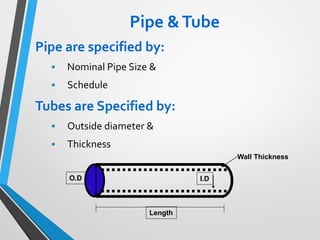
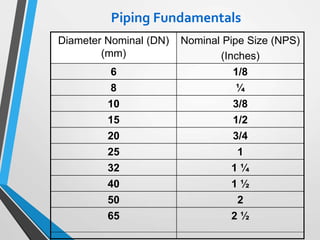
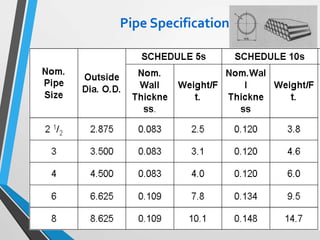
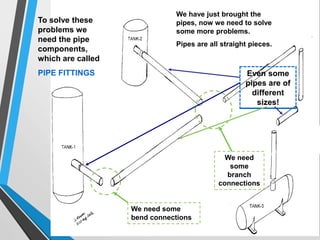
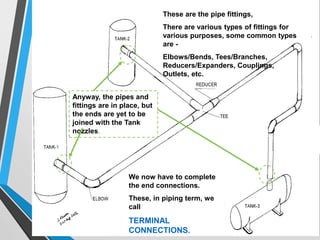
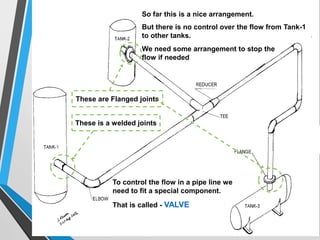
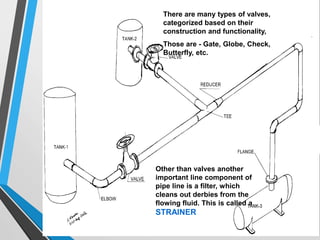
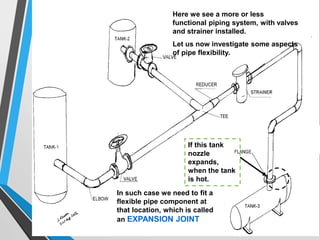
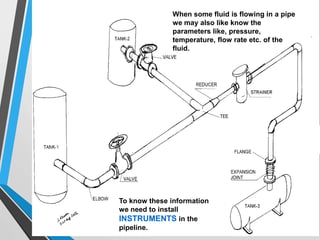
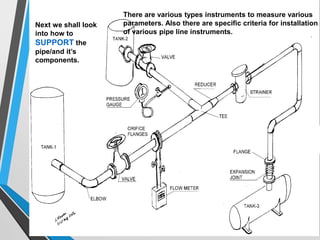
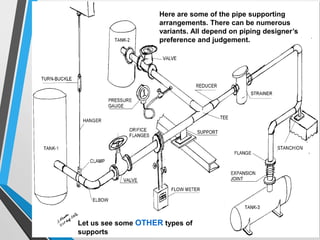
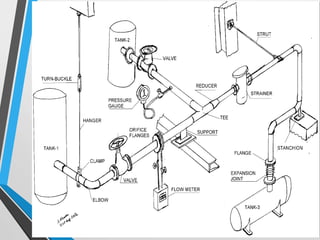
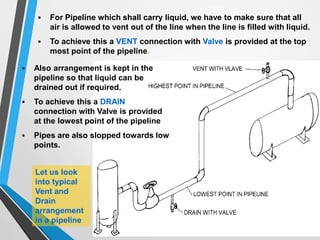
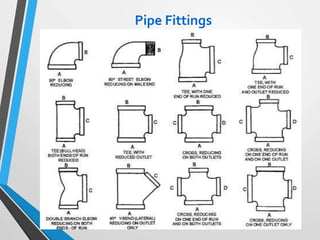
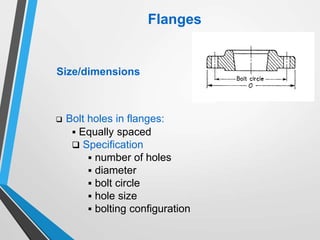
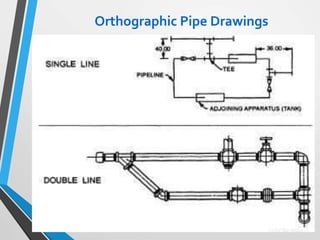
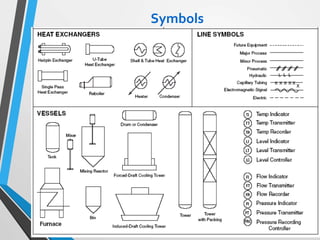
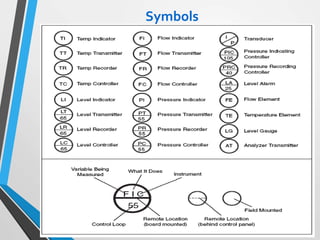
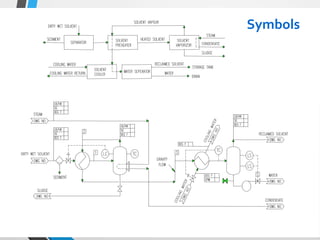
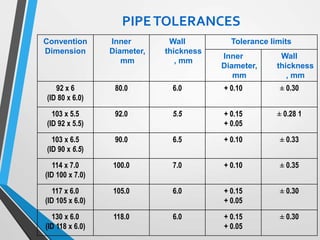
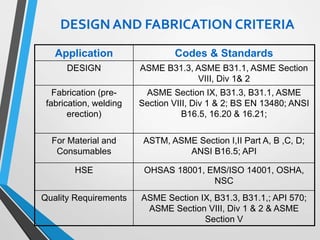
The document outlines the fundamentals of piping design and materials, focusing on the definitions, specifications, and applications of pipes and tubes, including their differences. It details various components such as fittings, valves, and instruments needed for effective fluid transfer in industrial settings, along with supporting structures and insulation requirements. Additionally, it addresses design codes, fabrication standards, and testing procedures essential for ensuring quality and safety in piping systems.