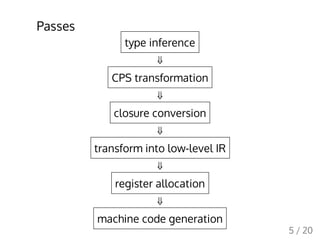
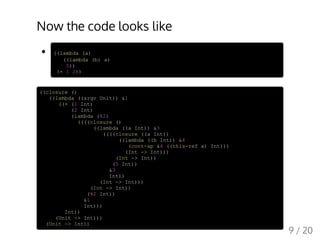
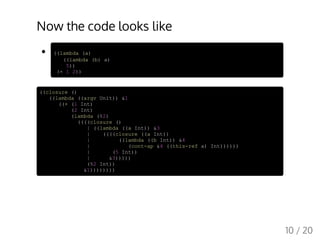
This document describes a simple compiler written in Scheme to compile a minimal functional language to x86 assembly. It discusses the key passes of the compiler including type inference, CPS transformation, closure conversion, generation of a low-level IR, register allocation, and machine code generation. While simple, the compiler demonstrates the major stages of a compiler from parsing and semantic analysis to code optimization and back-end code generation.



![Type Inference
Interpreter,
[()
`(() ,(prim-type 'Unit))]
[,x (guard (var? x))
`(,x ,(assq x mono-cxt))]
[(fix ,e)
(let [(a (fresh-var))
(built-e (build-type! e mono-cxt))]
(unify! (expr->type built-e) (fun-type a a))
`((fix ,built-e) ,a))]
[(lambda (,[xs ..]) ,e)
(let* [(obj-as (map (lambda (_) (fresh-var)) xs))
(built-e (build-type! e (append (map cons xs obj-as) mono-cxt)))
(obj-b (expr->type built-e))
(obj-xs (map list xs obj-as))]
`((lambda (,@obj-xs) ,built-e) ,(fun-type (tuple-type obj-as) obj-b)))]
[(,e1 ,[es ..])
(let* [(built-e1 (build-type! e1 mono-cxt))
(built-es (map (lambda (e) (build-type! e mono-cxt)) es))
(obj-a2b (expr->type built-e1))
(obj-as (map expr->type built-es))
(obj-b (fresh-var))]
(unify! obj-a2b (fun-type (tuple-type obj-as) obj-b))
`((,built-e1 ,@built-es) ,obj-b))]
6 / 20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/poormansundergraduatecompilers-140421081114-phpapp01/85/FT-11-suhorng-Poor-Man-s-Undergraduate-Compilers-6-320.jpg)
![CPS Transformation
interpreter,
(define cpsk ;; cpsk :: eT -> {(eT -> eC) | kC} -> eC
(lambda (expr k)
(match expr
[(,c ,t) (guard (prim-const? c))
(apply-cont k `(,c ,t))]
[(,x ,t) (guard (var? x))
(apply-cont k `(,x ,t))]
[((lambda (,[xs ..]) ,e) ,t)
(let [(k0 (fresh-var "&"))]
(apply-cont k `((lambda ,xs ,k0 ,(cpsk e k0)) ,t)))]
[((fix ,e) ,t)
(cpsk e (lambda (v)
`((fix ,(mark-type v e) ,(place-cont k)) ,t)))]
...
(define apply-cont
(lambda (k x)
(cond [(procedure? k) (k x)]
[else `(cont-ap ,k ,x)])))
(define place-cont
(lambda (k)
(cond [(procedure? k)
(let [(t (fresh-var "%"))]
`(lambda (,t) ,(k t)))]
[else k])))
7 / 20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/poormansundergraduatecompilers-140421081114-phpapp01/85/FT-11-suhorng-Poor-Man-s-Undergraduate-Compilers-7-320.jpg)
![Closure Conversion
interpreter...
Compute free variables
(match expr
[(,c ,t) (guard (prim-const? c))
'( () )]
[(,x ,t) (guard (var? x))
`( ((,x ,t)) )]
[((lambda (,[xs ..]) ,k ,e) ,t) ; lambda abstraction
(let [(var/e (uncover-free-vars e))]
`(,(remove-assoc* (map car xs) (car var/e)) ,var/e))]
Closure conversion
[((,x ,t) __) (guard (var? x))
(cond [(memq x bound-vars) `(,x ,t)]
[else `((this-ref ,x) ,t)])]
[(((lambda (,[xs ..]) ,k ,e) ,t) (,free-vars ,var/e));lambda abstraction
(let [(fv-ref (map (lambda (x) (closure-convert x `((x)) bound-vars))
free-vars))]
`((closure ,fv-ref
((lambda ,xs ,k ,(closure-convert e var/e (map car xs)))
,t))
,t))]
8 / 20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/poormansundergraduatecompilers-140421081114-phpapp01/85/FT-11-suhorng-Poor-Man-s-Undergraduate-Compilers-8-320.jpg)


