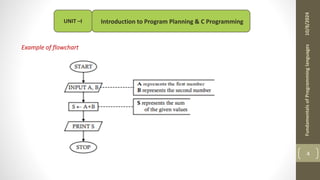
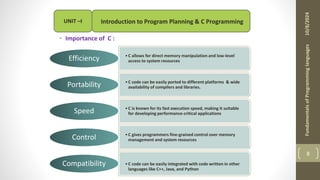
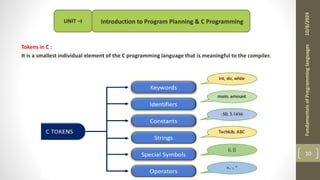
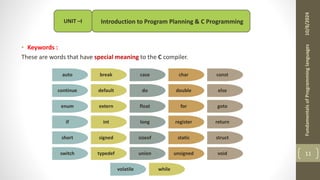
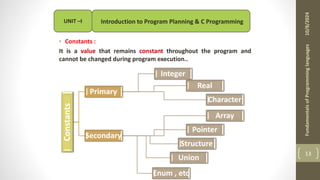
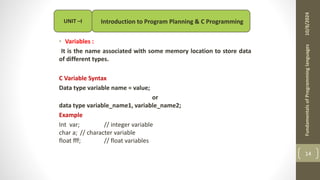
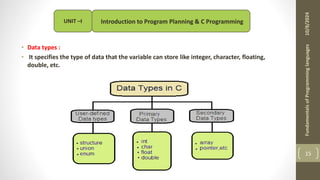
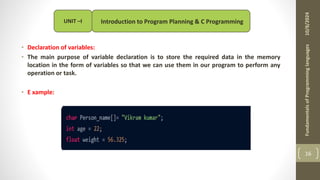
The document provides an overview of the C programming language, including its history, importance, and basic programming concepts such as algorithms, flowcharts, data types, constants, and variables. It explains the structure of algorithms and flowcharts with examples, and discusses the significance of C in terms of efficiency, portability, and speed. Additionally, it outlines key programming elements like keywords, identifiers, and the declaration of variables while highlighting the differences between constants and variables.