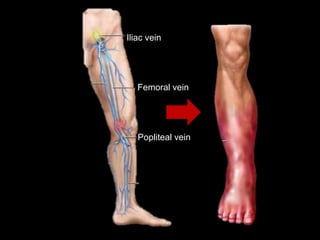
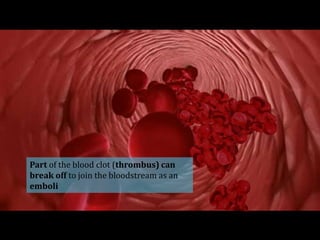
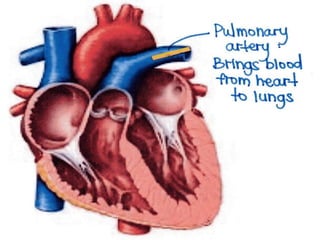
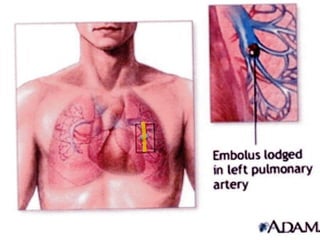
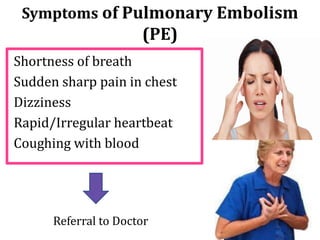
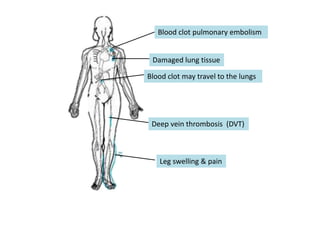
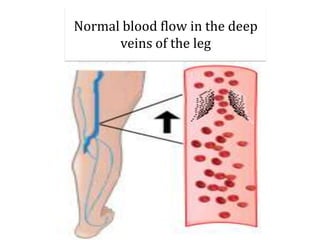
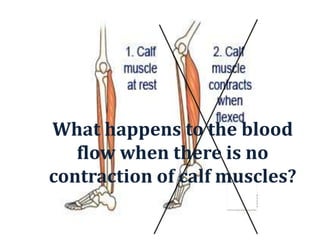
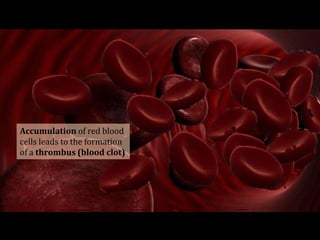
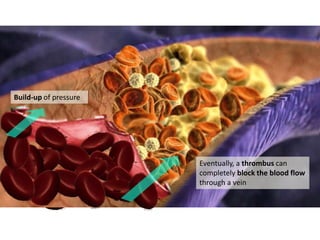
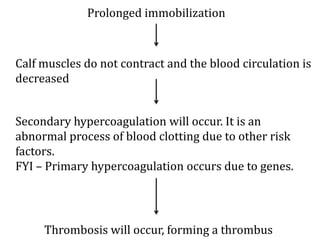
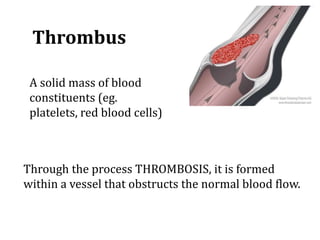
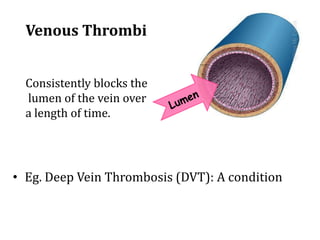
Deep vein thrombosis occurs when a blood clot forms in the deep veins of the leg, usually caused by prolonged immobility. When sitting for long periods, such as on a plane, the calf muscles do not contract and blood circulation decreases, allowing a clot to form. Part of the clot can break off and travel through the bloodstream as an embolism to the lungs, blocking vessels and causing a pulmonary embolism. Symptoms of deep vein thrombosis include leg pain and swelling, while a pulmonary embolism causes shortness of breath, chest pain, and other issues. Both conditions are serious and require medical treatment.



![Symptoms of Deep Vein Thrombosis
[DVT]
Pain or tenderness in area
Warmth in skin
Red or discoloured skin
Swelling of lower leg or vein](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fpathppt-130731213726-phpapp01/85/FPATH-12-320.jpg)