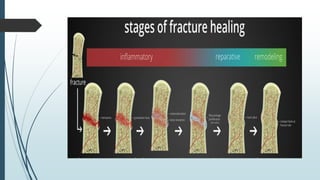
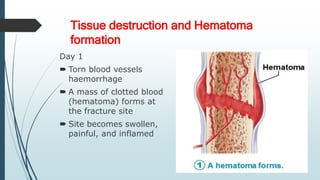
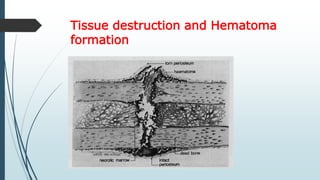
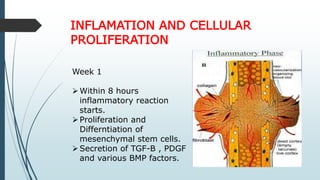
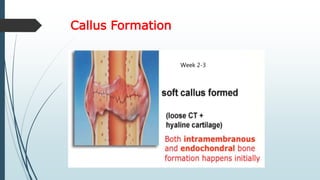
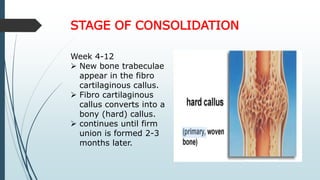
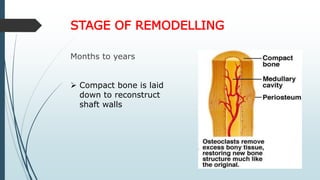
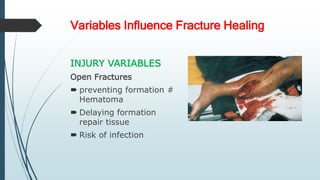
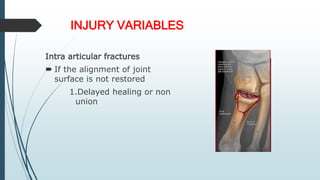
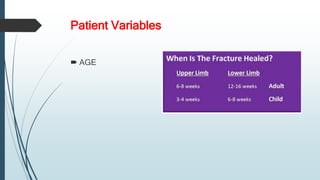
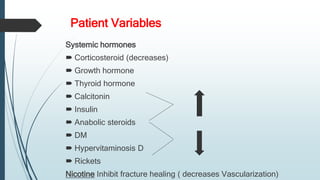
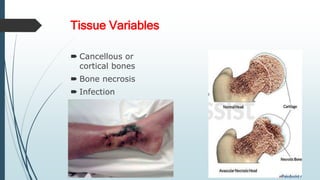
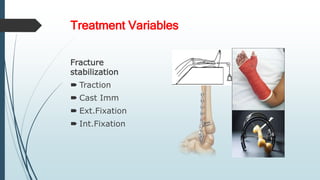
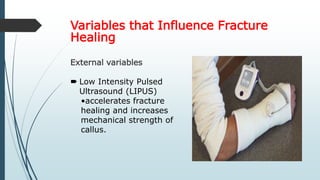
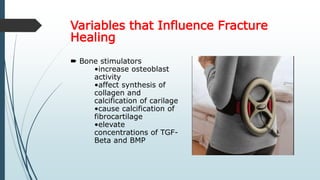
This document discusses fracture healing, describing the different types of fracture healing based on bone type, the stages of fracture healing from hematoma formation to remodeling, and the many factors that can influence and affect the fracture healing process. It outlines the basic tissue destruction and inflammatory response in the first week after injury, callus formation in weeks 2-3, consolidation from weeks 4-12 as new bone forms, and remodeling over months to years. Variables discussed include patient factors like age, diet, and medications; injury factors like open fractures; and treatment factors like stabilization methods.