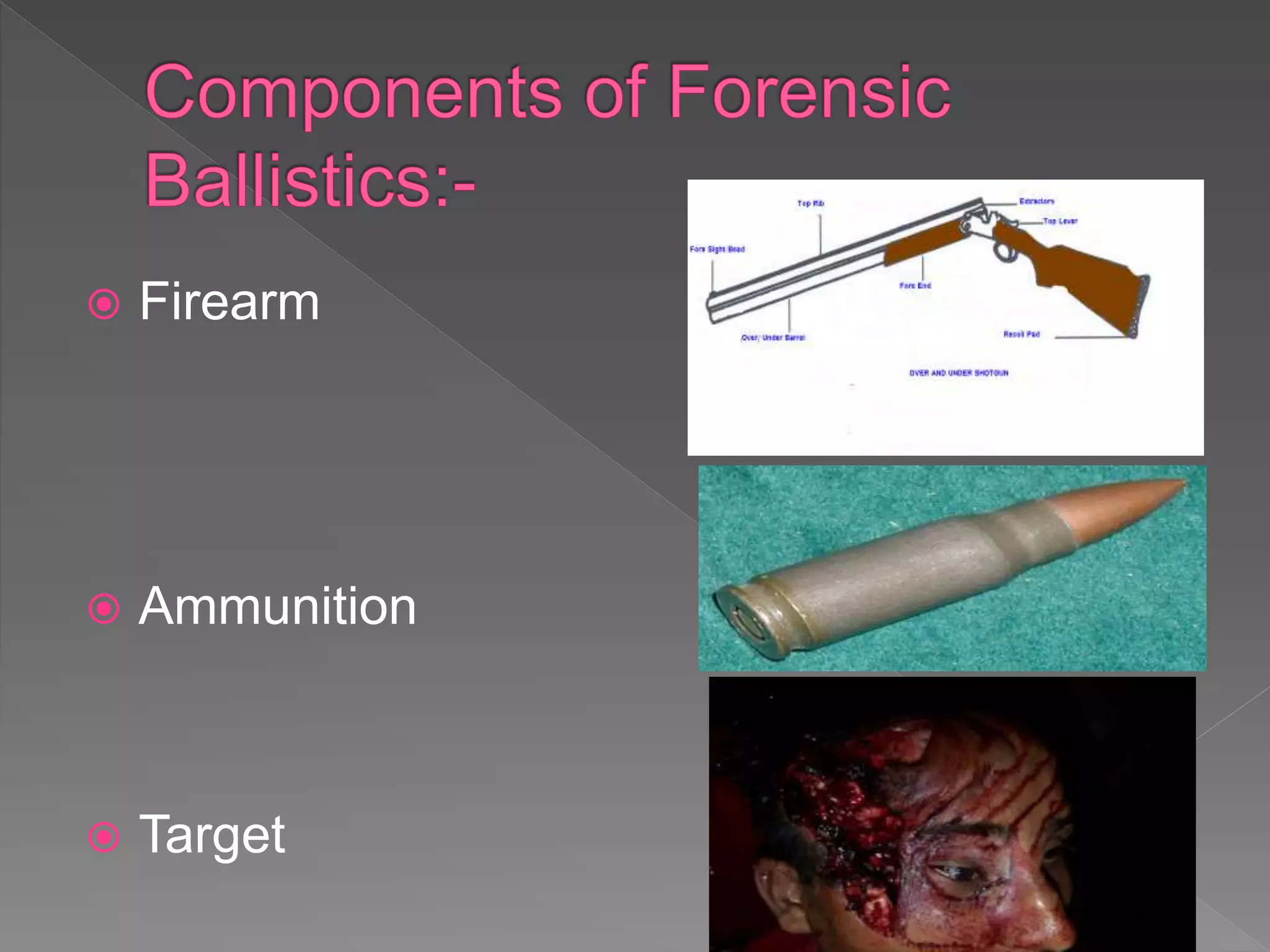
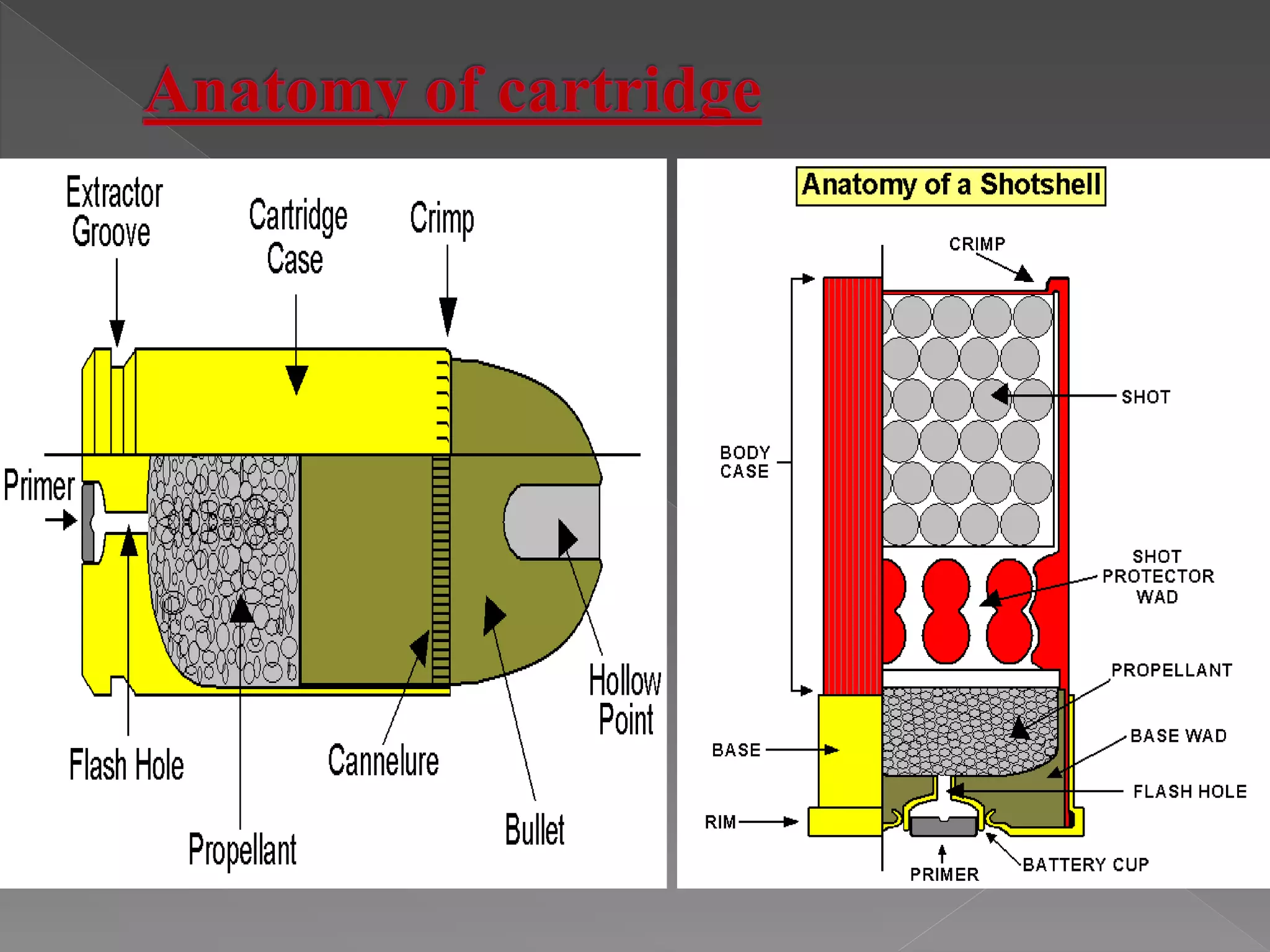
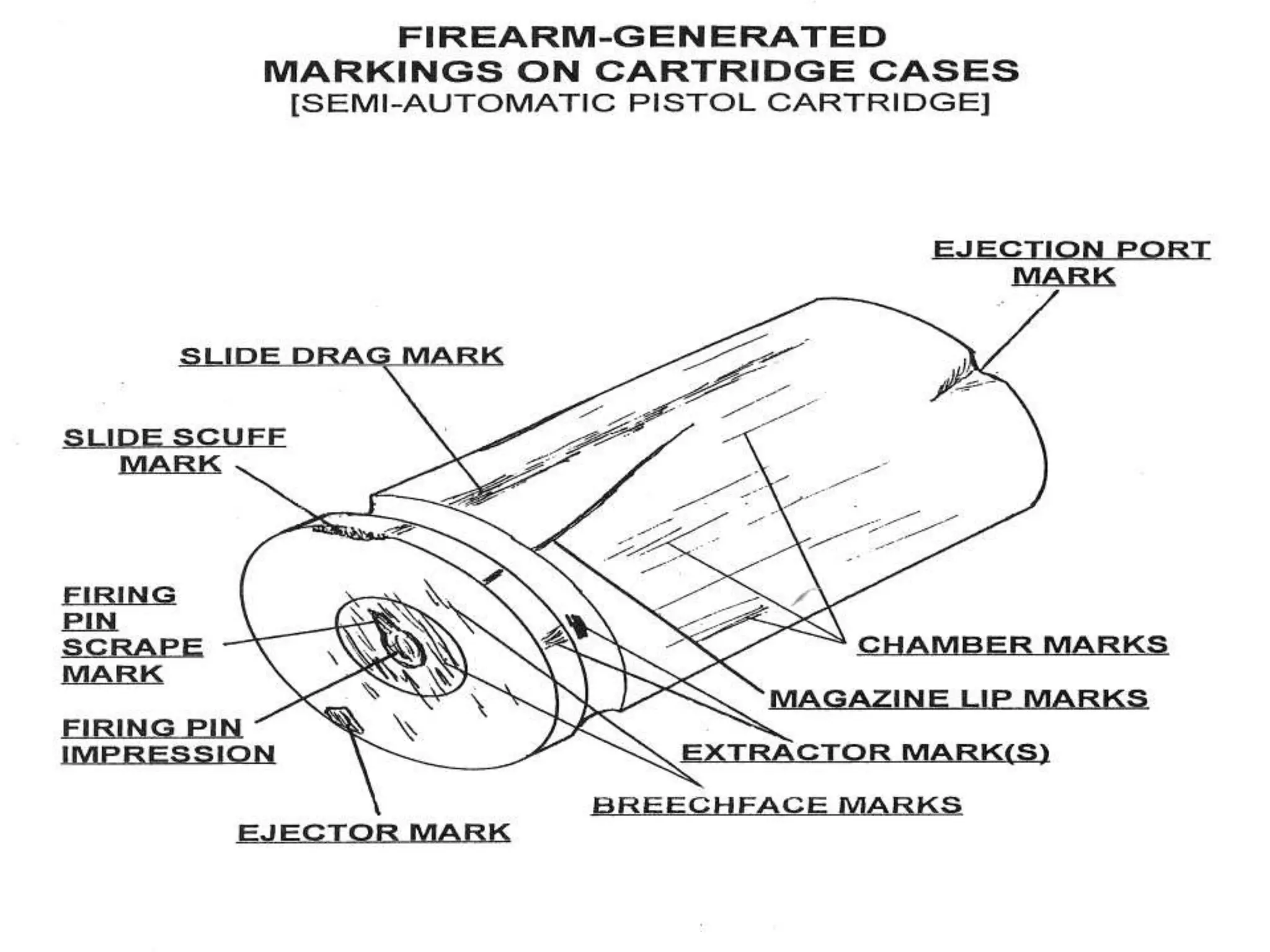
