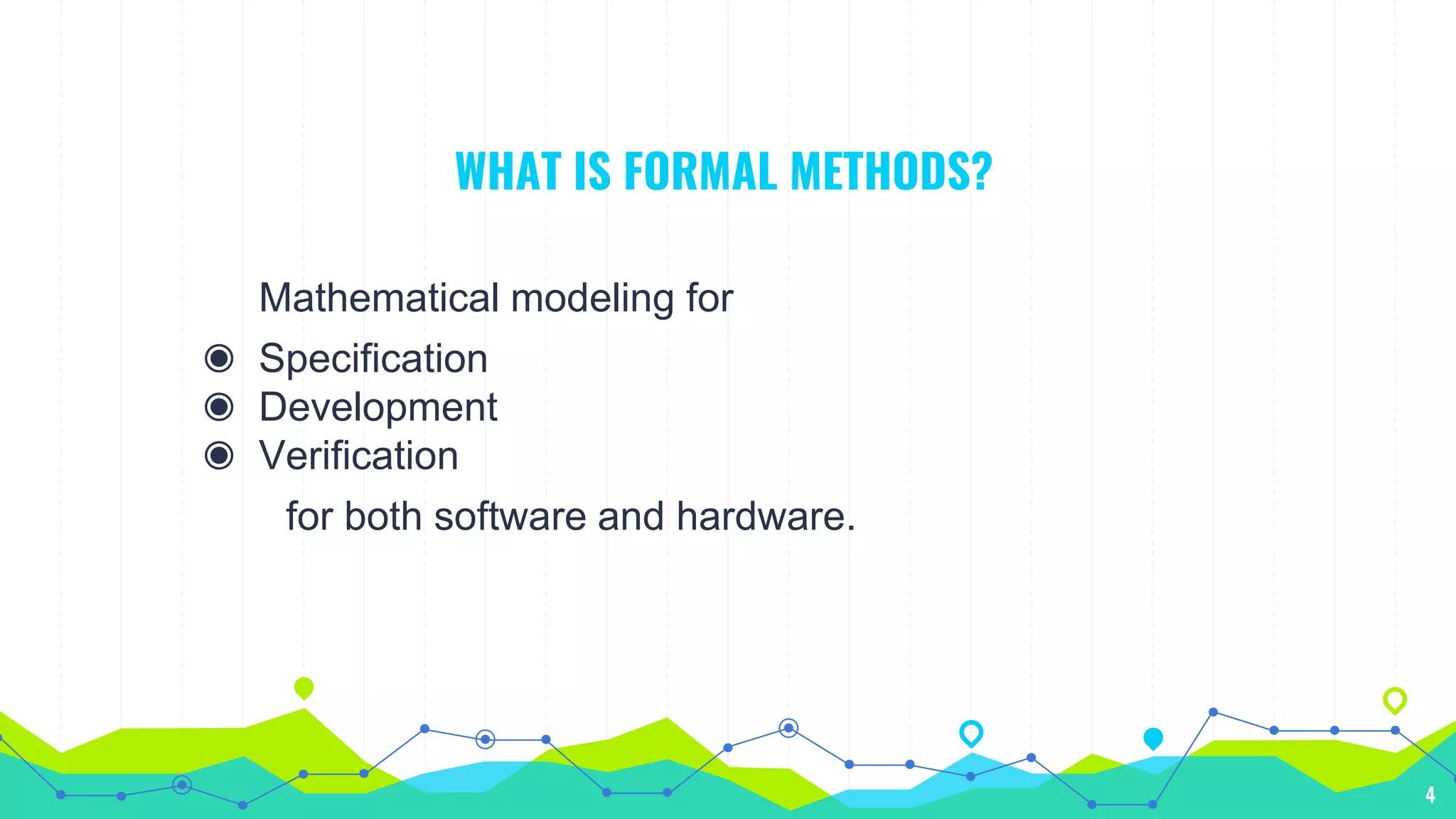
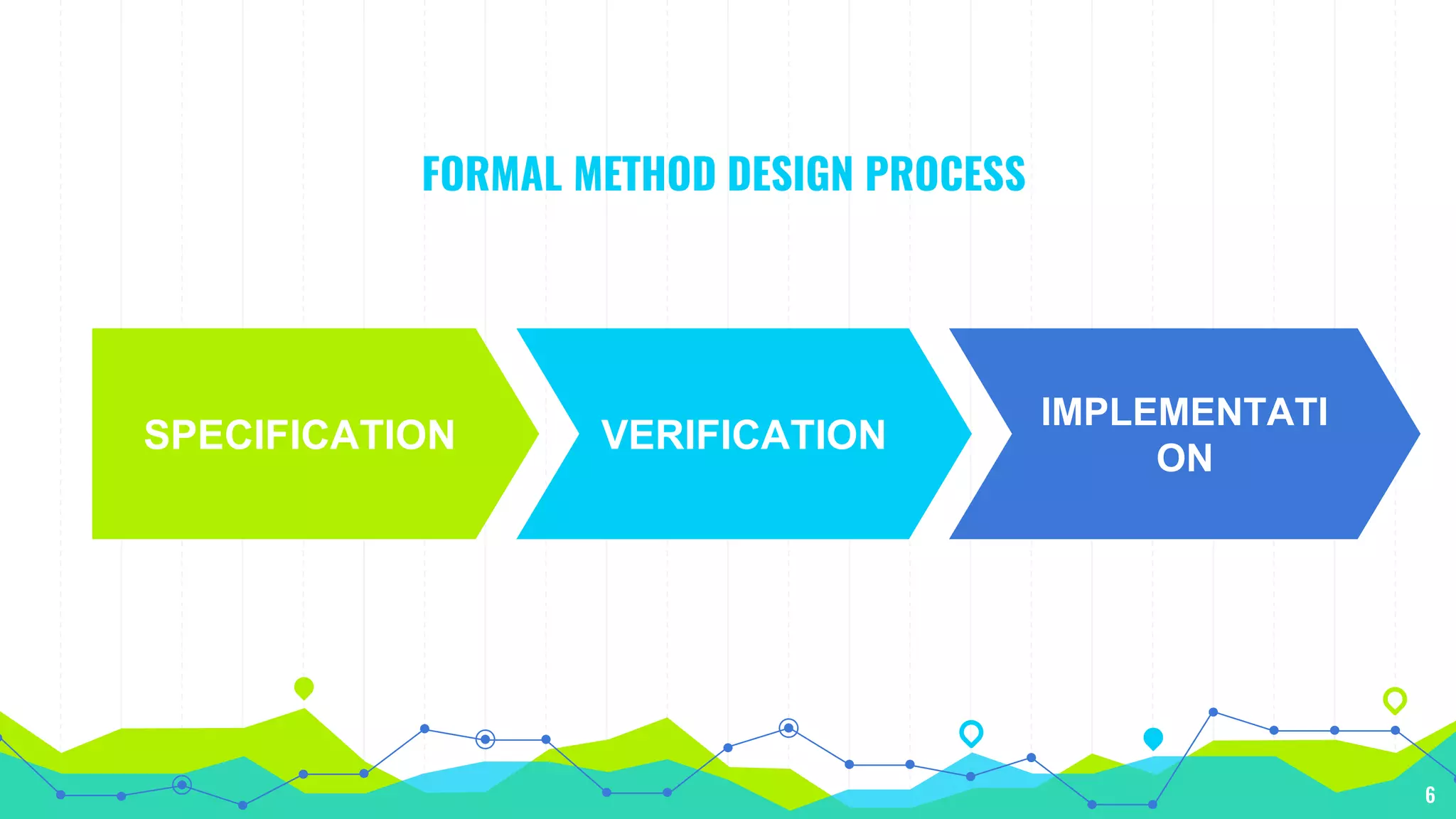
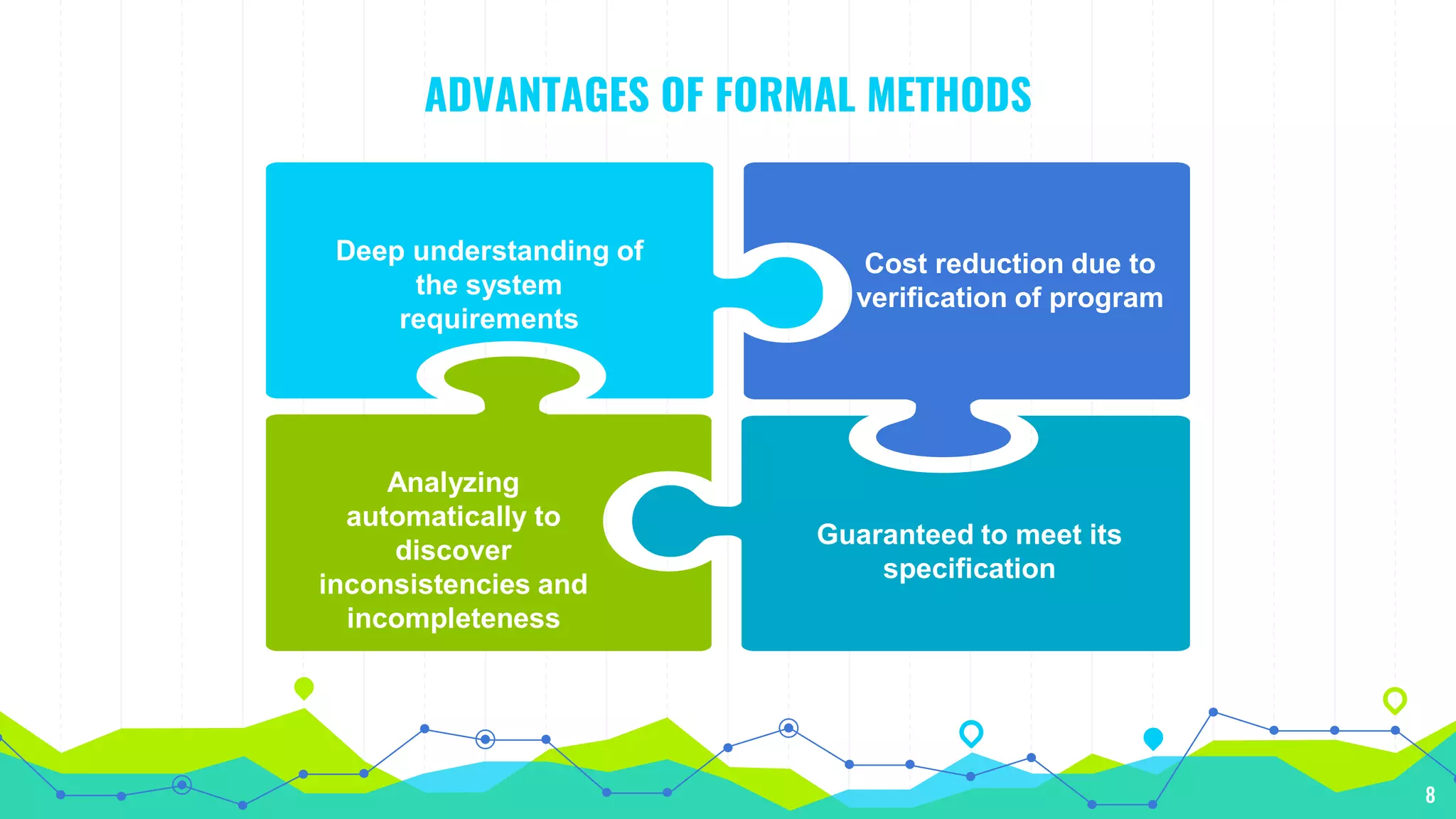
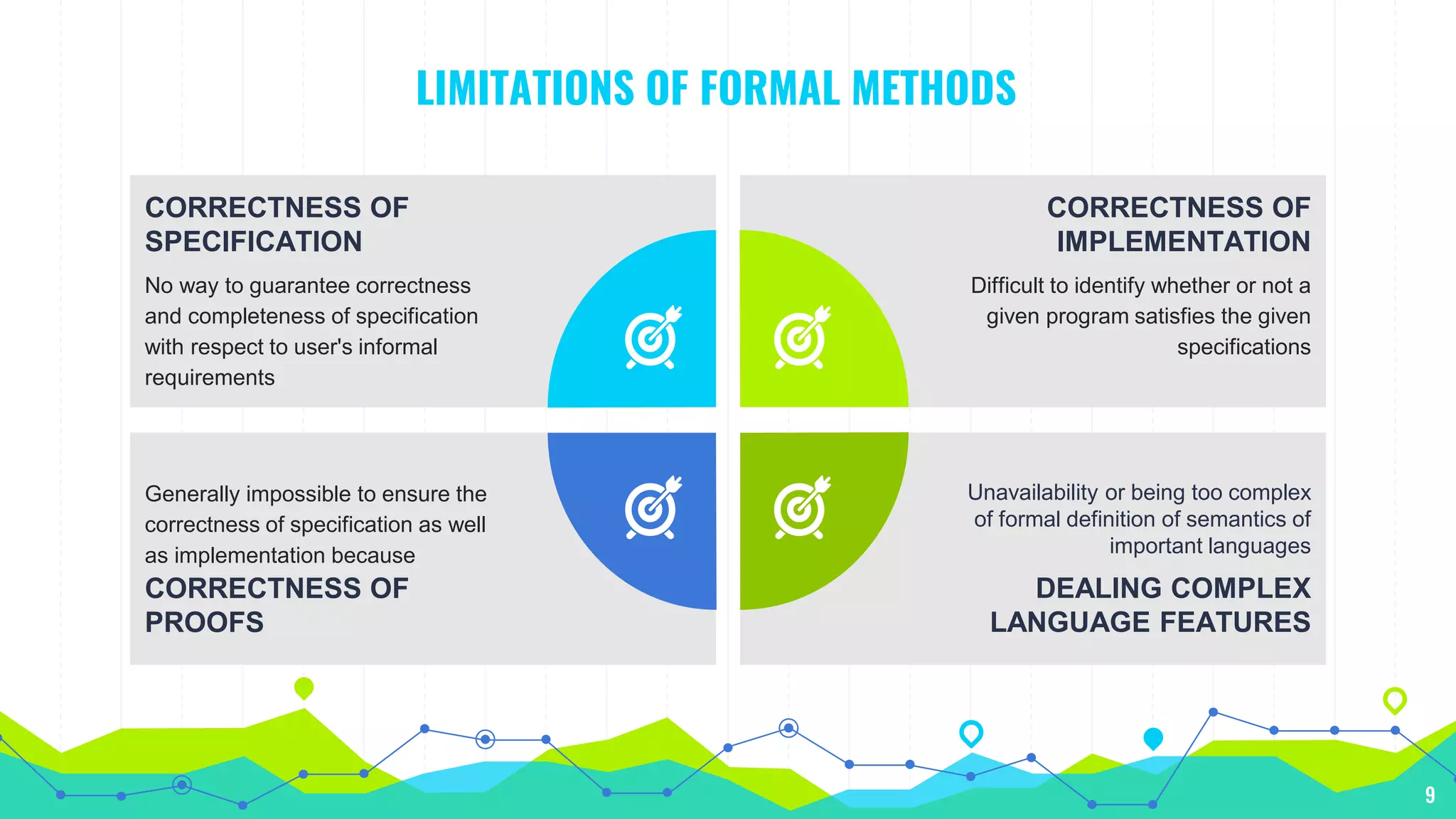
The document discusses formal methods in software engineering, including their role in specification, verification, and development of software and hardware. It highlights the advantages, such as error detection and cost reduction, while also addressing limitations like difficulties in guaranteeing correctness and challenges in large systems. Furthermore, it notes that formal methods are descriptive and analytical rather than creative, impacting software product quality and systems that interact with unpredictable external environments.