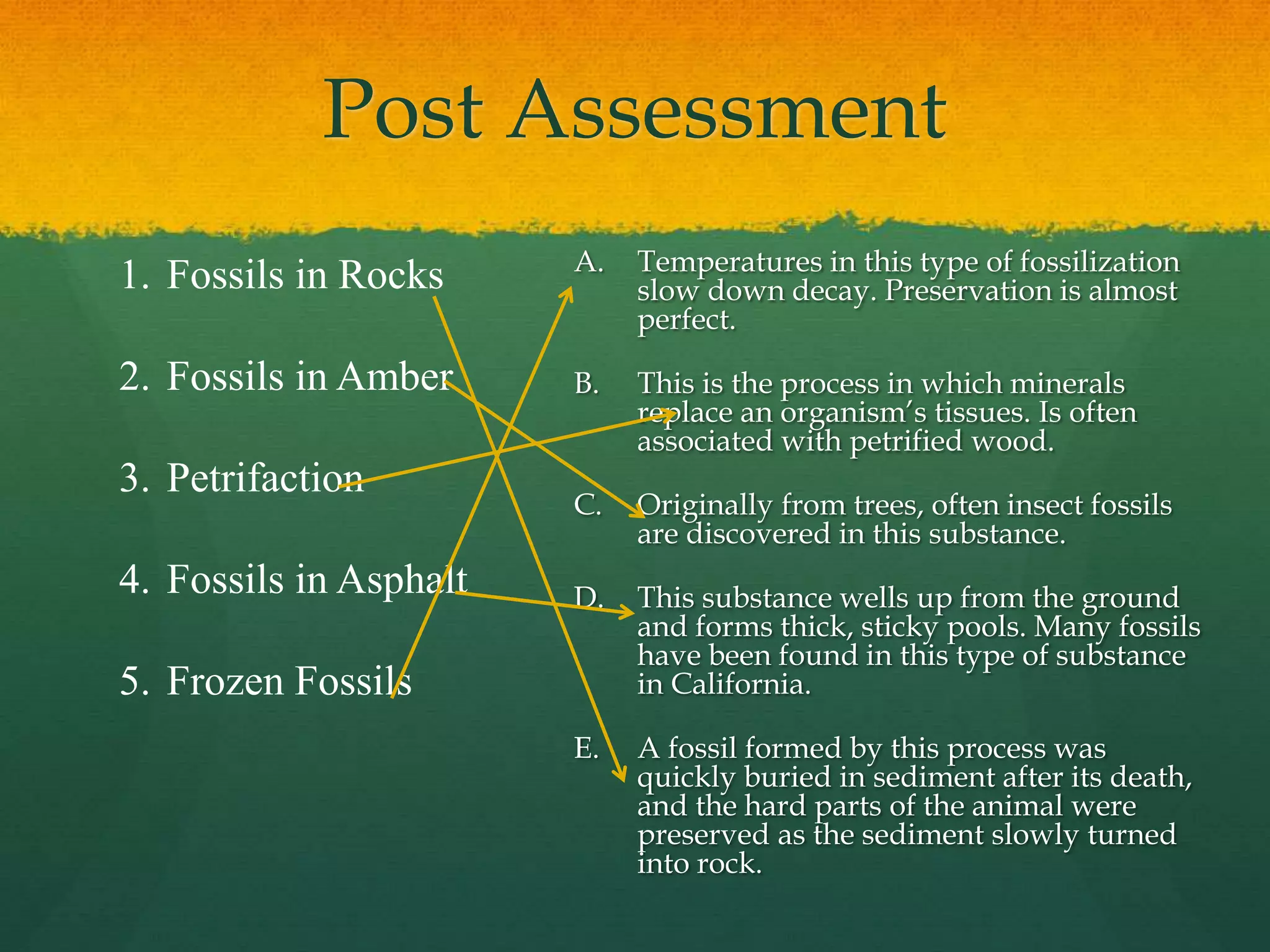
The document provides instructions for a student project on the different methods of fossilization. It discusses five main types of fossilization: fossils in rocks, amber, petrifaction, asphalt, and frozen fossils. Students are tasked with creating a step book that defines and describes each method using cited sources from materials provided, including an encyclopedia article, online resources, textbooks, and library books. Guidelines are provided on gathering information, illustrating examples, and citing sources for the project. A pre- and post-assessment quiz is also included to gauge students' understanding of the five fossilization methods.