This document provides an overview of functional programming concepts. It discusses why functional programming is useful for building concurrent and thread-safe applications. Key concepts explained include immutable data, first class and higher order functions, lazy evaluation, pattern matching, monads, and monoids. Code examples are provided in JavaScript and Haskell to demonstrate functional programming techniques.





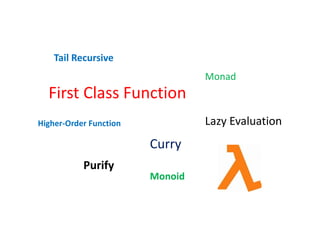

![Higher-Order Function
Functions that take other functions
Functions that return other functions
var people = [{name: "Fred", age: 65}, {name: "Lucy", age: 36}];
_.max(people, function(p) { return p.age });
function always(VALUE) {
return function() {
return VALUE;
};
};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/functionalprogramming-140317025557-phpapp02/85/Functional-Programming-8-320.jpg)
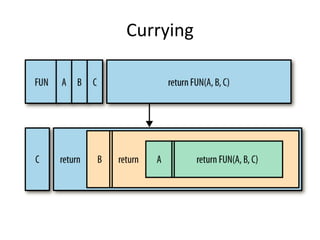





![Monoid
Just what is a monoid, then? It is simply an implementation of an interface
governed by some laws. Stated tersely, a monoid is a type together with an
associative binary operation (op) which has an identity element (zero).
trait Monoid[A] {
def op(a1: A, a2: A): A
def zero: A
}
def listMonoid[A] = new Monoid[List[A]] {
def op(a1: List[A], a2: List[A]) = a1 ++ a2
def zero = Nil
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/functionalprogramming-140317025557-phpapp02/85/Functional-Programming-18-320.jpg)




![Monad using Javascript
var stack = [];
stack.push(4);
stack.push(5);
stack.pop(); // 5
stack.pop(); // 4
Normal Style
http://igstan.ro/posts/2011-05-02-understanding-monads-with-javascript.html](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/functionalprogramming-140317025557-phpapp02/85/Functional-Programming-23-320.jpg)





