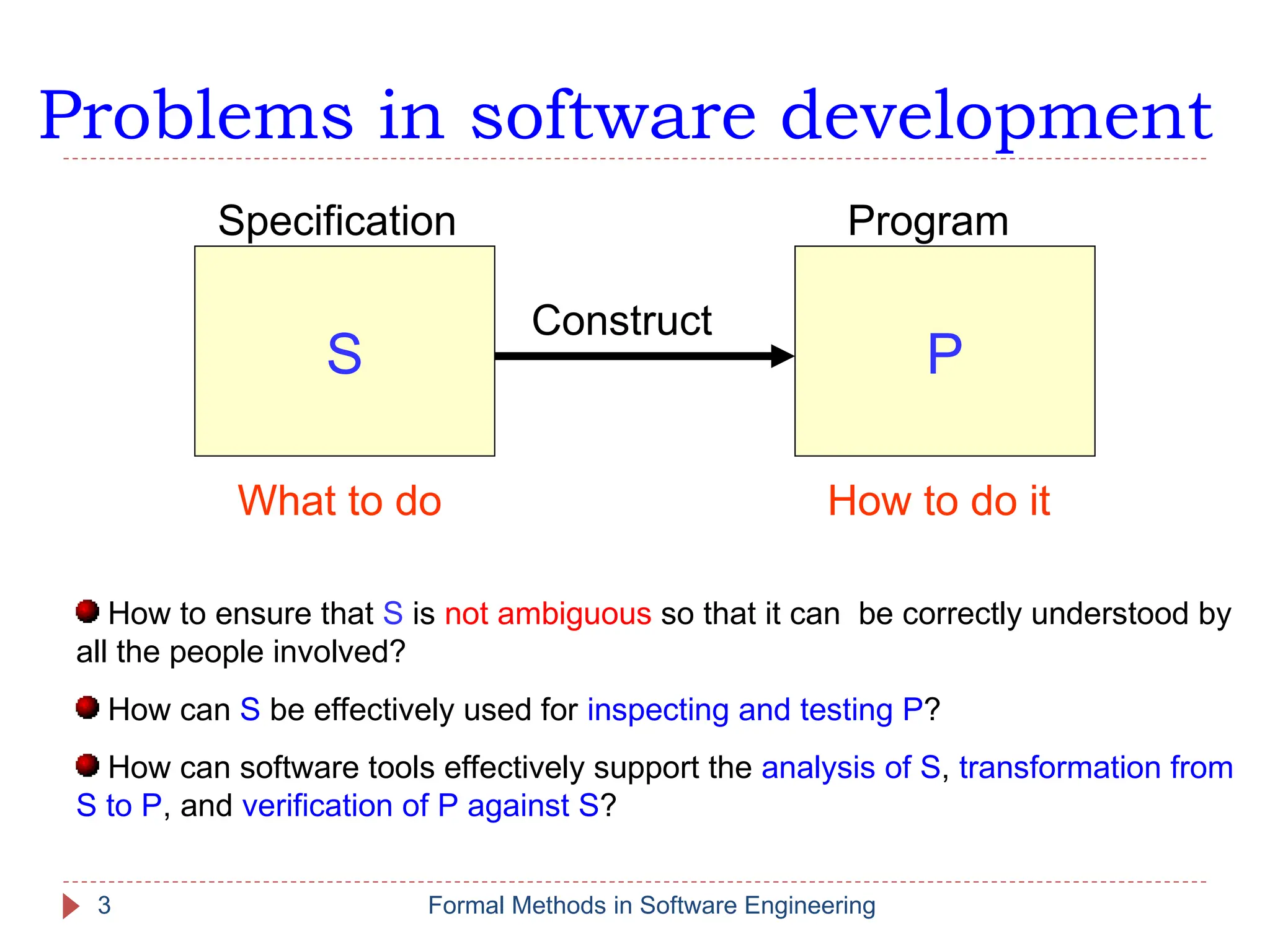
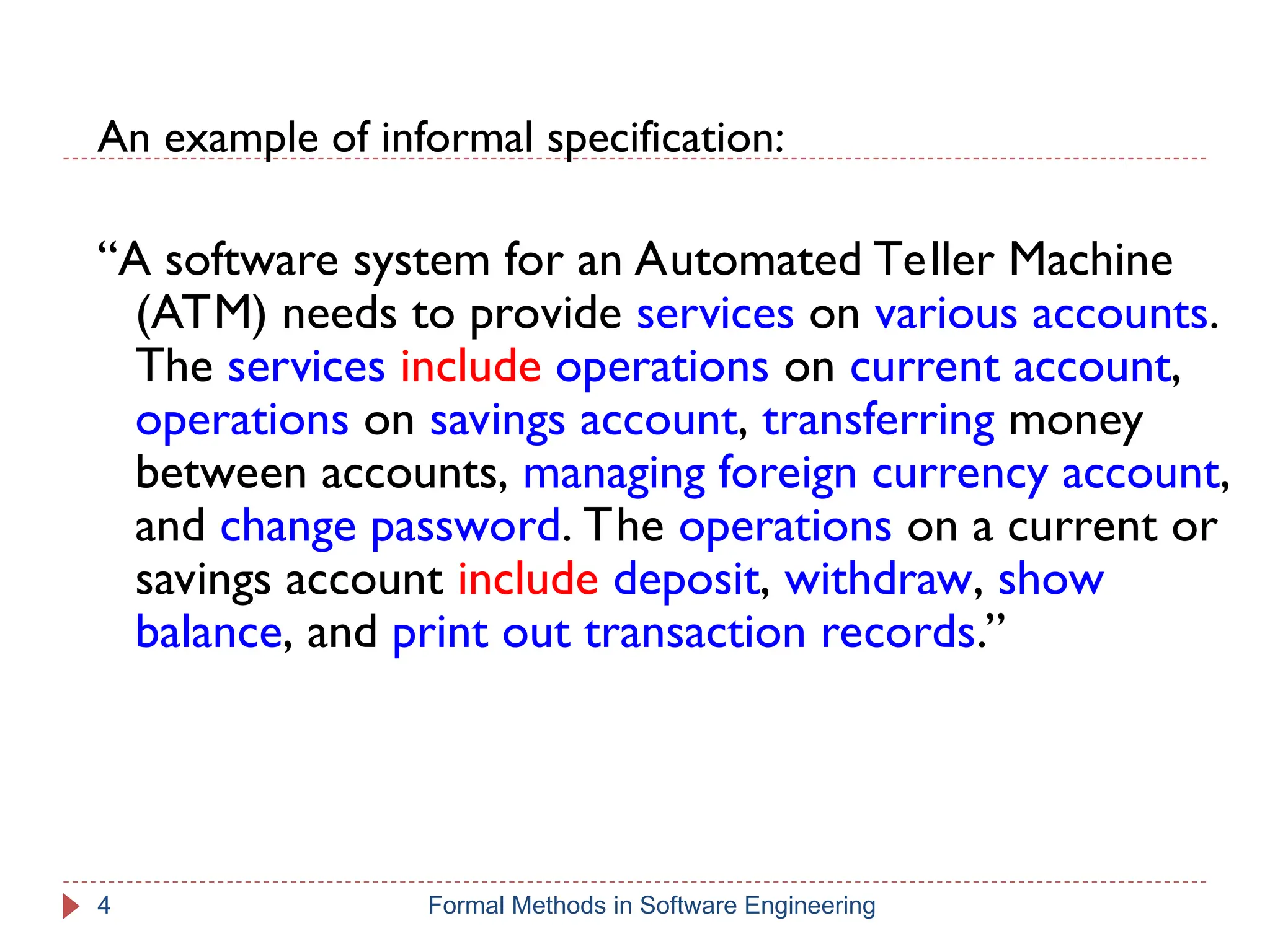