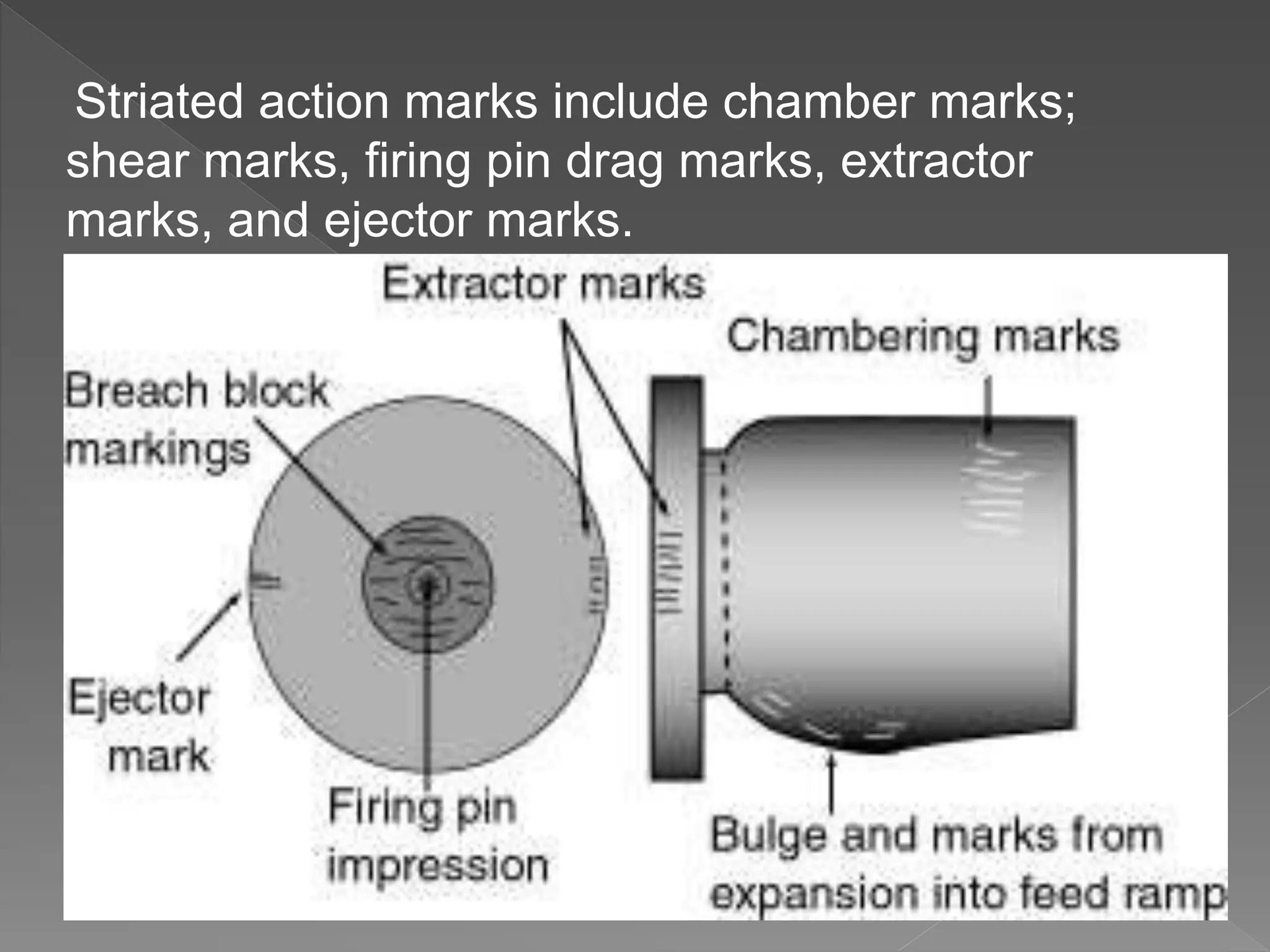
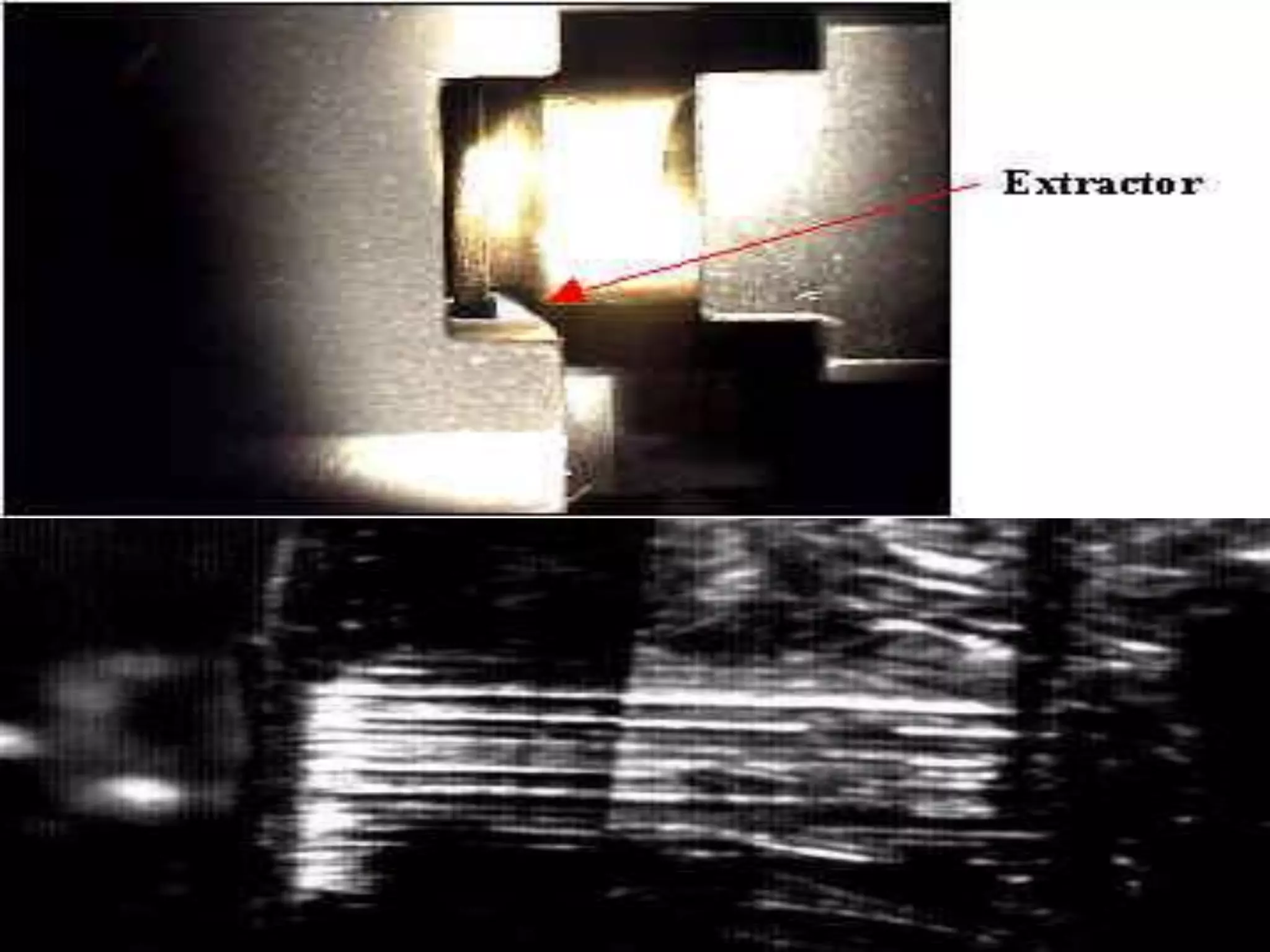
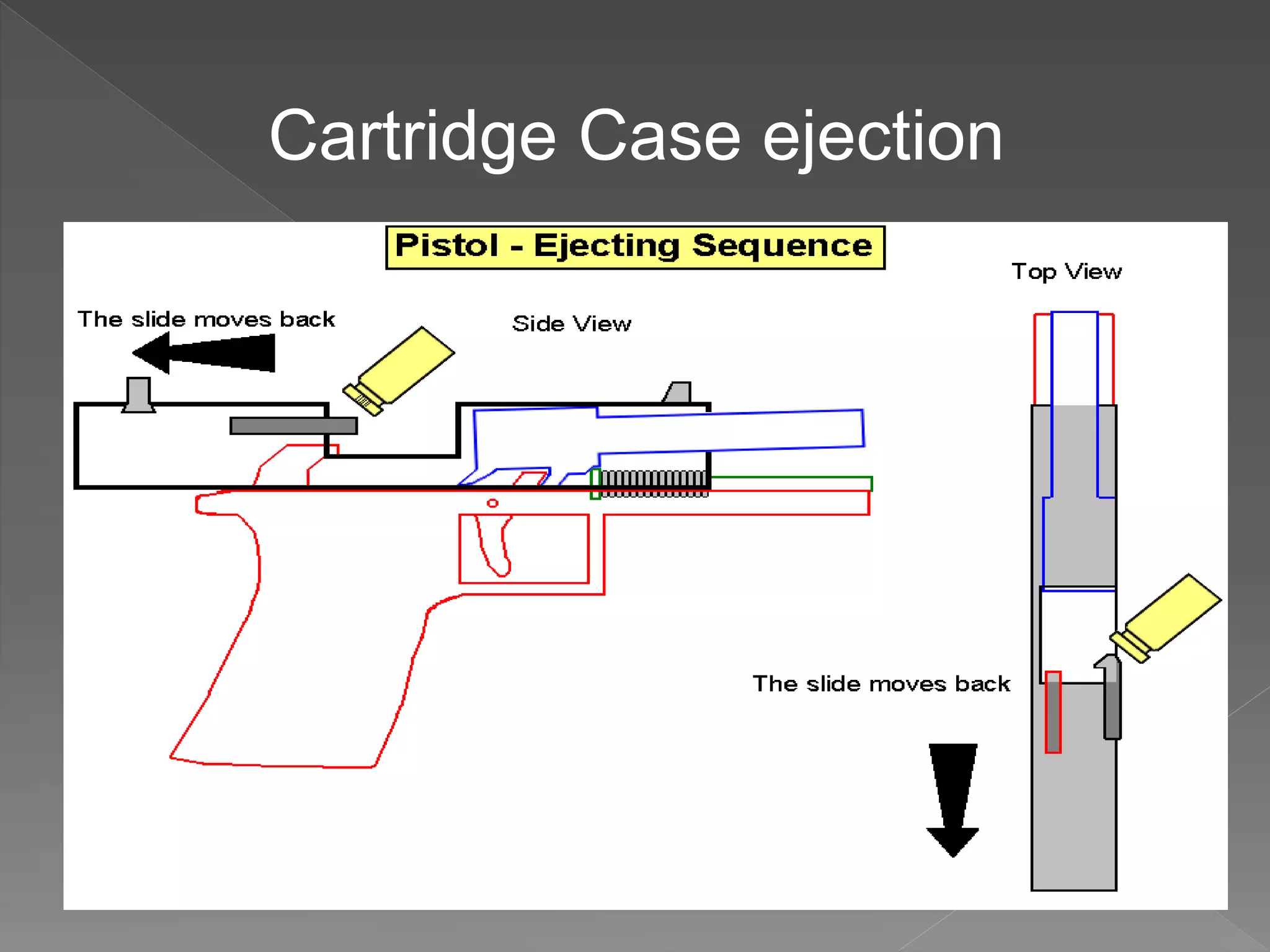
