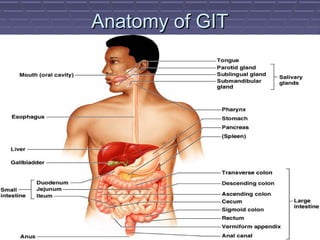
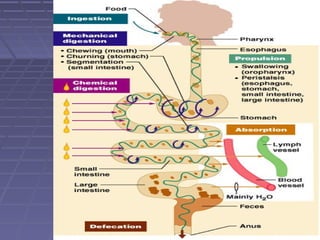
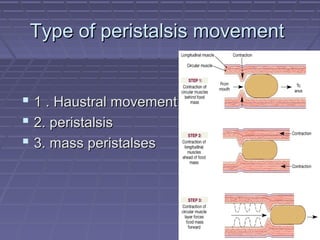
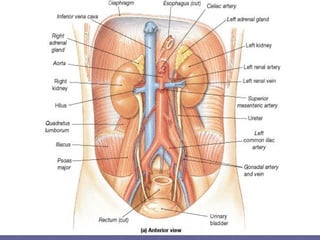
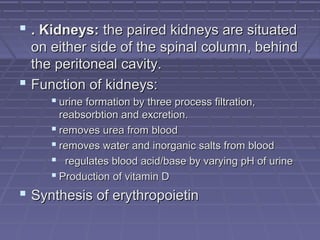
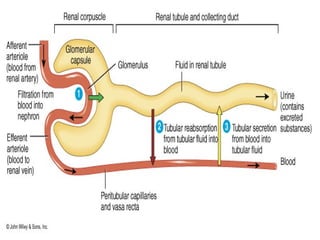
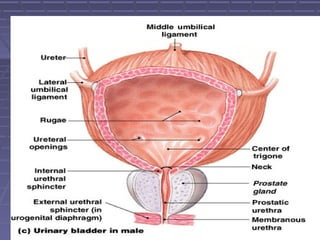
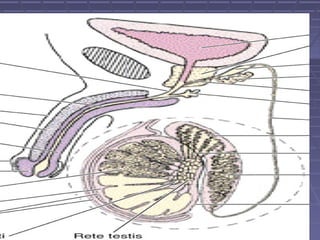
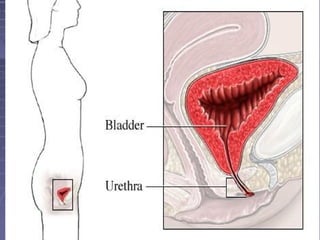
This document discusses the function of the lower intestinal tract and urinary system. It describes the anatomy and physiology of defecation and urination. Common fecal elimination problems like constipation, fecal impaction, and diarrhea are defined. Factors that influence defecation and urinary elimination are identified. Nursing assessments, diagnoses, and interventions related to maintaining normal bowel and urinary function are outlined.