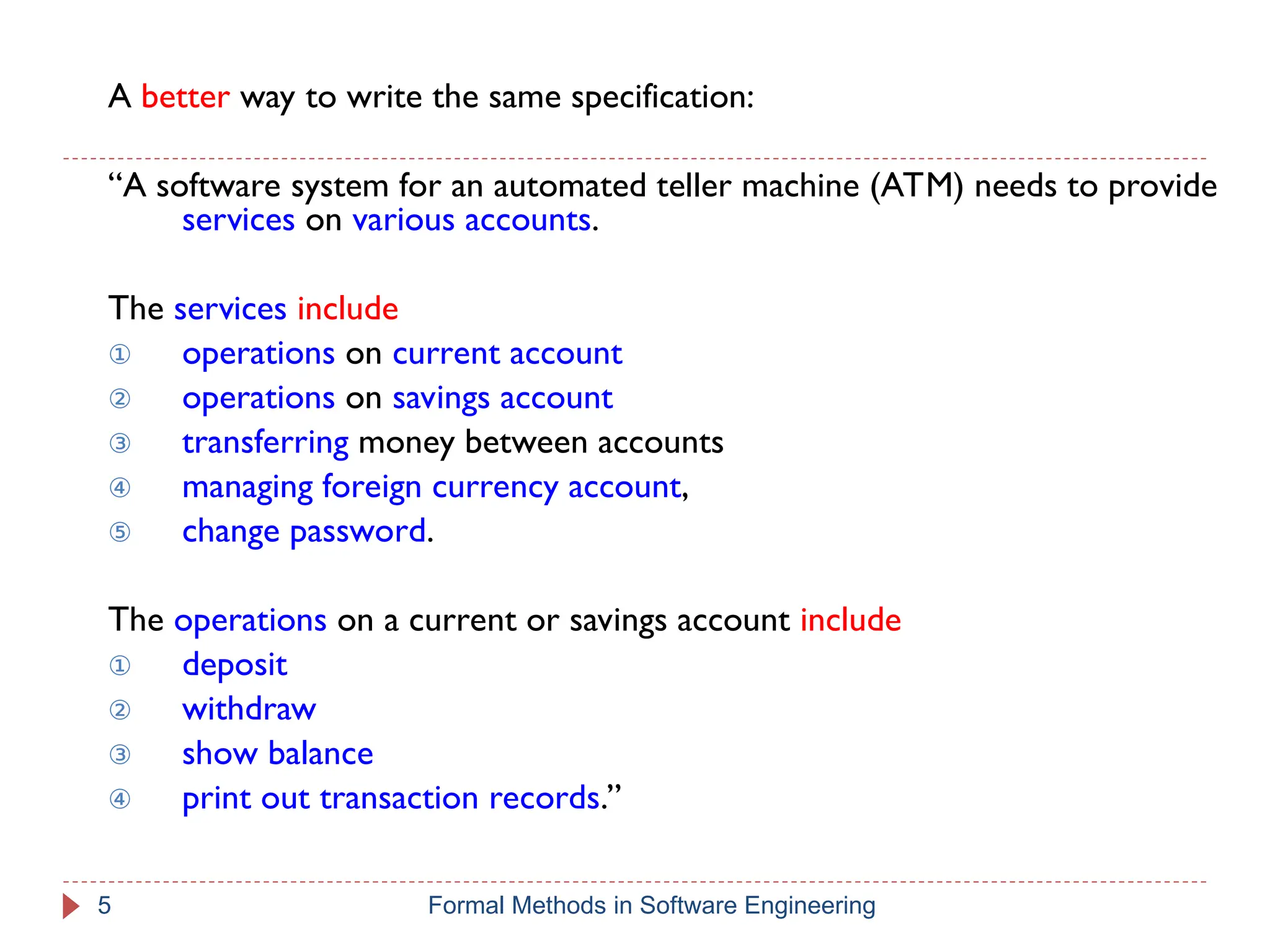
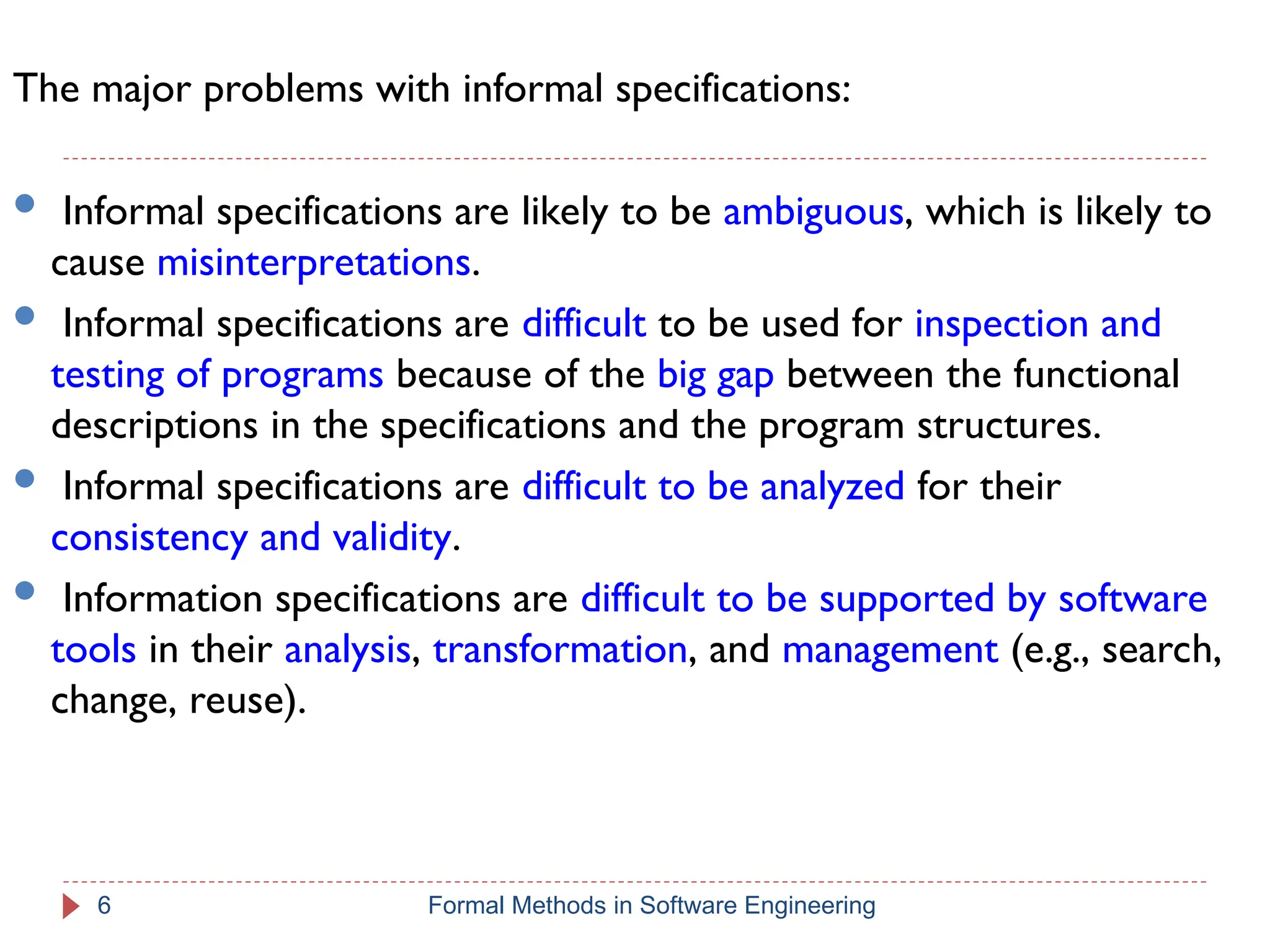
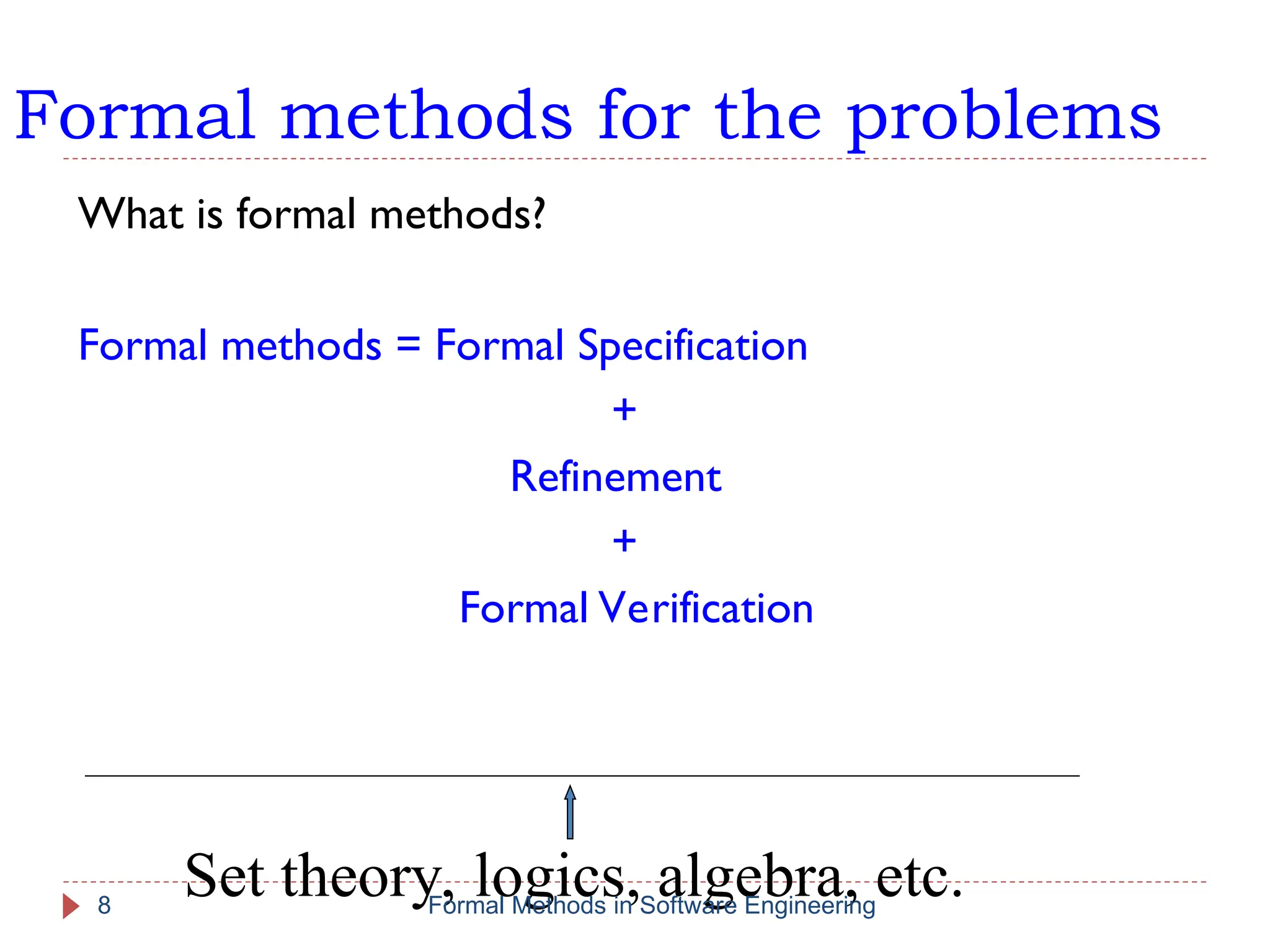
