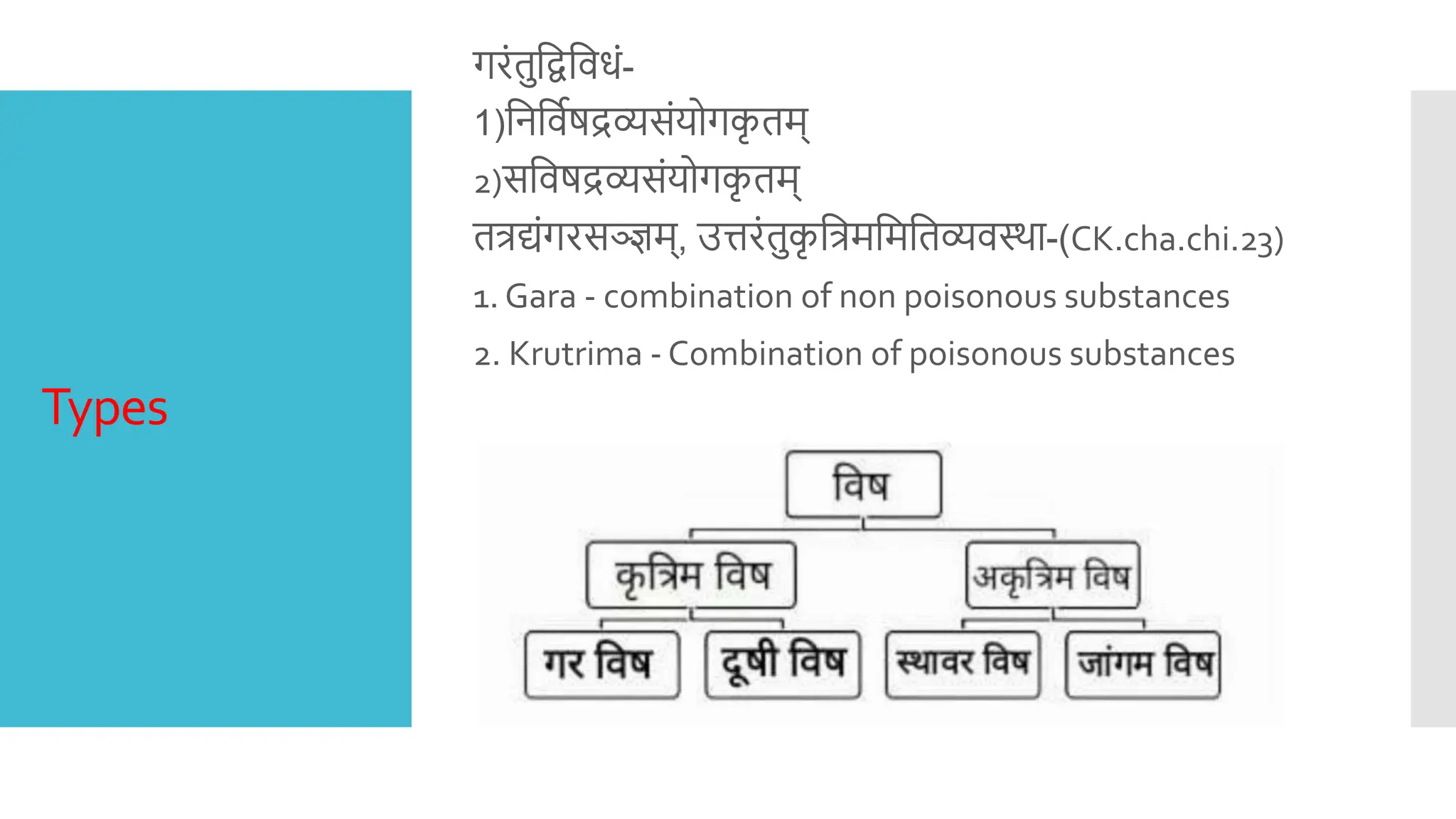
This document provides an overview of garavisha (artificial poisoning) in Ayurveda. It defines garavisha as a type of artificial poison produced by combining substances like excreta, incompatible drugs, and mild poisons. It causes chronic toxicity if consumed regularly. The document outlines the various types, routes of administration, signs and symptoms, and treatments described in Ayurvedic texts for garavisha poisoning, including vamana (emesis therapy) and administration of hemacurna (gold ash).