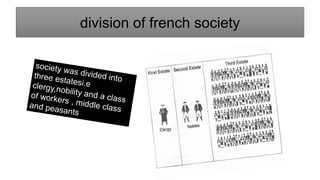
The document summarizes the economic and social conditions in France prior to the French Revolution. It discusses how King Louis XVI faced an empty treasury and immense debt upon taking the throne. To raise funds, he increased taxes, which angered the middle class who had to bear the burden. Rising bread prices and poor harvests also led to widespread poverty and unrest among the common people. Enlightenment philosophers further challenged the absolute power of the monarch. When Louis called the Estates-General to approve more taxes, the Third Estate walked out and formed the National Assembly, marking the beginning of the Revolution.