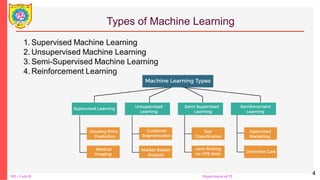
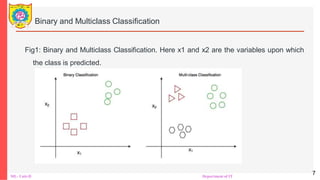
The document provides an overview of machine learning, detailing its types including supervised, unsupervised, semi-supervised, and reinforcement learning. It explains key concepts such as dataset preparation, algorithms used for different learning types, advantages and disadvantages, and real-world applications like image segmentation and fraud detection. Additionally, it covers specifics about classifiers, regression methods, and the mechanisms behind reinforcement learning.