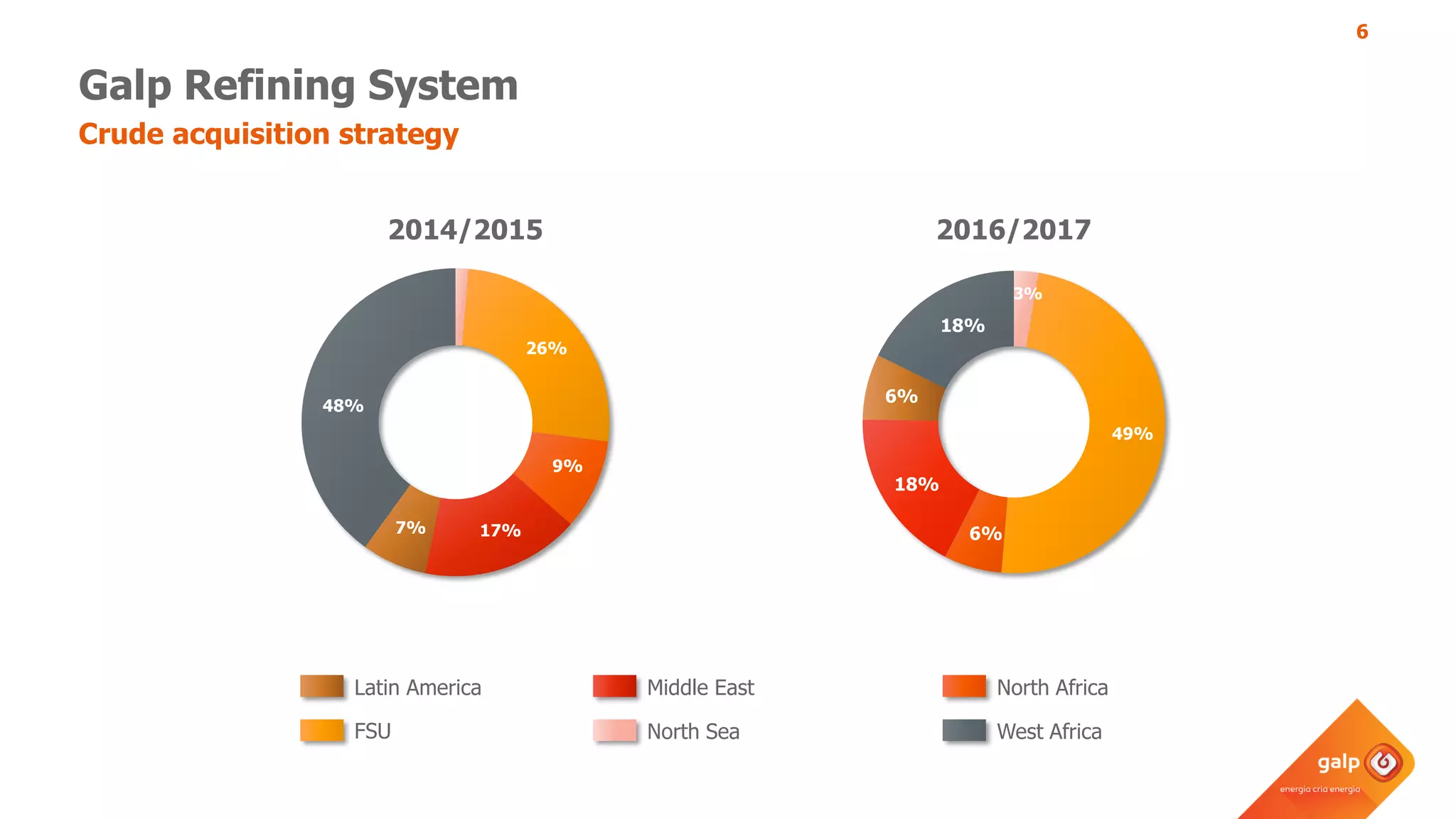
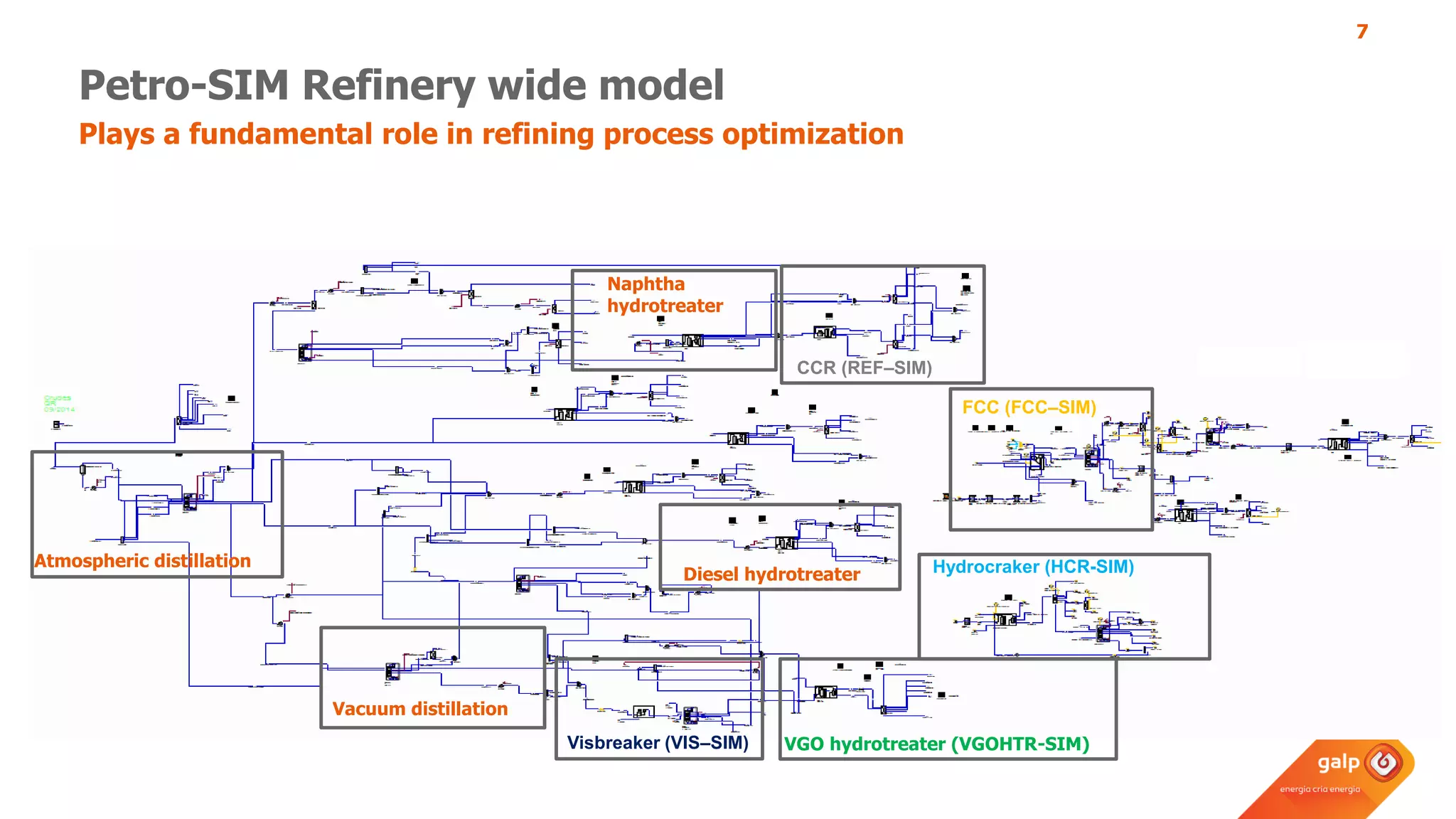
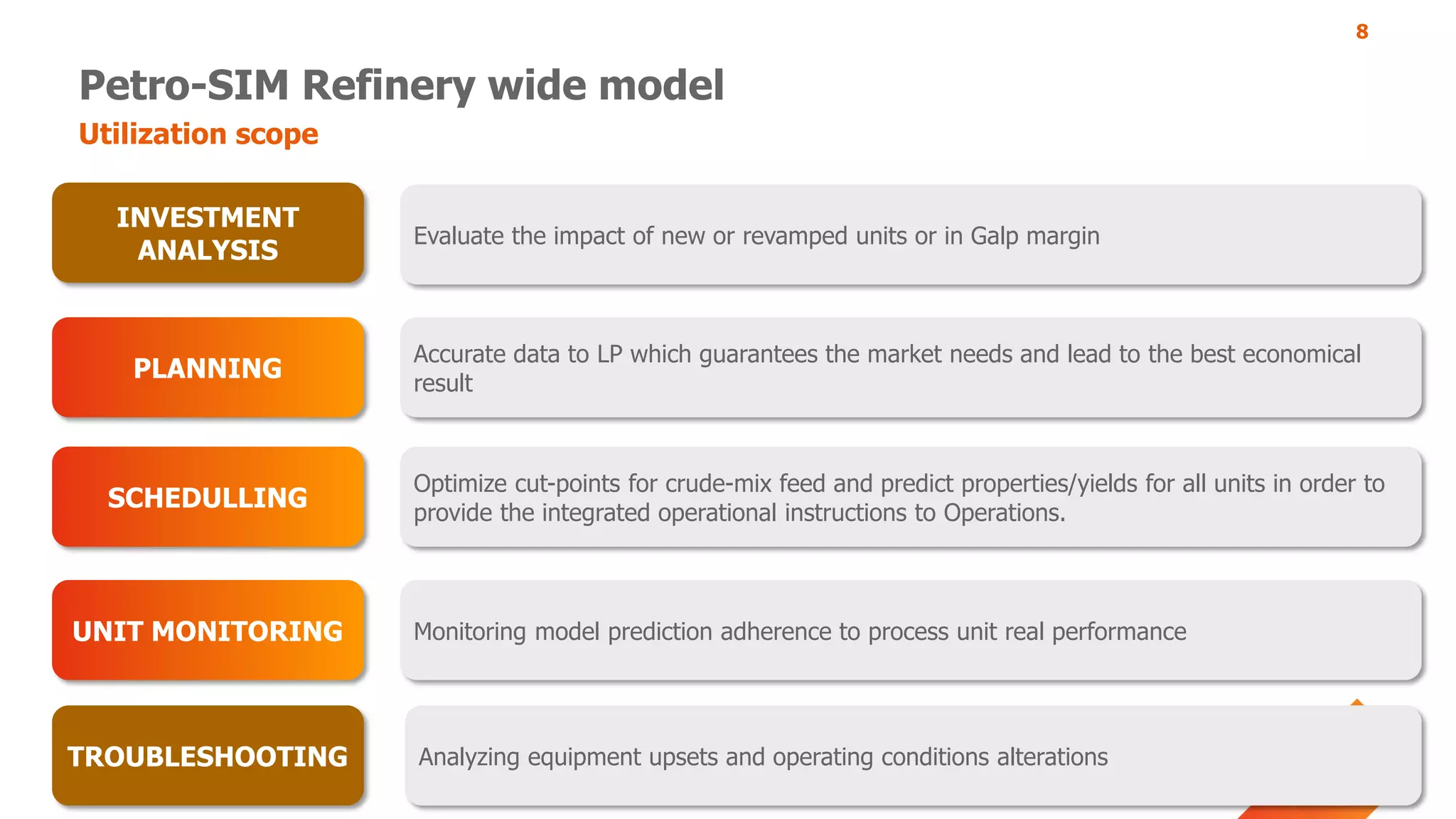
