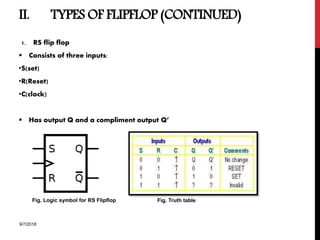
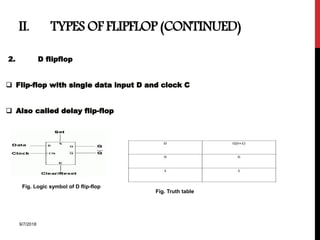
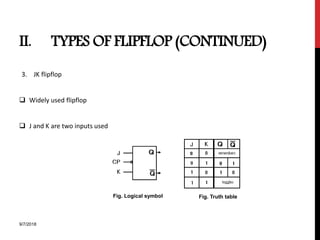
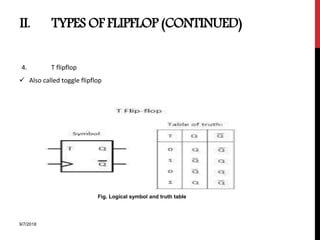
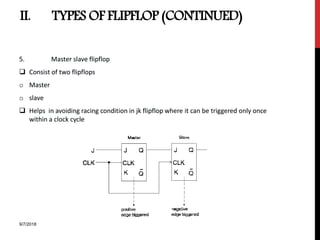
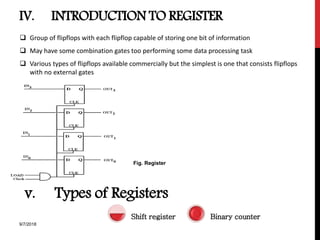
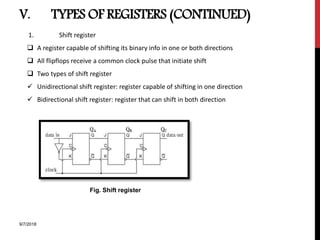
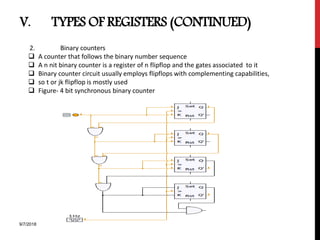
The document provides an overview of flip-flops and registers, including their types and applications in digital systems. It details various flip-flop types such as RS, D, JK, T, and master-slave, highlighting their functionalities and use cases like storage and counting clock pulses. Additionally, the document discusses registers, including shift registers and binary counters, and their roles in data processing and storage.