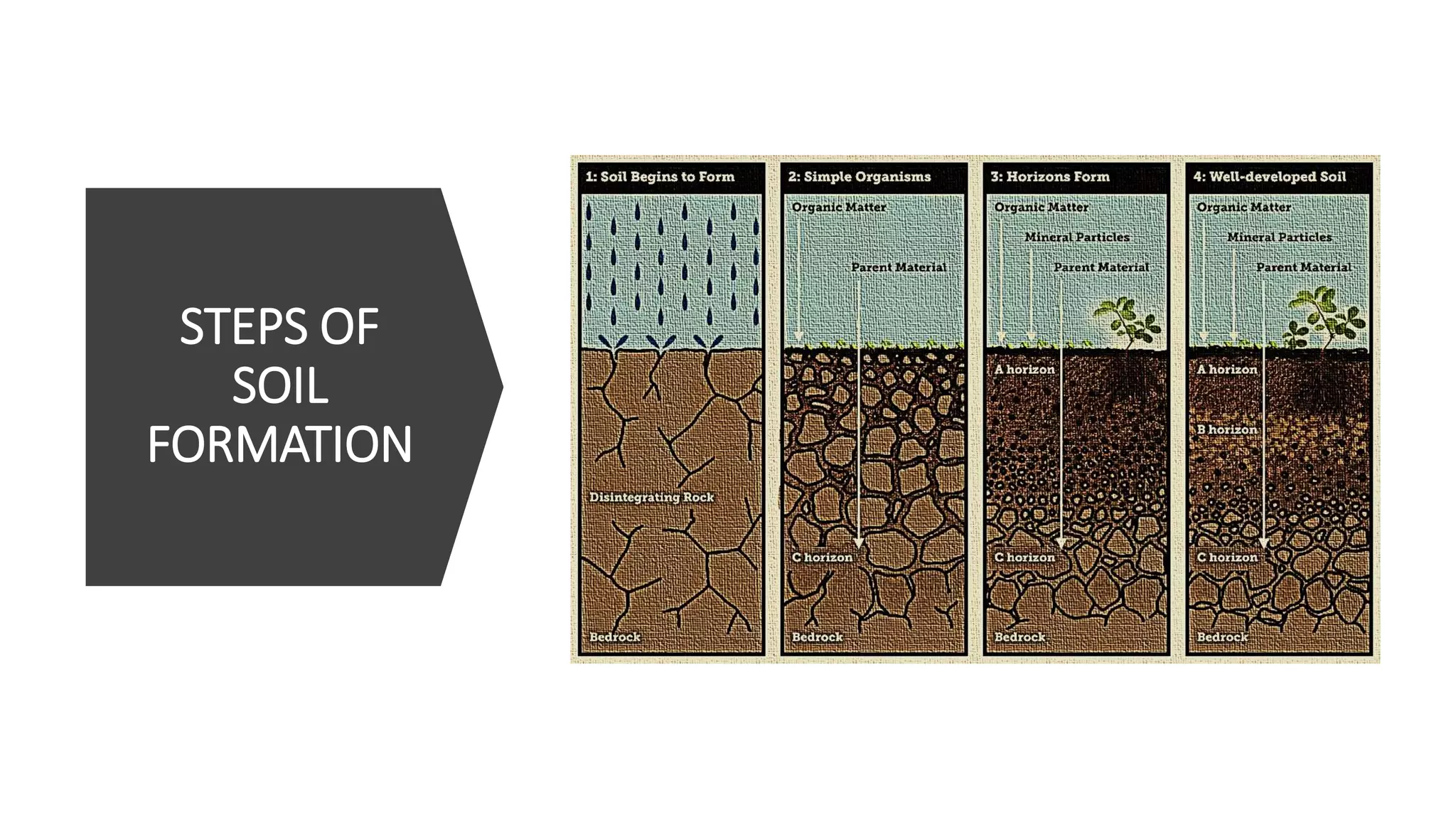
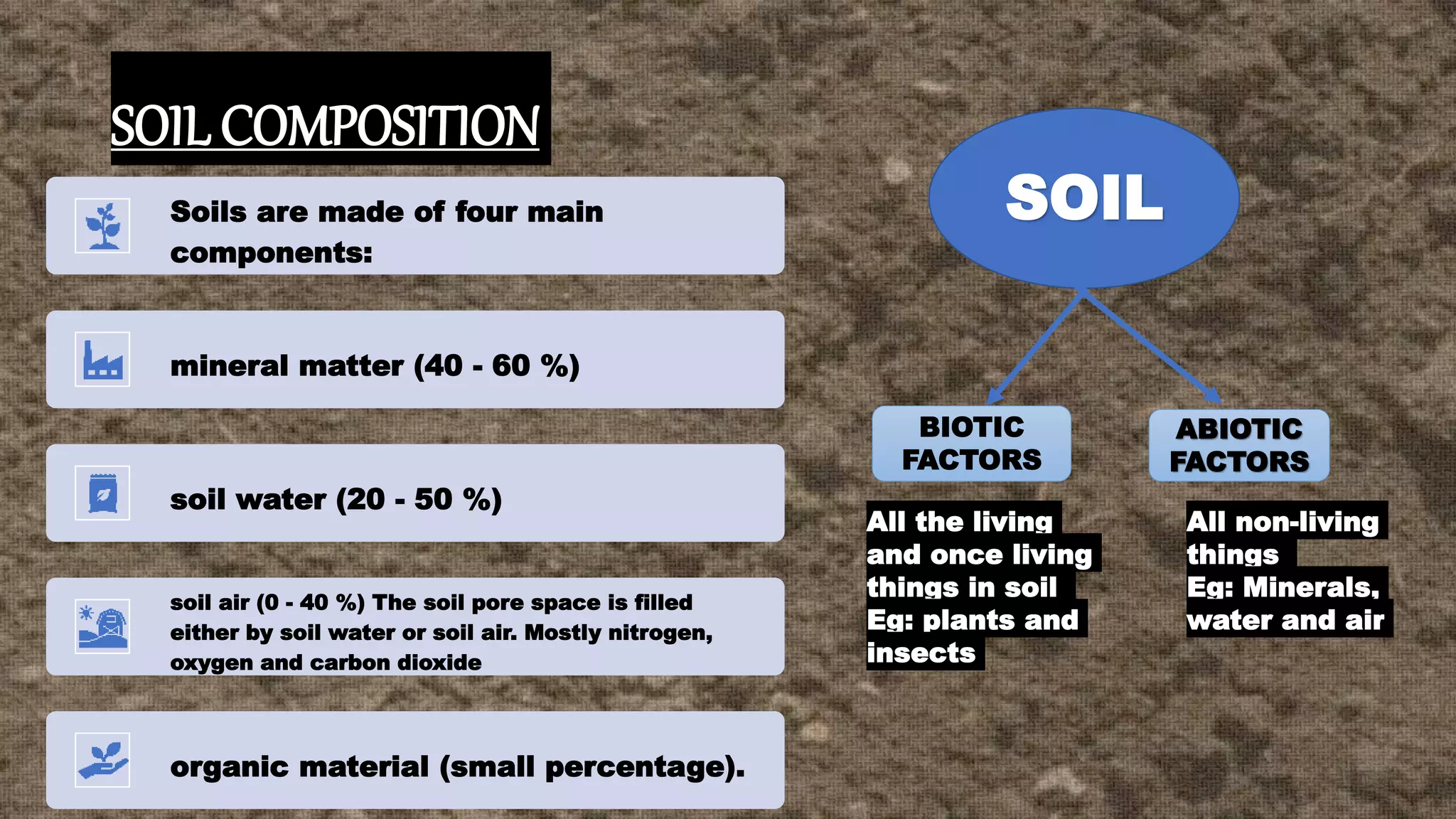
Soil is a complex material consisting of minerals, organic matter, water, and air, with unique properties that can serve as identification markers similar to fingerprints. The document discusses soil formation, composition, characteristics, and the importance of soil in forensic examinations, noting its value as physical evidence in various crimes. It highlights the individualistic nature of soils and methods for their analysis and identification.