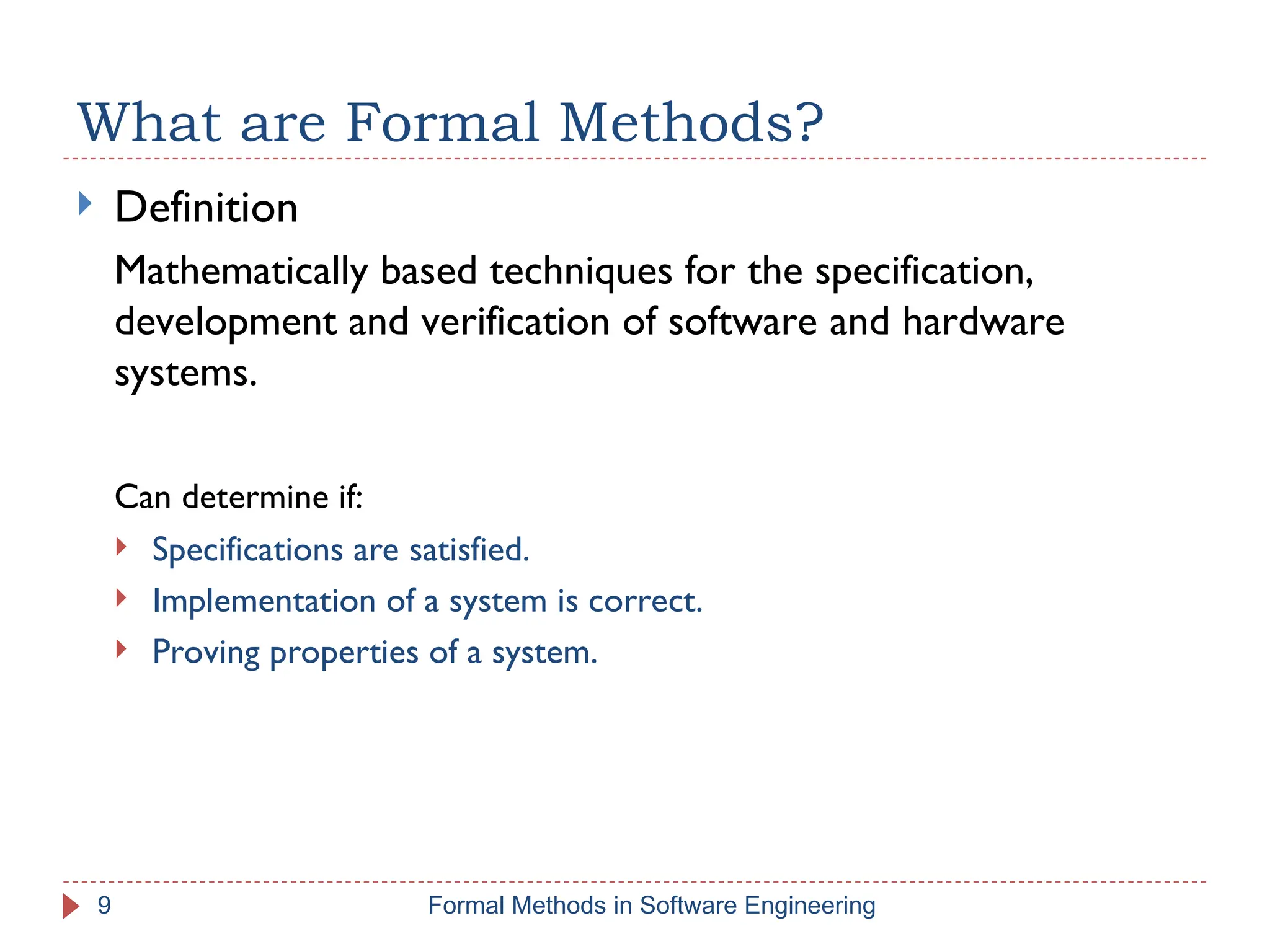
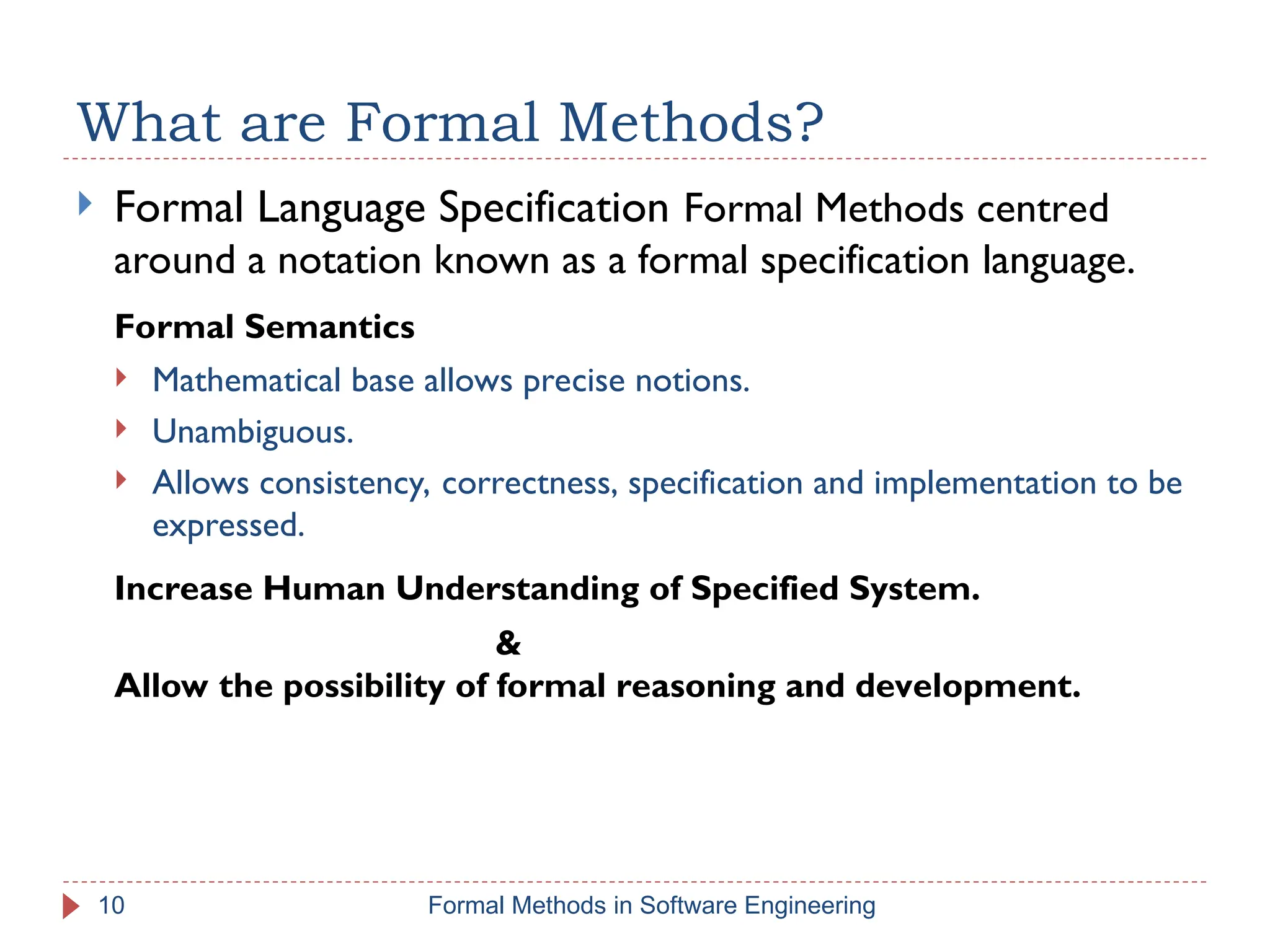