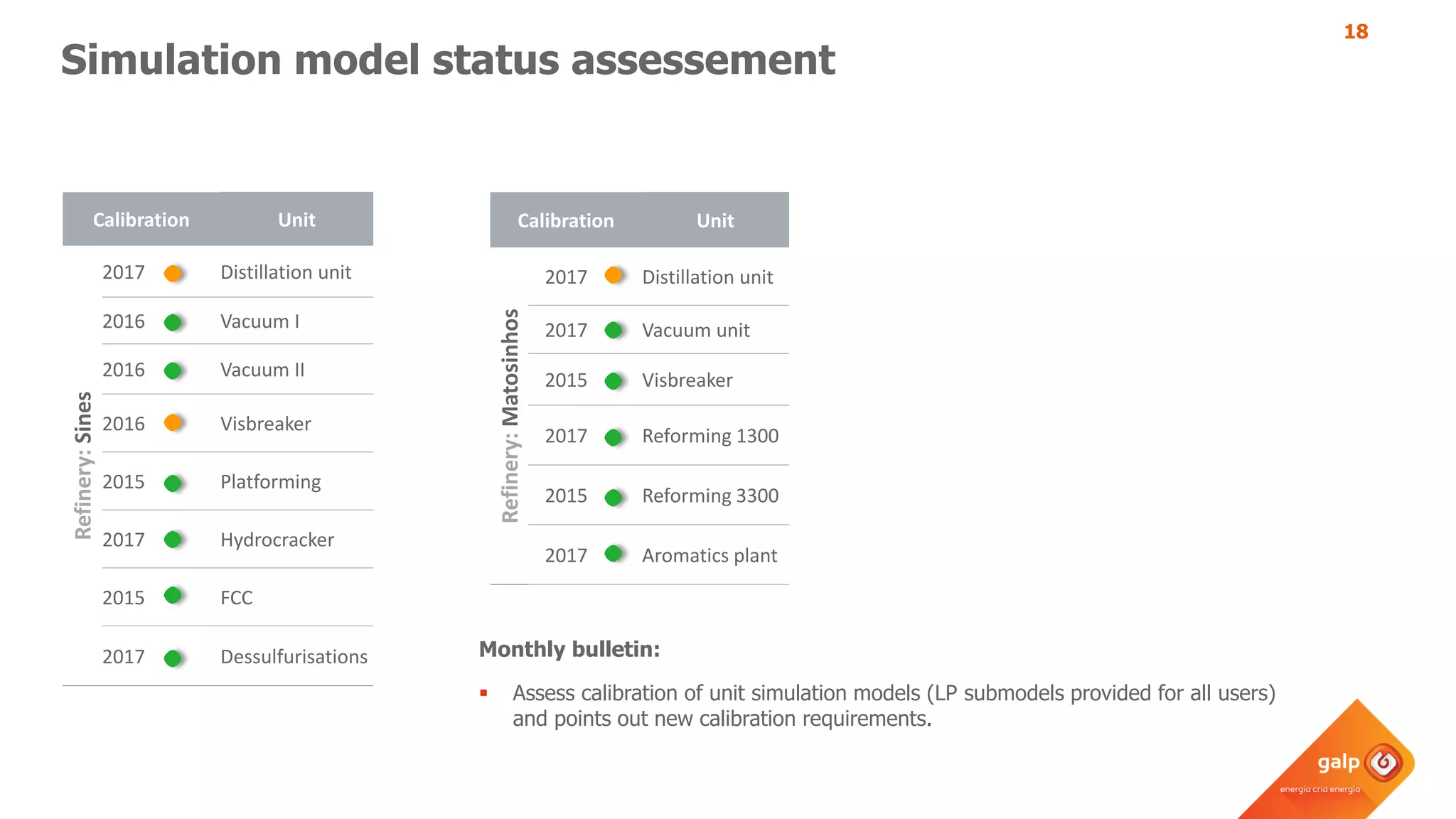
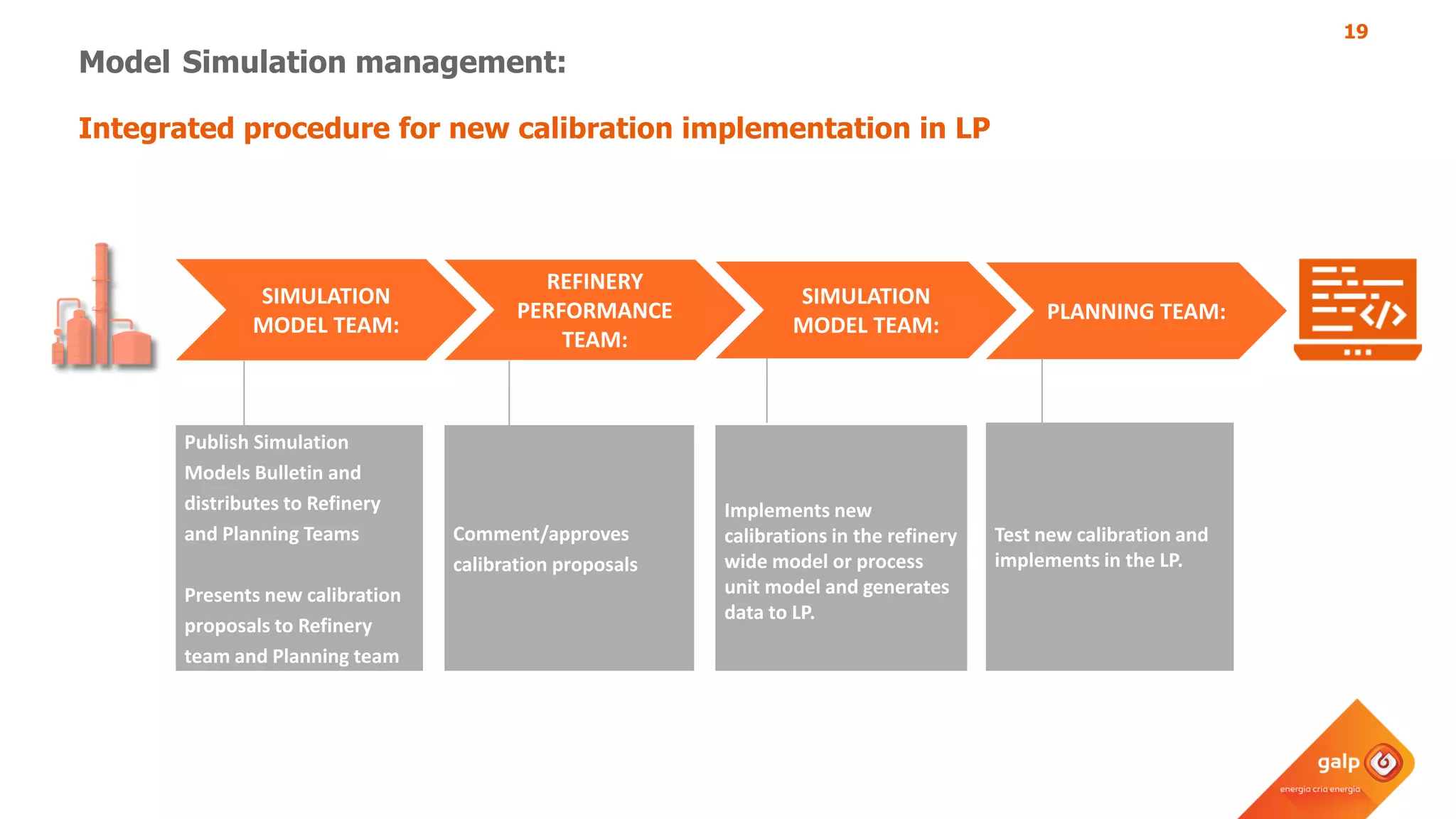
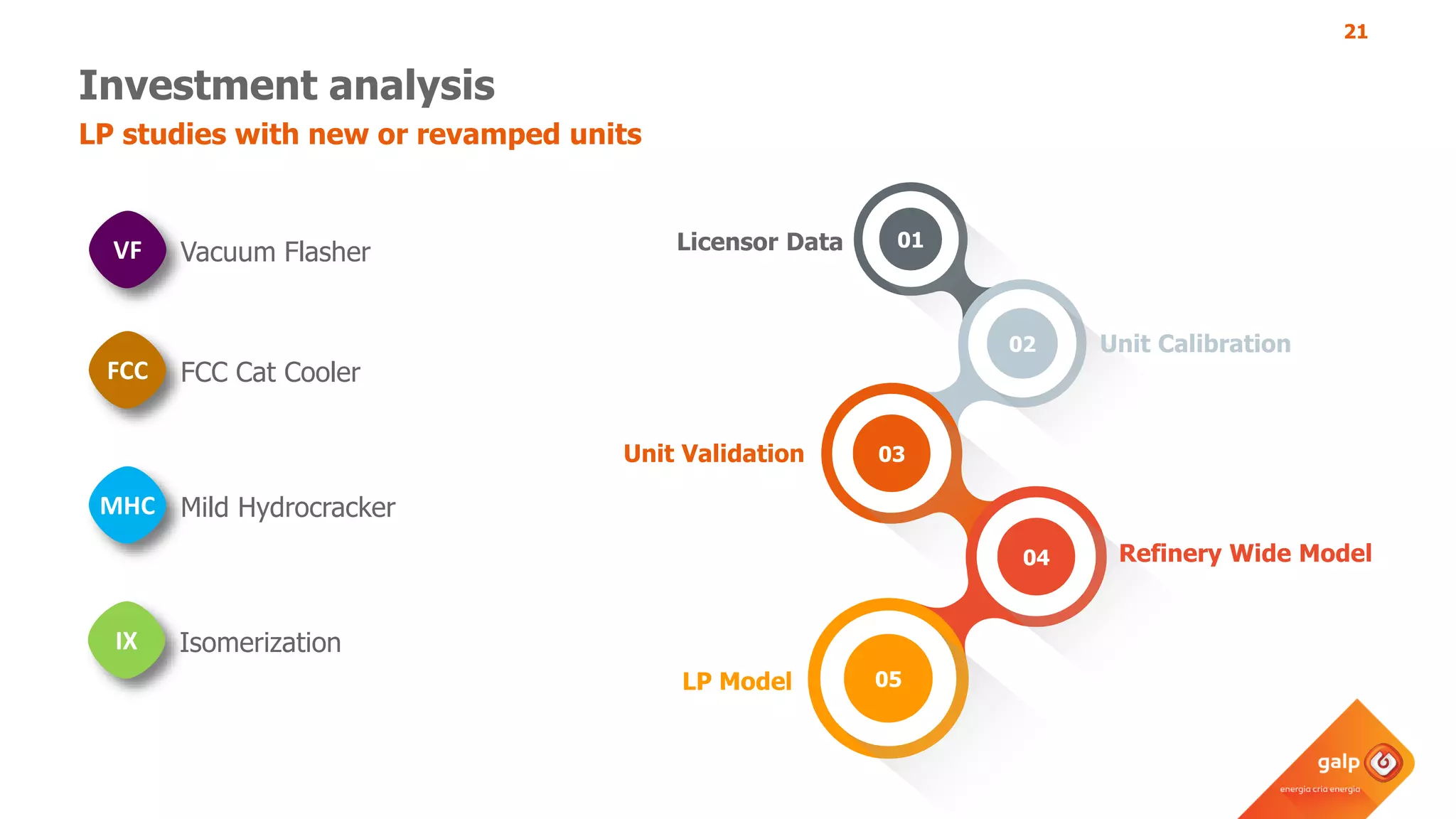
