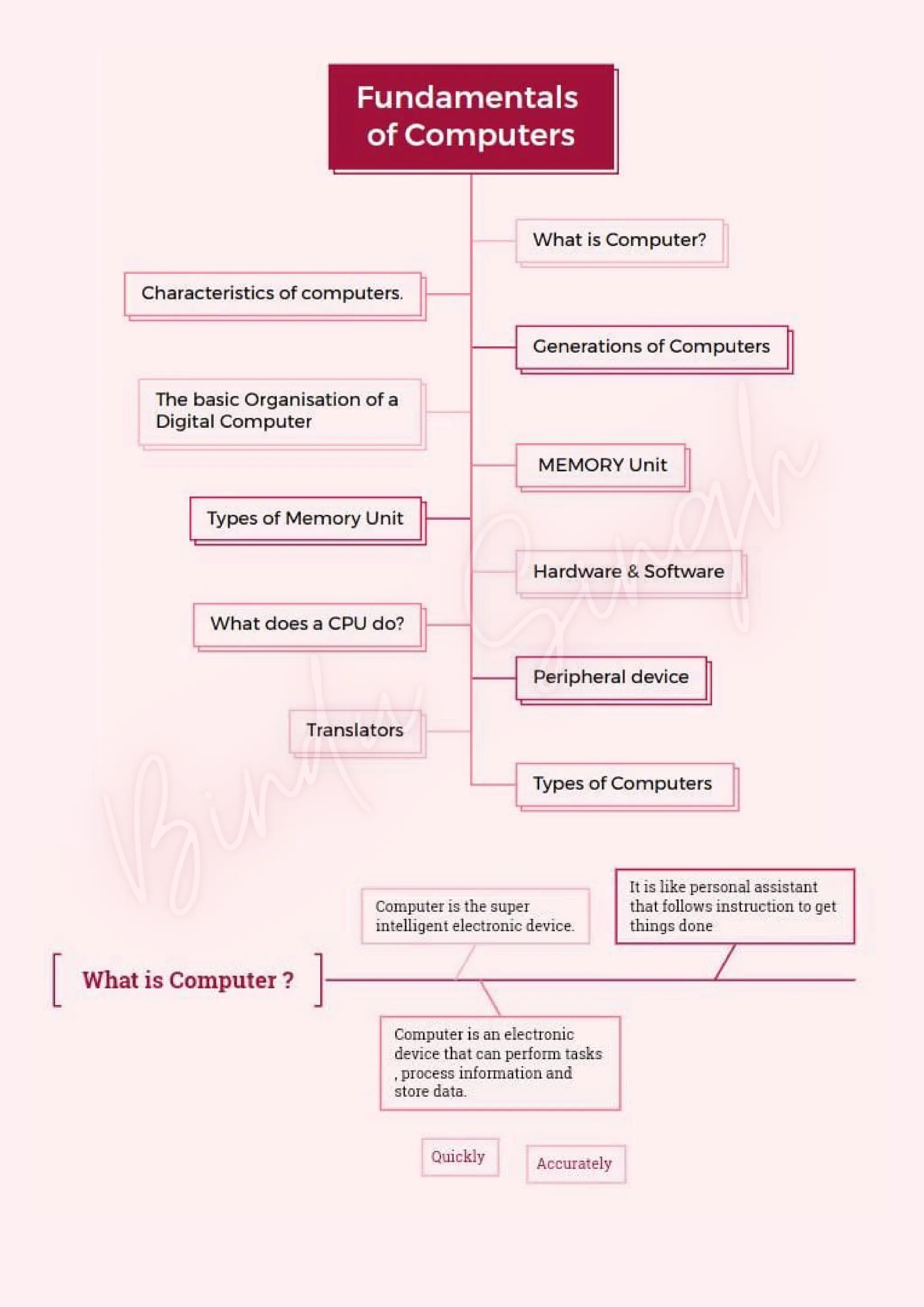
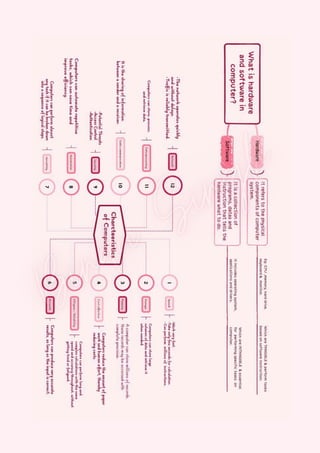
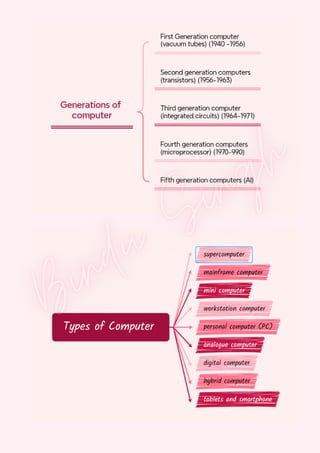
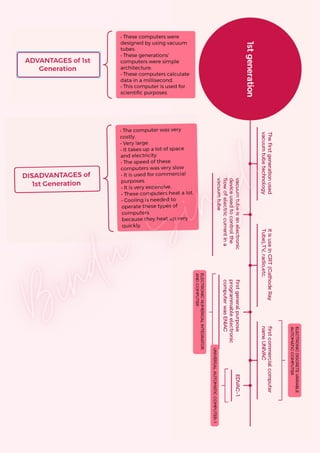
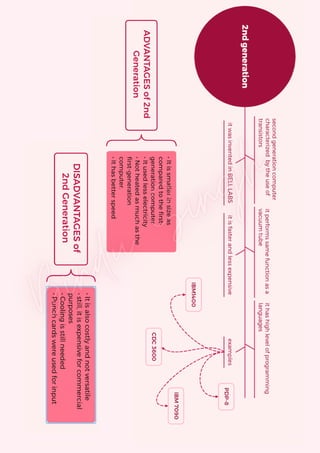
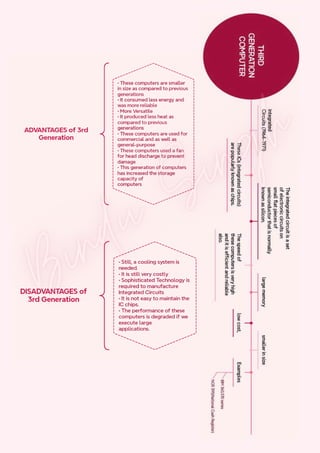
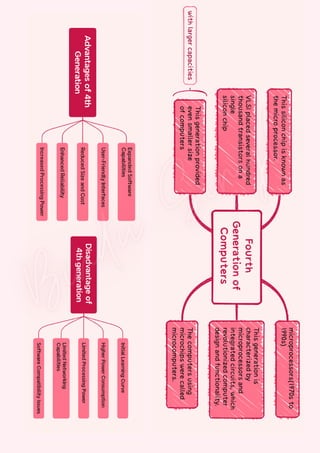
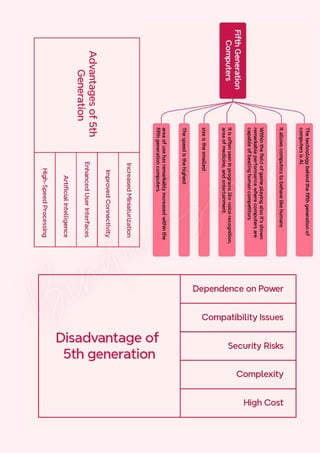
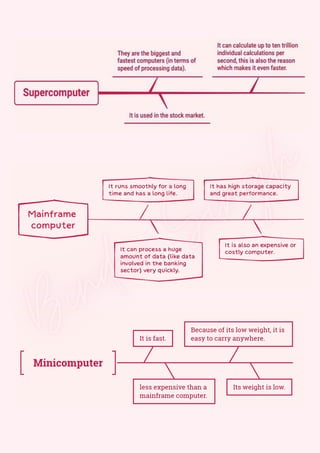
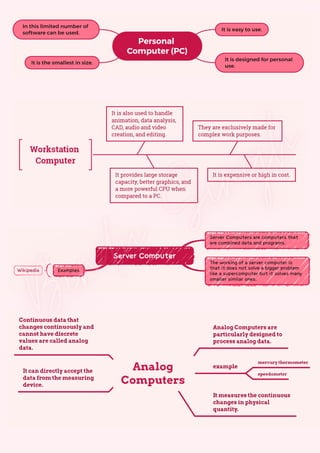
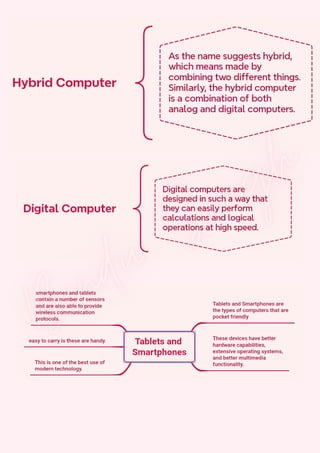
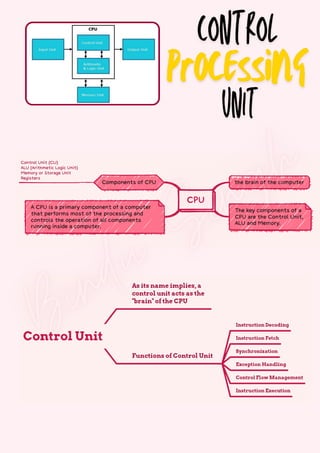
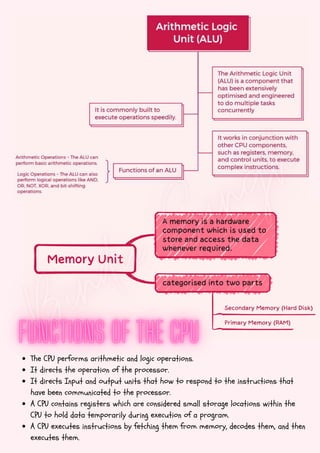
