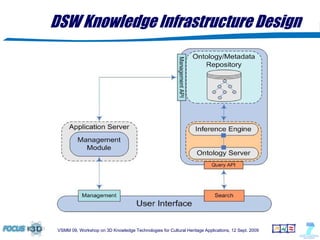
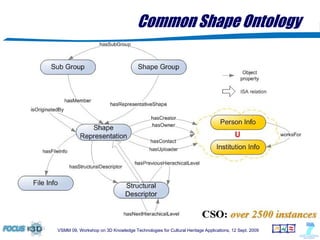
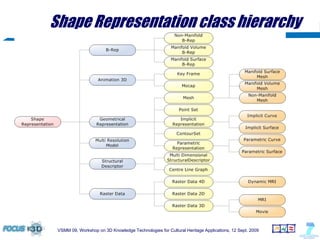
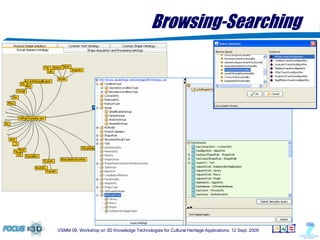
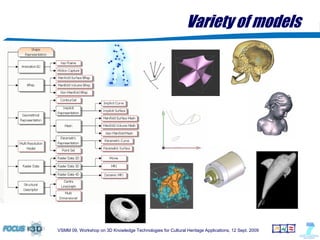
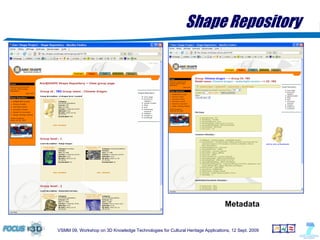
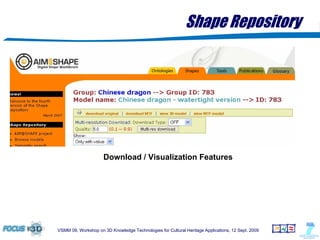
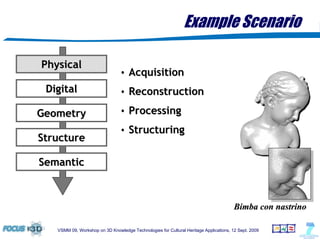
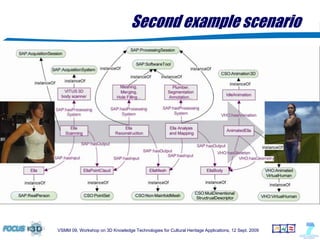
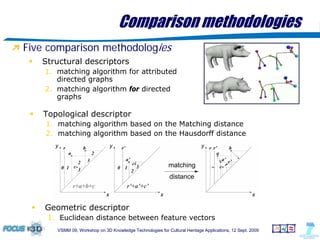
The document outlines a semantic-based framework called the Digital Shape Workbench (DSW) for managing, searching, and retrieving 3D resources, integrating various components through ontological structures. Key features include resource management, advanced searching, and browsing of a substantial knowledge base comprising over 1000 models and various software tools, as well as multiple ontologies for improved resource categorization. The DSW serves as a comprehensive knowledge management system, supporting significant achievements in the field of cultural heritage applications.