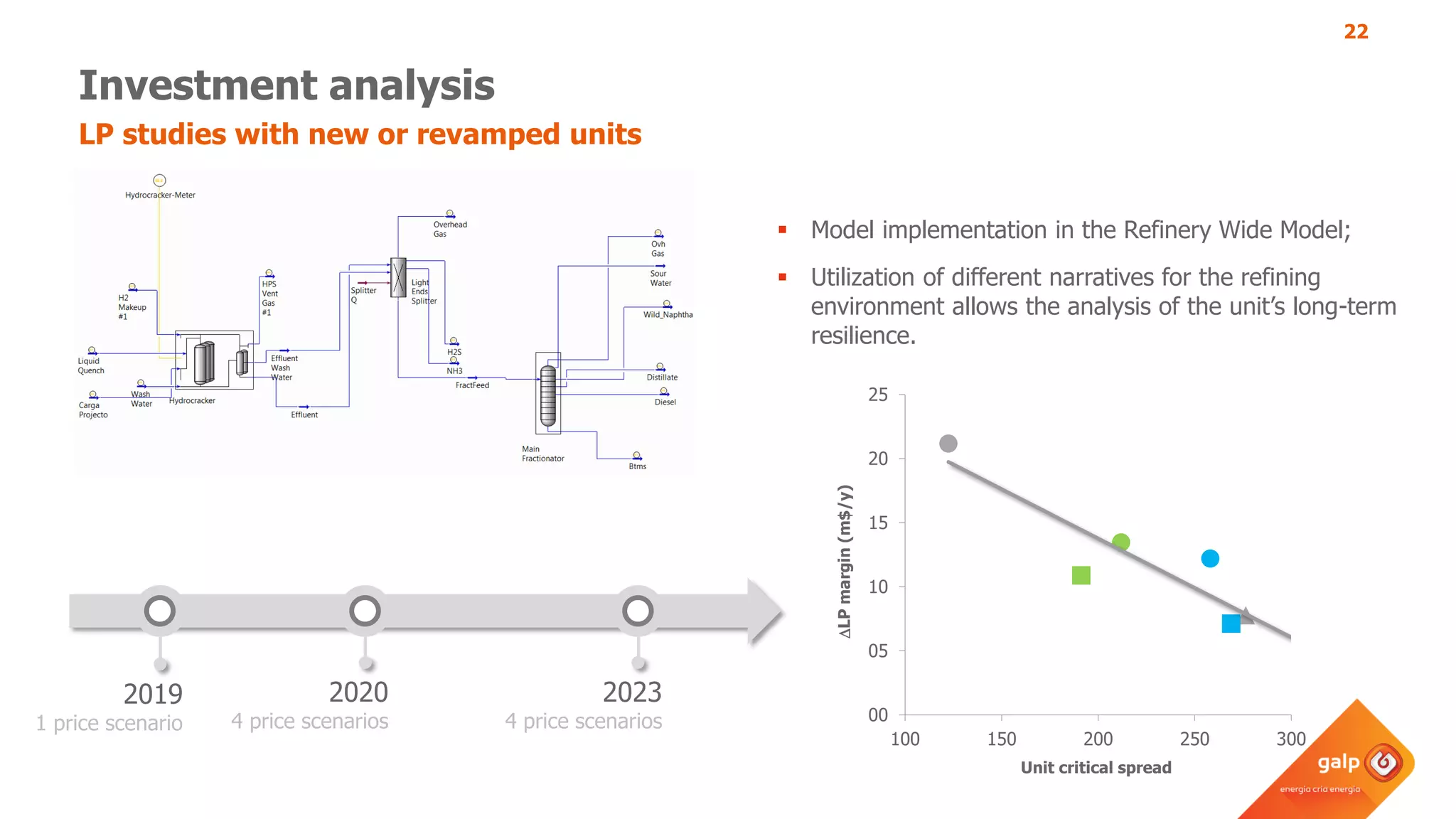
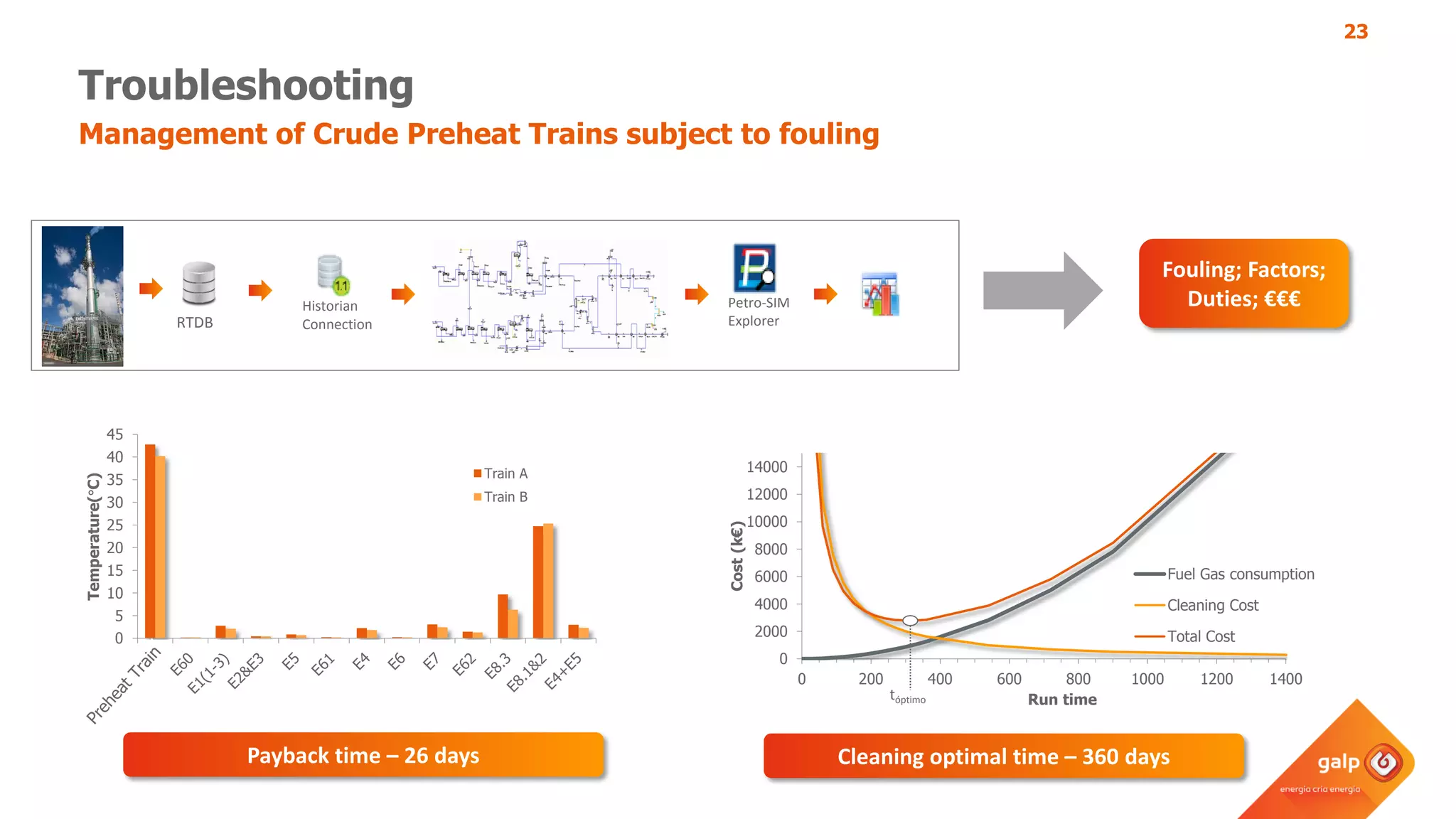
The document discusses