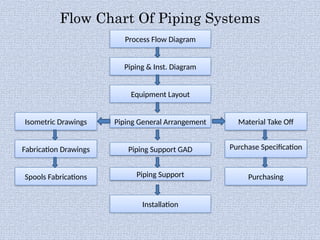
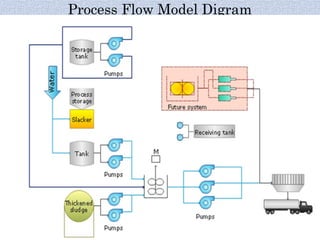
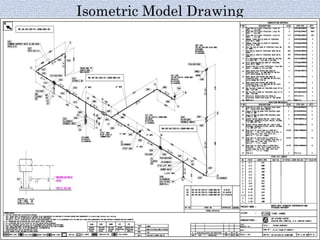
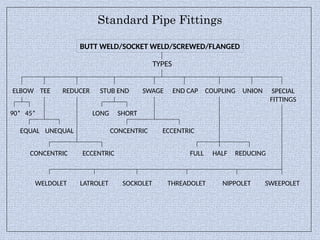
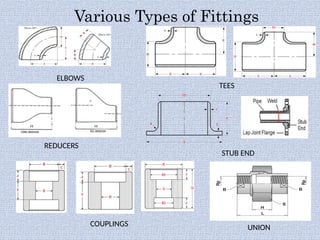
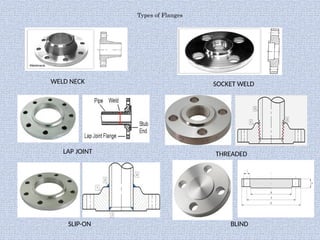
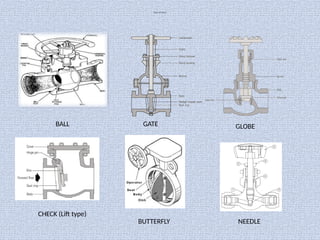
Piping systems are networks of pipes that transport fluids and include components such as fittings, valves, and flanges. Various standards govern different types of piping, while detailed design and engineering drawings are crucial for installation and maintenance. Testing for integrity and safety, including hydro-testing and pneumatic testing, is essential to ensure the quality of piping systems.