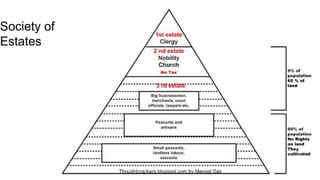
The document details the historical context and key events leading to the French Revolution from 1453 to 1799, focusing on the transition from the Valois to the Bourbon dynasties and the societal structures of the time. It describes the financial crises faced by Louis XVI, the growing dissatisfaction among the Third Estate, and the ultimate formation of the National Assembly which led to the abolition of feudalism. Key themes include the emergence of the middle class, demands for political rights, and the establishment of a constitutional monarchy, culminating in the establishment of the French Republic and the subsequent rise of Napoleon Bonaparte.