Galp's use of a refinery-wide model to optimize operations. It summarizes:
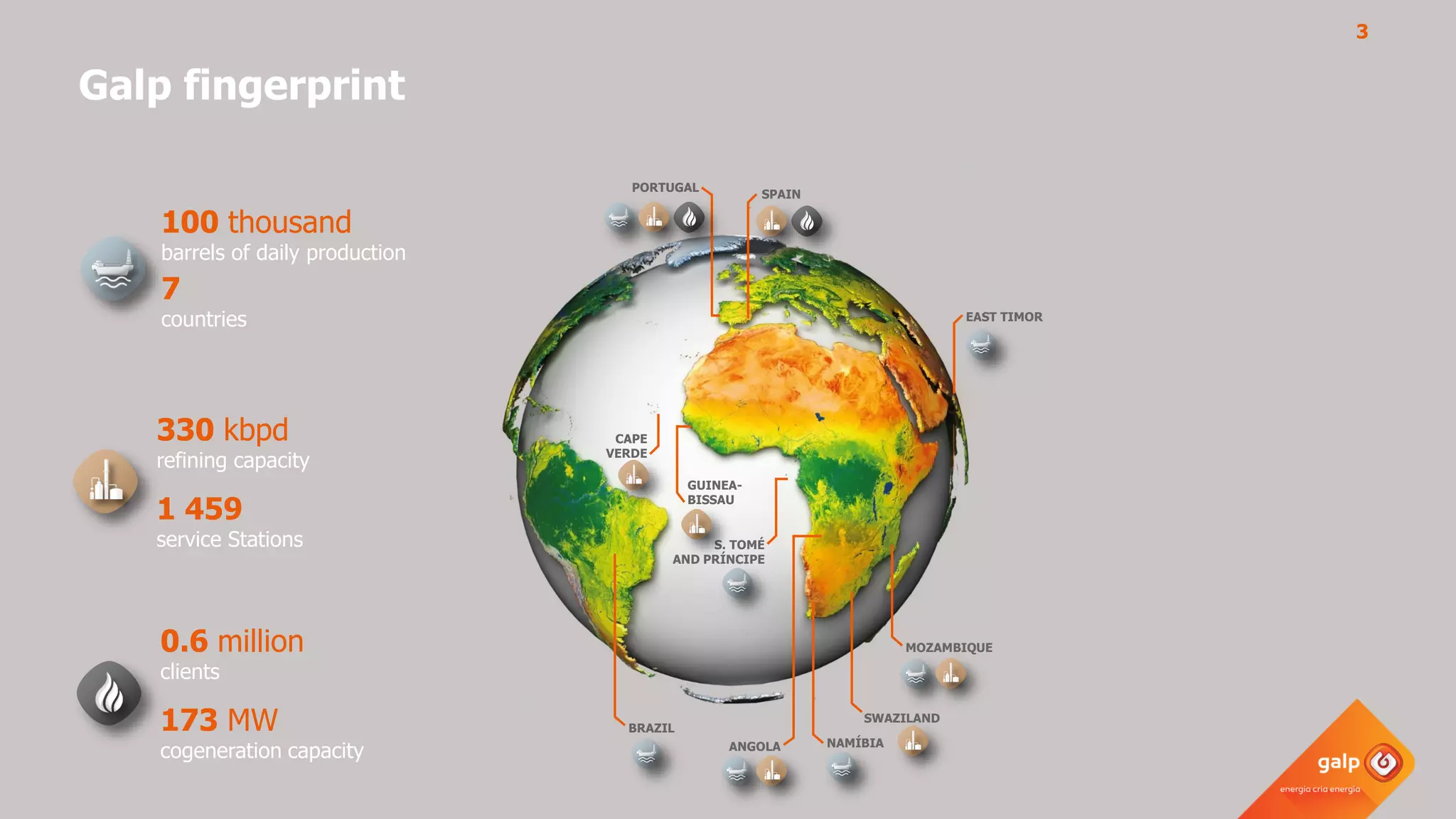
