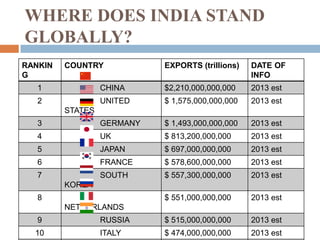
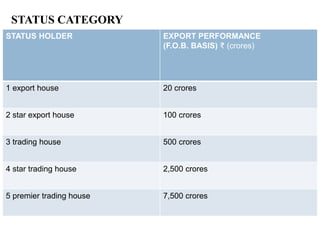
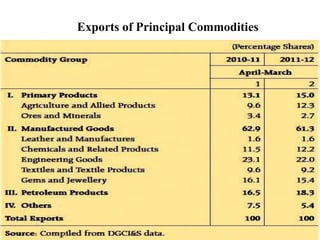
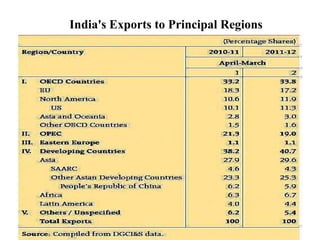
The document summarizes India's Foreign Trade Policy for 2009-2014. It outlines the objectives of promoting exports and increasing India's competitiveness globally. It provides details on export status holders and the incentives they receive, such as longer credit periods and exemption from customs clearances. It also highlights sectors that received new support under the policy, including gems and jewelry, leather, tea, and automobiles.