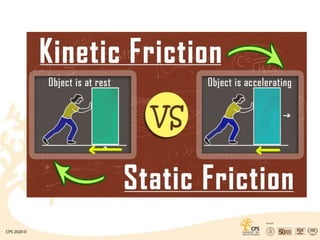
Friction is the force opposing motion between two surfaces in contact and varies based on weight and surface irregularities. It can be classified into static, kinetic, sliding, and rolling friction, with rolling friction being less than sliding friction. While friction has advantages such as aiding movement and stopping, it also has drawbacks like energy wastage and increased wear.