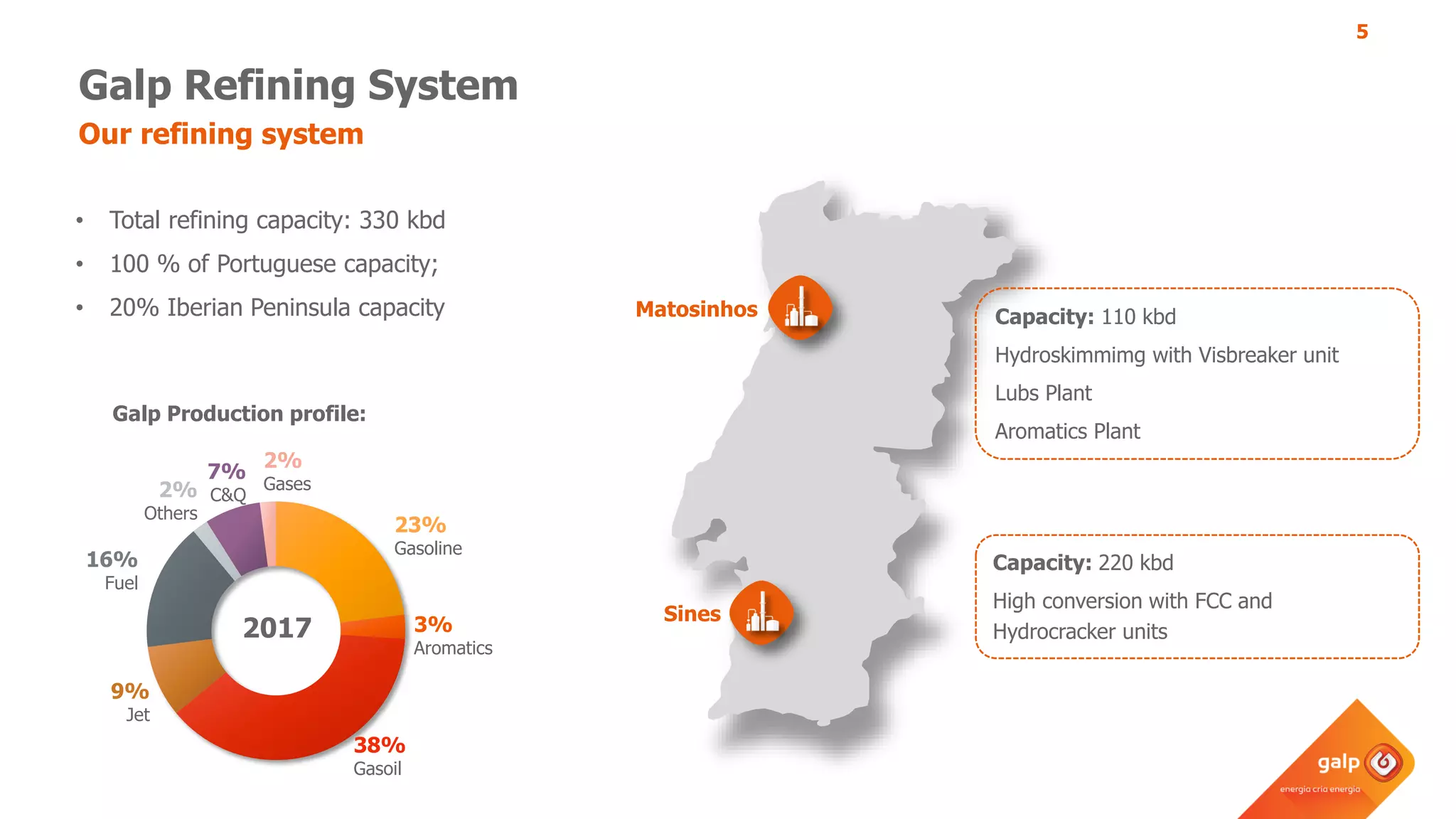
- Galp's refining capacity across multiple refineries in Portugal and Spain.
