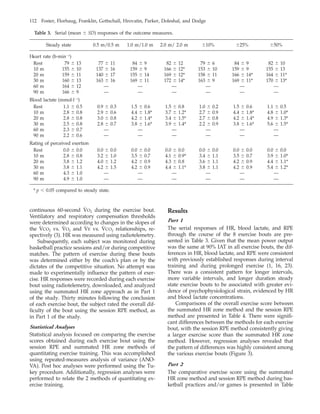
This study evaluated a new method of monitoring exercise training called the session rating of perceived exertion (RPE) method. The session RPE method uses a participant's perceived exertion after a training session as a marker of training intensity. The study compared the session RPE method to an objective heart rate (HR) monitoring method during steady state and interval cycling, as well as basketball practice. It found a consistent relationship between the two monitoring methods, though the session RPE scores were generally higher. Even with different subjects, the relationships between the methods were similar. The study concluded the session RPE method is a valid way to quantify training during various types of exercise when objective monitoring is not possible.