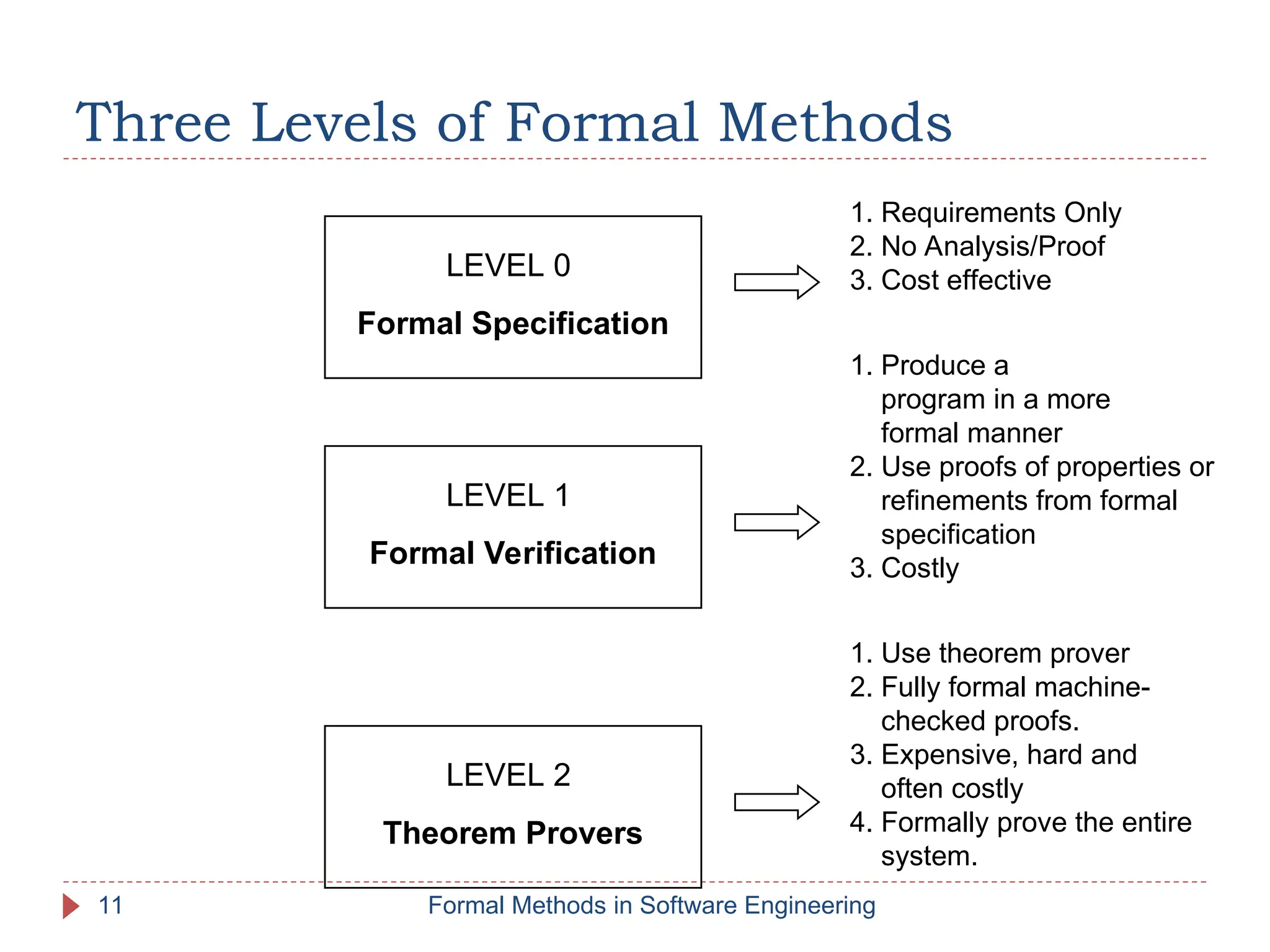
The document outlines formal methods in software engineering, highlighting their importance in ensuring precise specifications, reliable program inspections, and accurate verifications. It points out major issues with informal specifications, such as ambiguity and difficulty in analysis, and proposes formal methods as a solution. The content also discusses different levels of formal methods, their definitions, and relevant techniques for specification and verification.