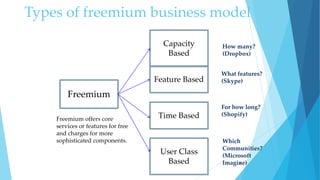
The document outlines the freemium business model, which offers basic services for free while charging for advanced features, and discusses its building blocks, types, and industries using this model. It analyzes critical factors for success, pitfalls to avoid, and provides examples of companies thriving under this model. Key considerations include customer segments, value propositions, and revenue streams, along with guidance on whether the freemium model is suitable for a specific business.