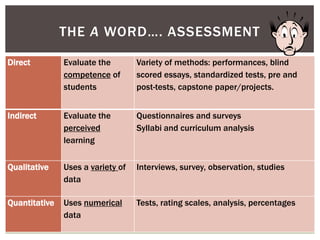
This document summarizes a presentation on teaching information literacy skills for the workplace. The presentation discusses defining information literacy, assessing student learning, and incorporating real-world skills into assignments. Attendees participated in activities to brainstorm outreach strategies, map assignments to information literacy standards, and develop assessment methods. The goal is to ensure students graduate with skills employers need by designing assignments around authentic tasks and evaluating learning through work-relevant assessments.