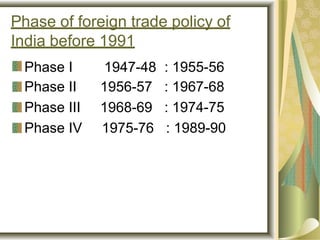
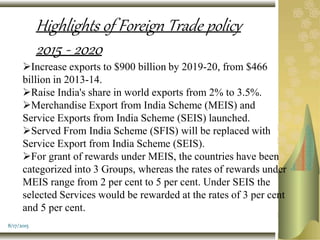
The foreign trade policy of India has evolved over time and can be classified into the period before 1991 and after 1991. Before 1991, the policy focused on import substitution and restrictive trade policies. After 1991, the policy shifted toward export promotion and import liberalization by removing restrictions. Key goals of recent policies include raising India's share of global exports to 3.5% by 2020 and increasing merchandise exports to $900 billion by 2019-20. Major initiatives include Make in India, Digital India, and Skills India. Policies aim to simplify procedures and move towards paperless and online processes.