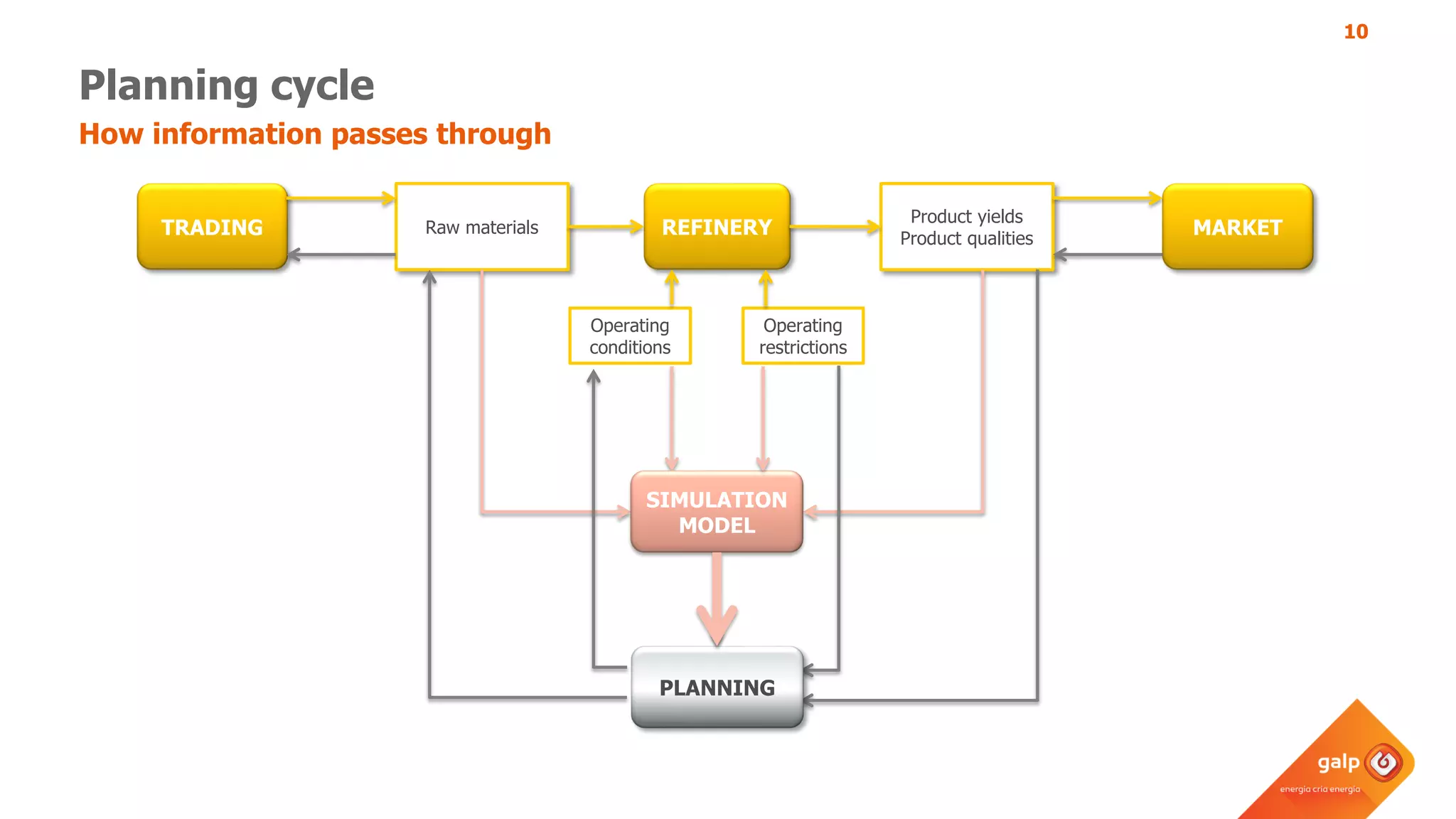
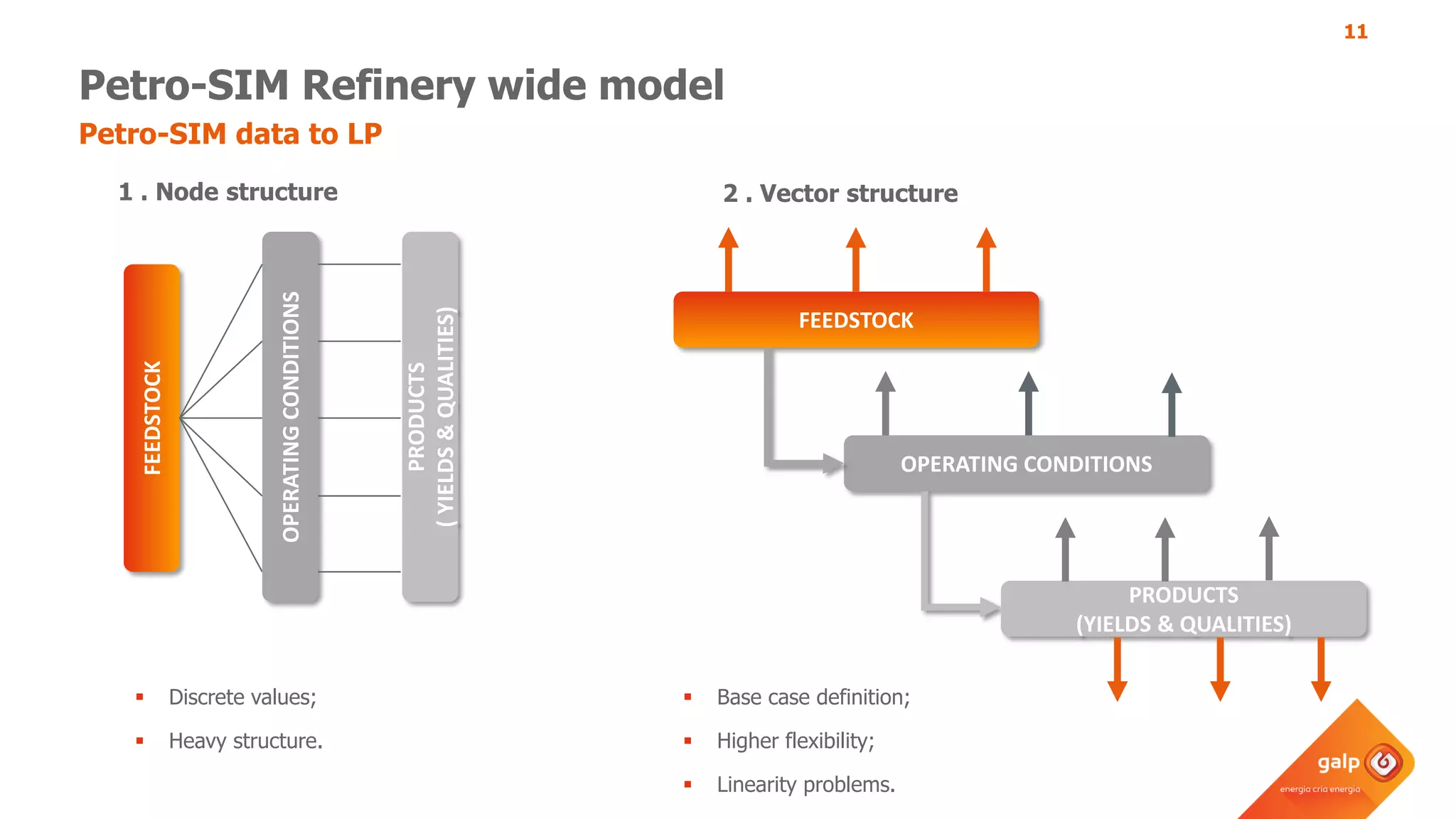
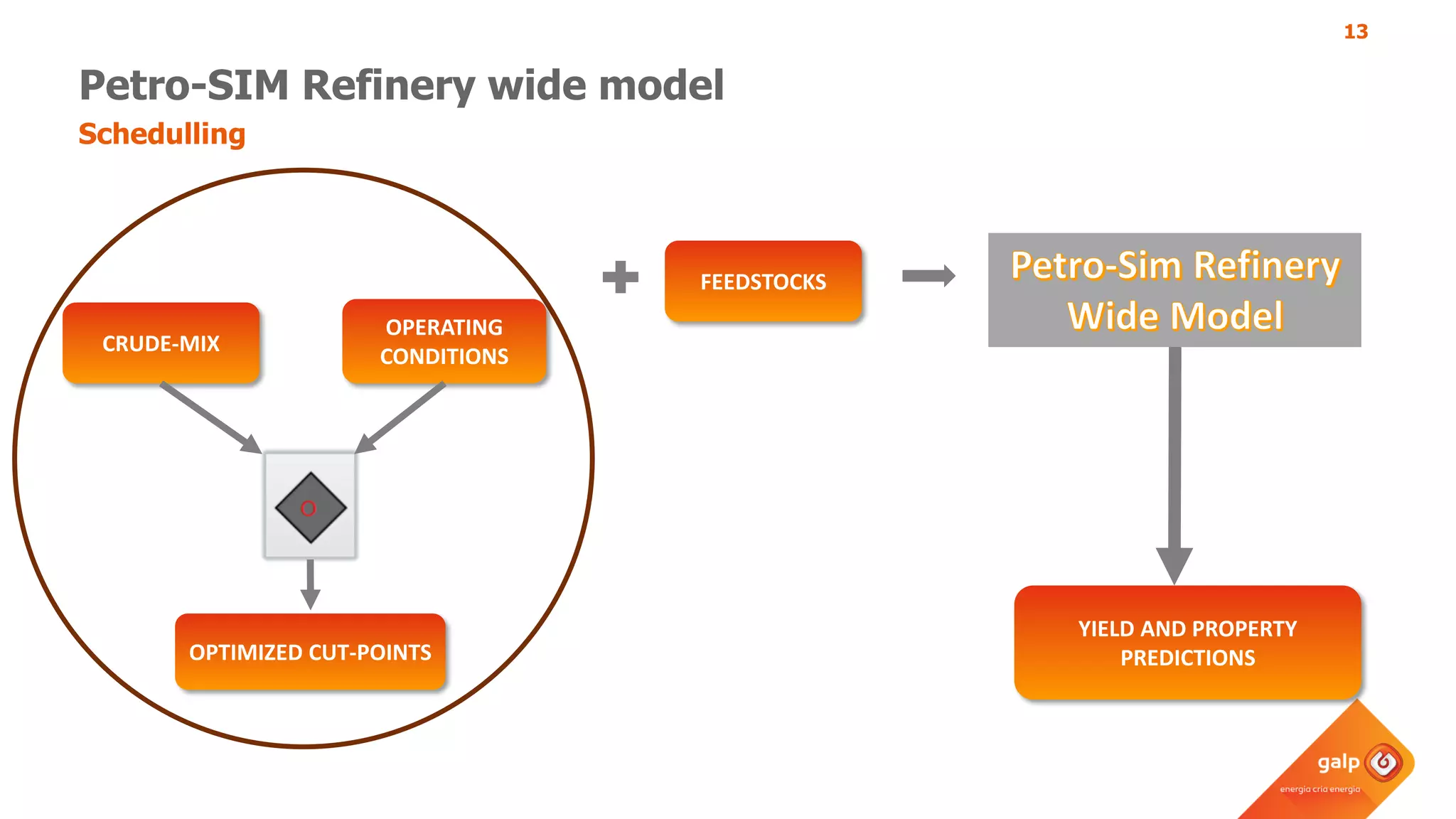
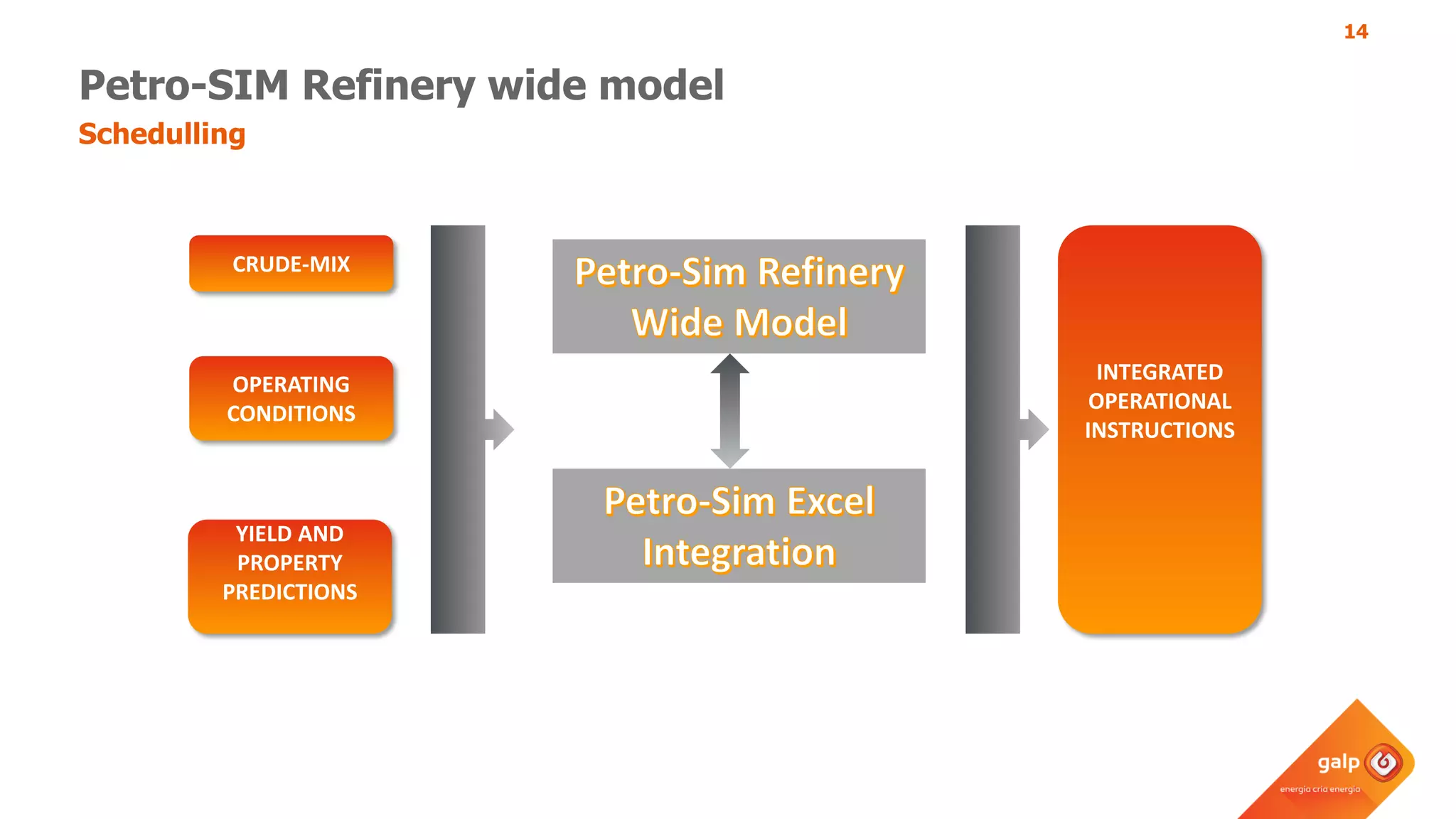
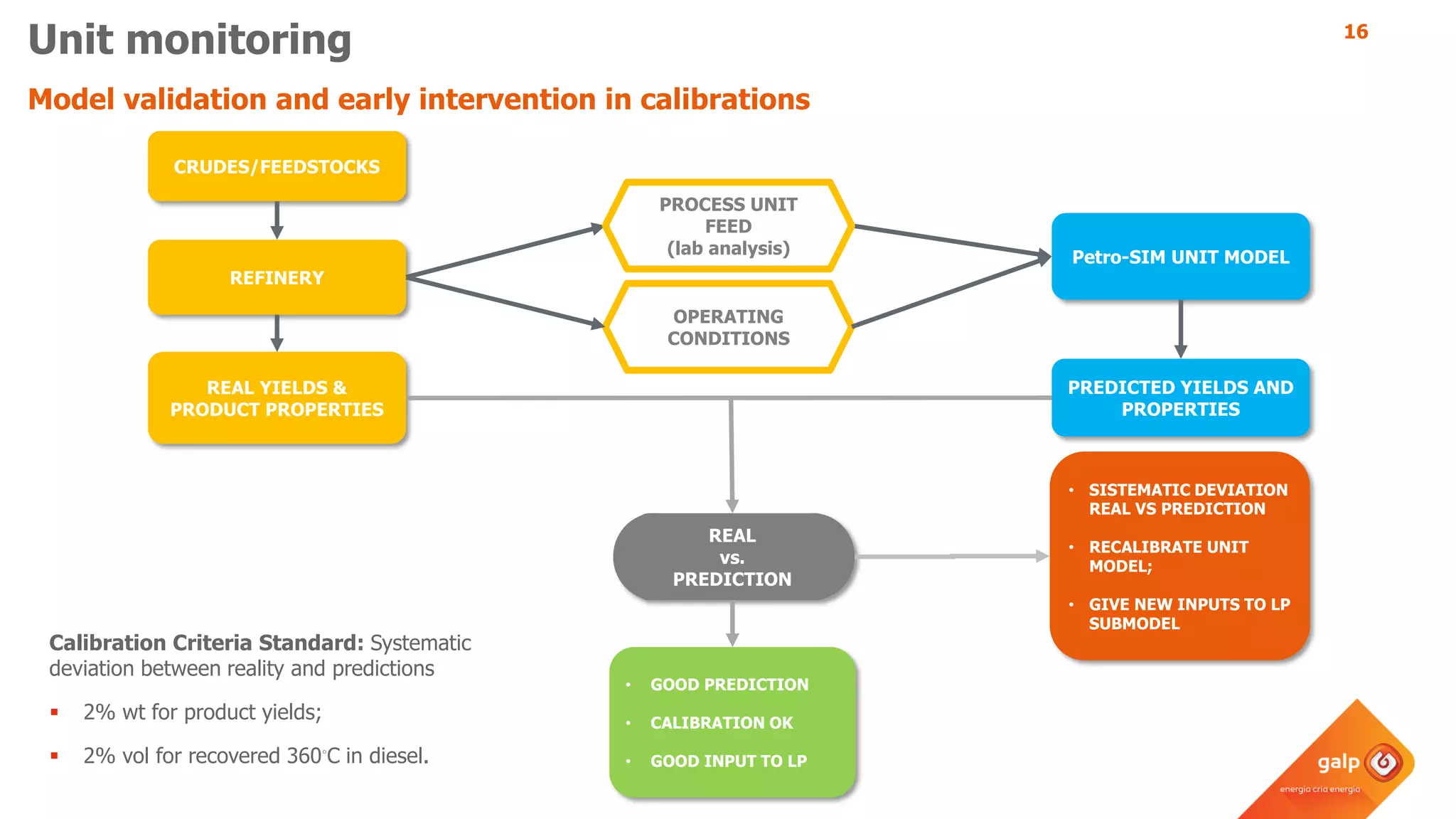