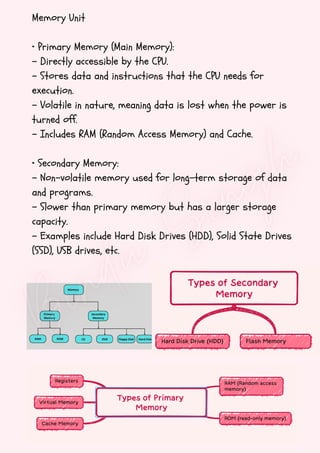
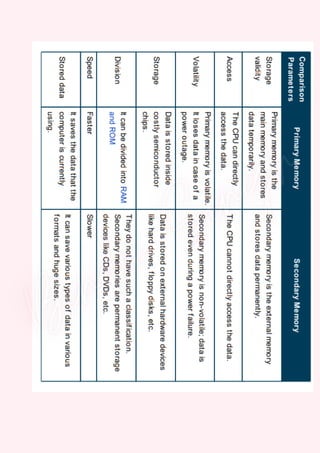
Computers are classified by size, functionality, and data handling capabilities, with the CPU performing key functions such as fetching, decoding, executing, and storing instructions. Peripheral devices enhance computer functionality by providing input, output, and storage capabilities. Primary memory is volatile and directly accessible by the CPU, while secondary memory is non-volatile and used for long-term storage.