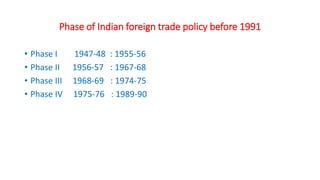
The document summarizes India's foreign trade policies from 1947 to the present. It discusses the objectives and key highlights of different phases of foreign trade policy before 1991, which focused on import substitution and export promotion. After 1991, policies liberalized trade and promoted exports. Recent policies aim to increase India's share of global exports to 3.5% by 2019-2020 and double exports of goods and services by 2014 through various incentive schemes like MEIS, SEIS, and EPCG which allows import of capital goods at concessional duty rates with export obligations.