- How the refinery-wide model is used for planning, scheduling, unit monitoring, and investment analysis to optimize crude selection and refining processes.
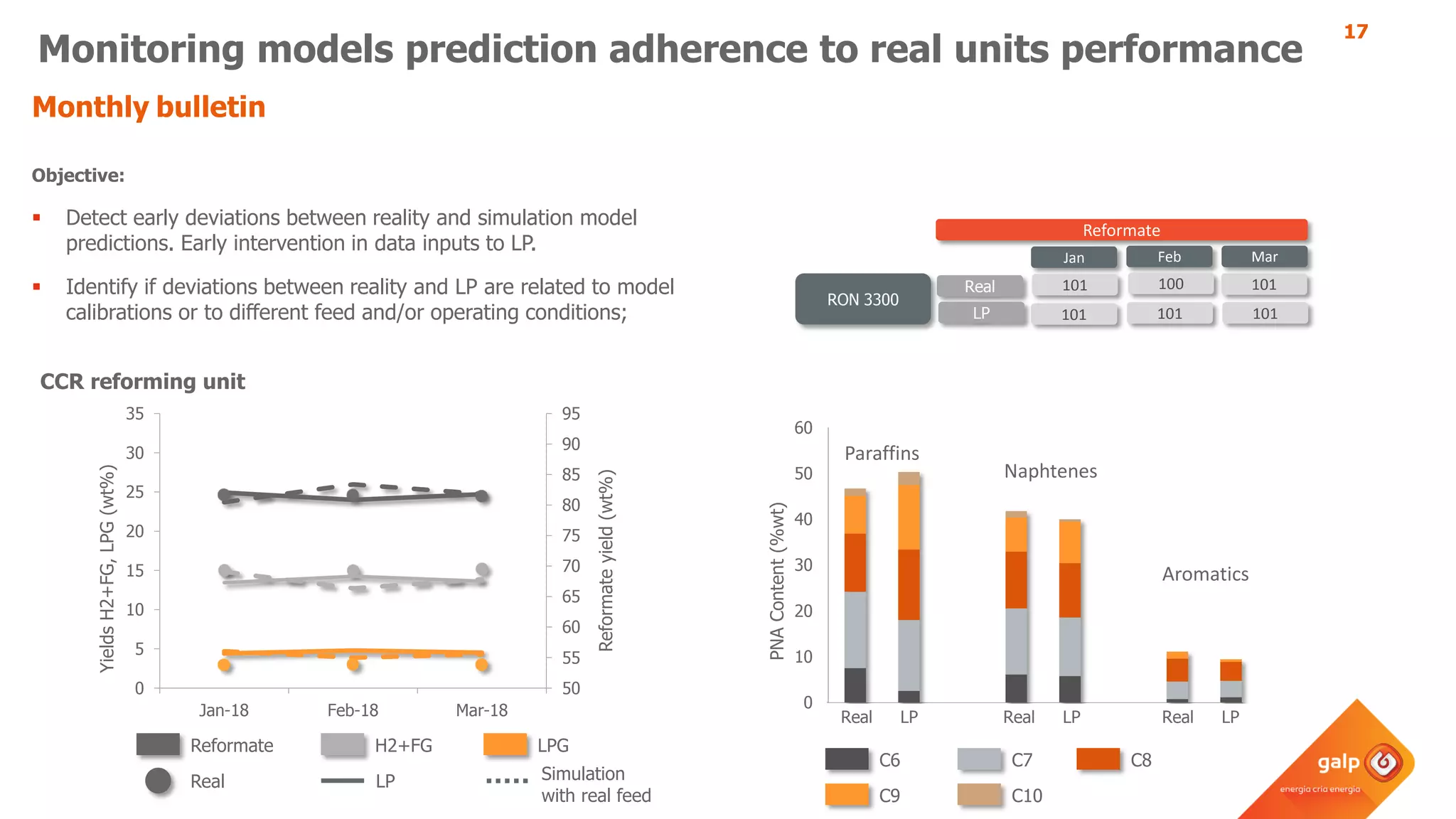
- Examples of how the model predicts yields and properties to support scheduling crude slates and unit cut points and validates predictions against real unit performance.