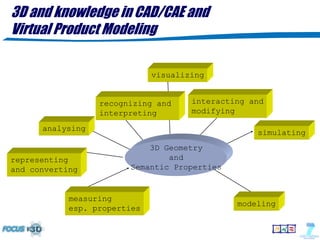
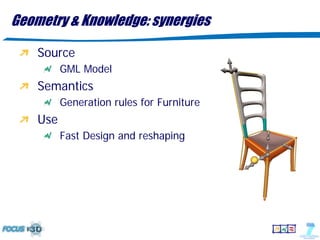
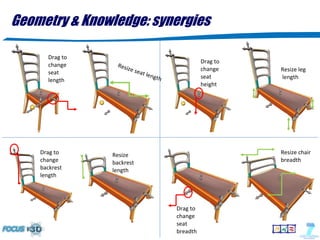
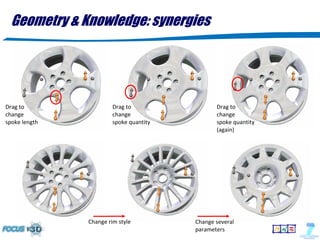
The document discusses the evolution of 3D shape modeling in CAD/CAE, emphasizing the need for semantic recognition and self-awareness of shapes beyond mere geometry. It introduces generative modeling language (GML) as a transformative approach that allows for high-level shape design by defining operations rather than static objects. Key challenges identified include the lack of links between 3D models and product properties, the complexity of mechatronic systems, and the necessity for better interoperability in simulation frameworks.