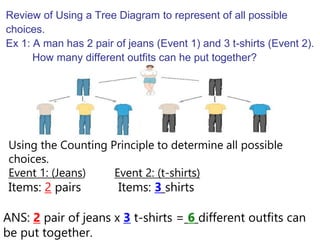
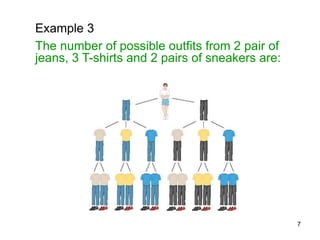
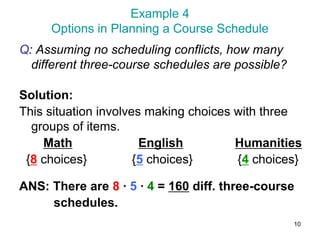
The document discusses the fundamental counting principle for determining the number of possible outcomes in a given situation. It provides examples of applying the principle to situations with two or more groups of items that can be chosen from. These include determining the number of possible outfits given various clothing items, the number of ways to order a two-course meal from menu options, and the number of possible schedules or multiple-choice test answers involving multiple choice groups. The principle states that if one event can occur in m ways and another in n ways, the number of ways both can occur is m×n, and if there are more than two groups, the counts are multiplied across all groups.