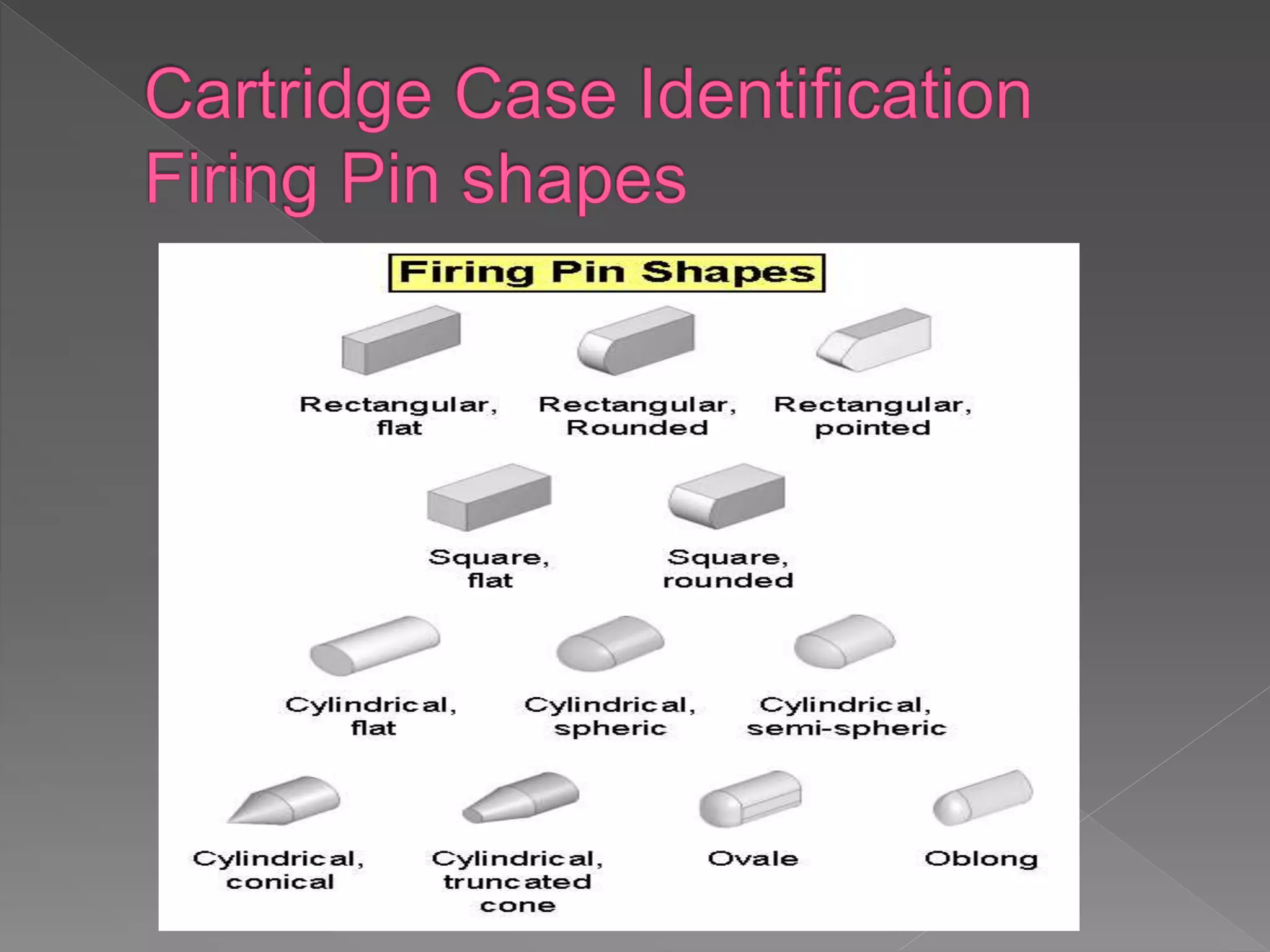
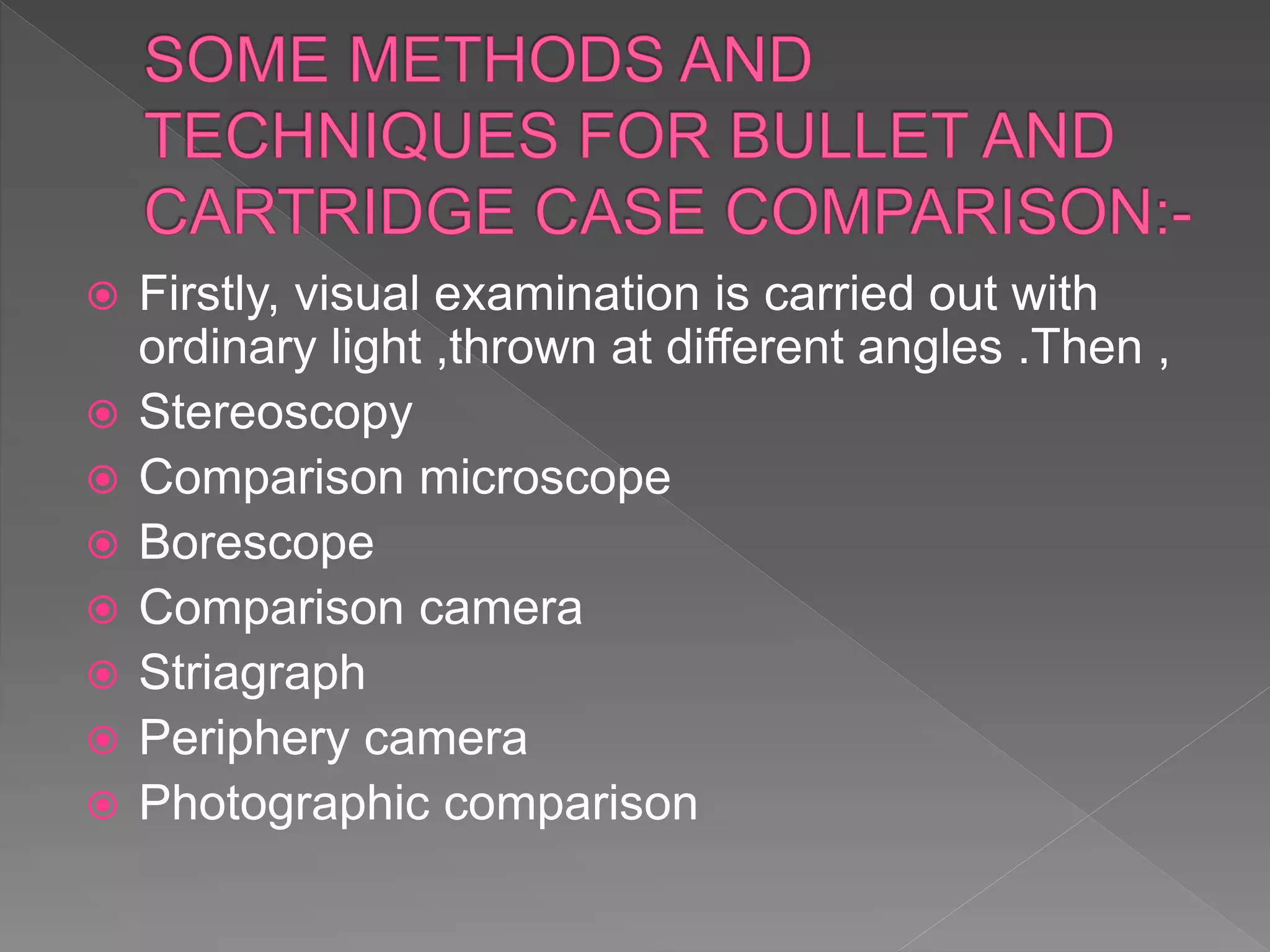
The document provides an in-depth overview of forensic ballistics, a science dealing with shootings to support justice, including concepts such as firearm identification and the various types of ballistics: internal, external, and terminal. It explains how firearms function, the characteristics of ammunition, the importance of identifying specific firearms through unique markings left on bullets and cartridge cases, and techniques used in forensic analysis. Advanced imaging technologies such as IBIS and BulletTrax-3D are detailed for enhancing the accuracy of bullet and cartridge case comparisons.