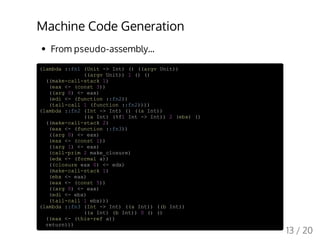

![Tail Calls
;#######################################
; _ss_function_fn3: ((* Int Int) -> Int)
; parameters:
; ((n Int) (sum Int))
; free variables:
; ((loop ((* Int Int) -> Int)))
;#######################################
_ss_function_fn3_code: ; Note: this function doesn't have a frame
cmp dword [esp + 4], 0
jne .L1
mov eax, [esp + 8]
ret 8 ; terminating loop
.L1:
mov eax, [esp + 8] ; eax := sum
add eax, [esp + 4] ; eax (sum') += n
mov edx, [esp + 4]
add edx, -1 ; edx (n') := n - 1
sub esp, 8 ; place arguments as usual
mov [esp], edx ; | sum' | esp+4
mov [esp + 4], eax ; | n' | esp
mov edi, [edi + 4] ; load closure pointer
lea edx, [esp + 8]
mov ecx, [esp + 8] ; move new arguments up
mov eax, [esp + 4]
mov [edx + 8], eax ; sum' overrides sum,
mov eax, [esp]
mov [edx + 4], eax ; so does n'!
mov [edx], ecx
mov esp, edx
jmp [edi]
16 / 20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/poormansundergraduatecompilers-140421081114-phpapp01/85/FT-11-suhorng-Poor-Man-s-Undergraduate-Compilers-16-320.jpg)

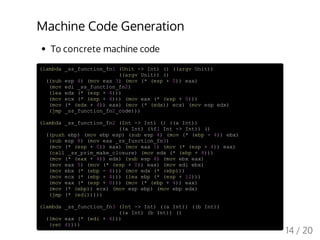
![-- all are interpreters
alphaConvAST s@(S.Block _ _) =
runLocal $ alphaConvBlock' s
alphaConvAST (S.Expr ty line rand rators) =
S.Expr ty line rand <$> mapM alphaConvAST rators
alphaConvAST (S.ImplicitCast ty' ty e) =
S.ImplicitCast ty' ty <$> alphaConvAST e
buildMStmt (P.While line whcond whcode) = do
whcond' <- buildMStmts whcond
whcode' <- runLocal (buildMStmt whcode)
return $ S.While line whcond' whcode'
buildMStmt (P.Identifier line name) = do
currScope <- get
upperScope <- ask
let ty = fmap S.varType $ lookup name currScope <|> lookup name upperScope
case ty of
Just S.TTypeSyn -> tell [errorAt line $ "Unexpected type synonym '" ++ name ++ "'"]
Nothing -> tell [errorAt line $ "Undeclared identifier '" ++ name ++ "'"]
otherwise -> return ()
return $ S.Identifier (error "buildMStmt:Identifier") line name
tyCheckAST (S.Expr _ line rator [rand1, rand2]) | rator `elem` logicOps = do
rand1' <- tyCheckAST rand1
rand2' <- tyCheckAST rand2
let (t1, t2) = (S.getType rand1', S.getType rand2')
when ((not $ tyIsScalarType t1) || (not $ tyIsScalarType t2)) $
tell [errorAt line $ "'" ++ show rator ++ "' is applied to operands of non-scalar typ
return $ S.Expr S.TInt line rator [rand1', rand2']
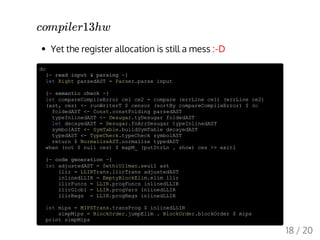
compiler13hw
19 / 20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/poormansundergraduatecompilers-140421081114-phpapp01/85/FT-11-suhorng-Poor-Man-s-Undergraduate-Compilers-19-320.jpg)
