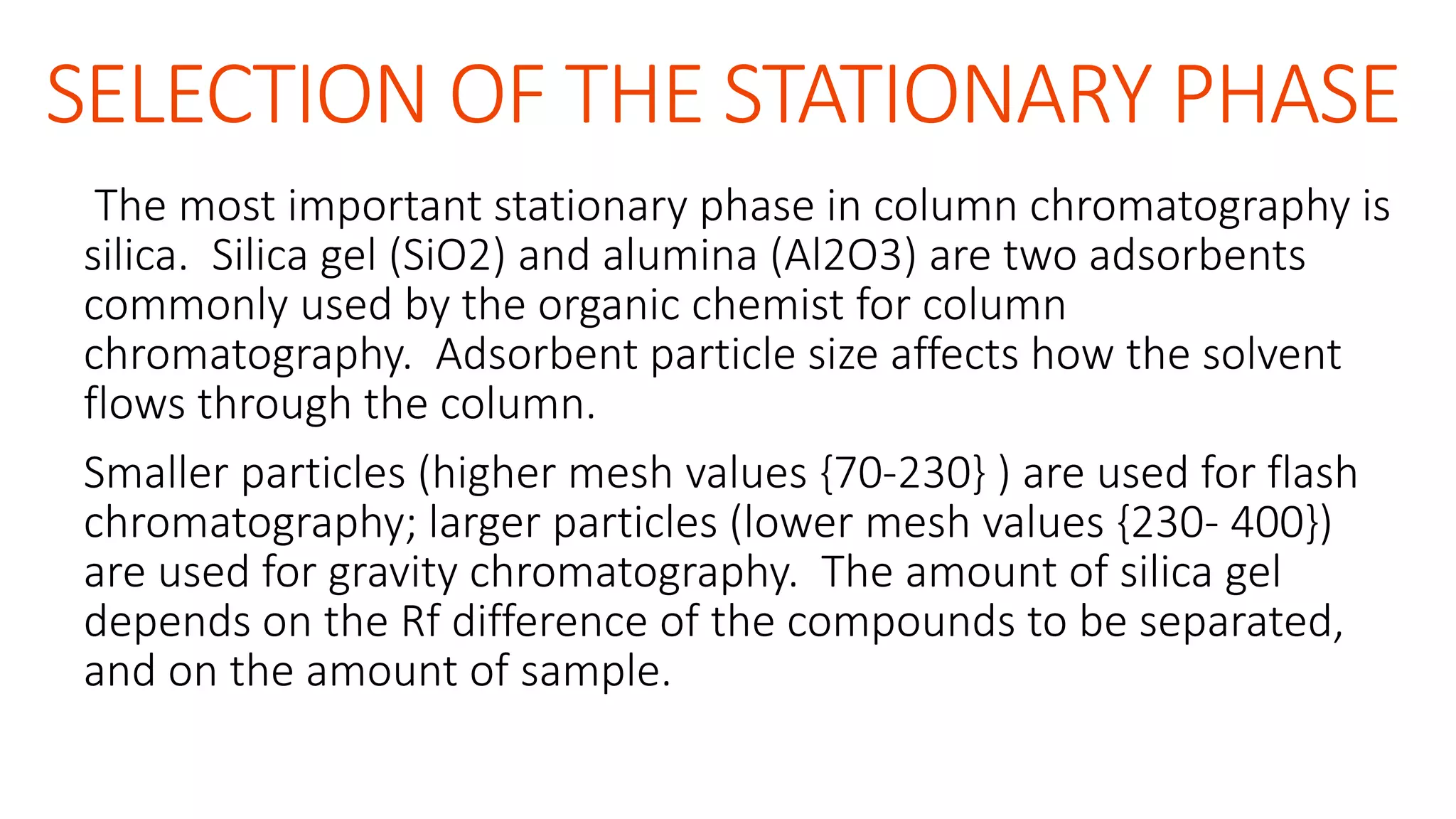
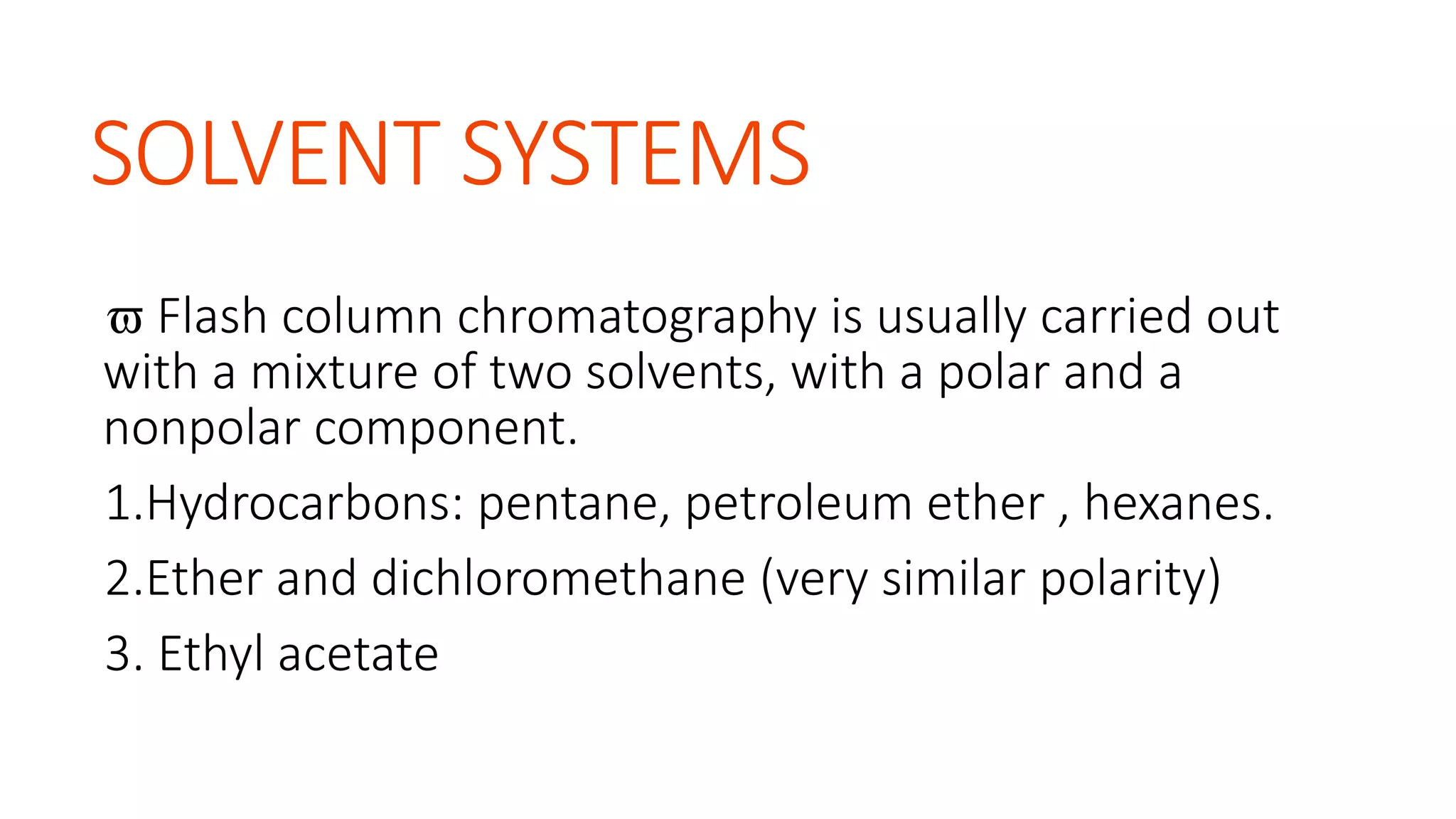
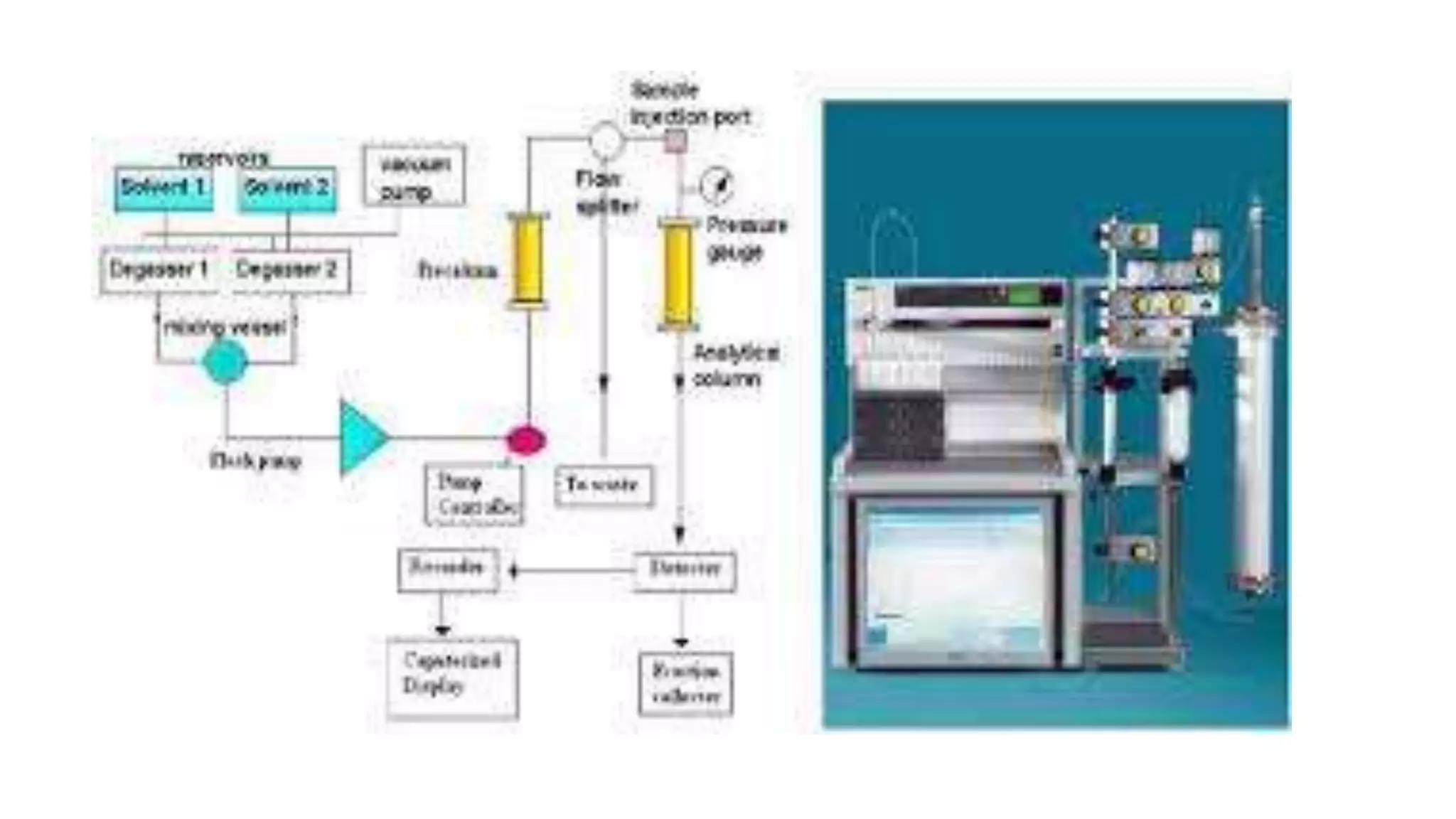
Flash chromatography is a technique used to rapidly separate mixtures. It uses slightly smaller silica gel particles and pressurized gas to drive solvents through the column faster than gravity chromatography. Key aspects include using a stationary phase like silica gel and solvent systems to differentially elute compounds. Samples can be loaded wet or dry onto the column then eluted with solvents. Flash chromatography provides a fast, economical method for separating gram quantities of compounds in the lab. It has applications in natural products, pharmaceuticals, and other areas.