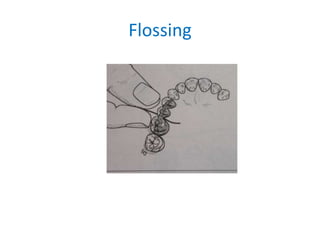
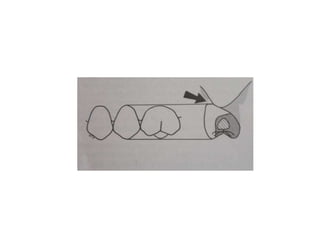
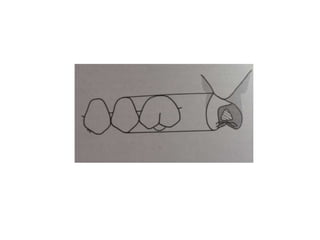
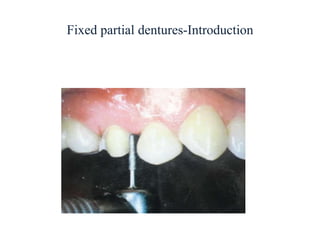
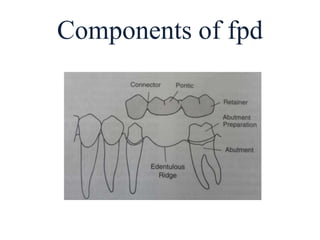
- A fixed partial denture (FPD) replaces missing teeth and is cemented permanently to adjacent natural teeth or implants.
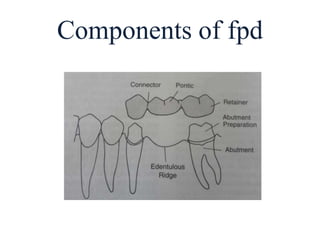
- Key components of an FPD include retainers attached to abutment teeth, a pontic that replaces the missing tooth, and a connector that joins the pontic and retainer.
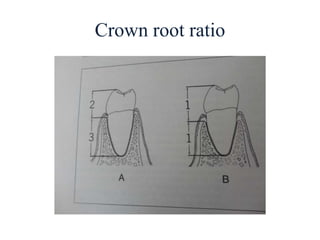
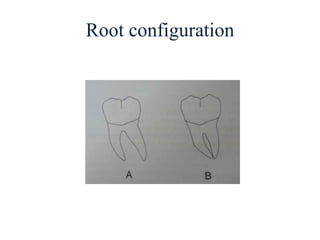
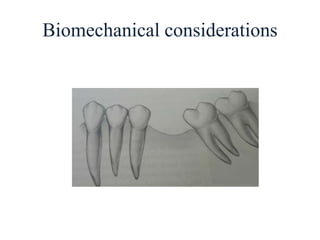
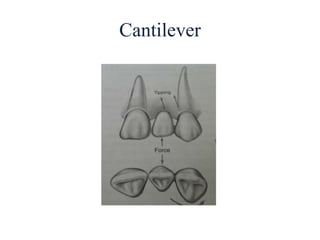
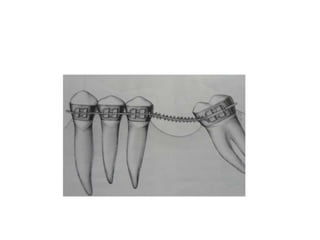
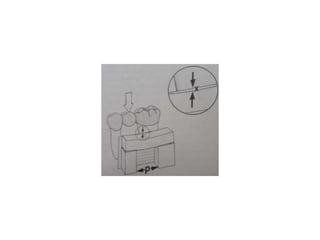
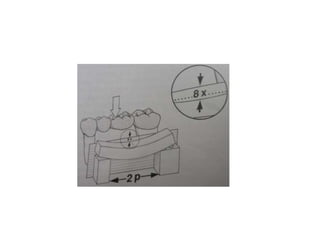
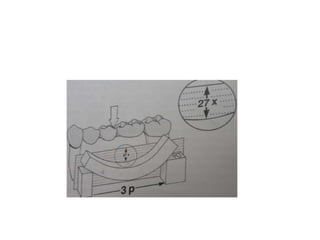
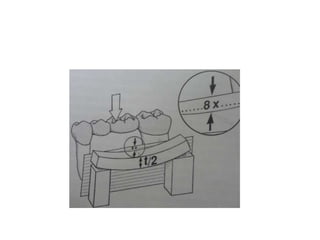
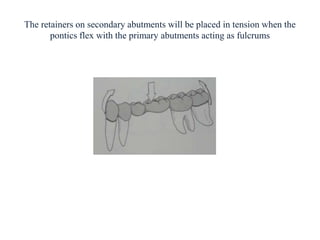
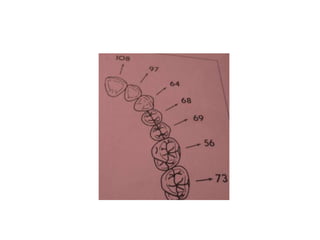
- Proper evaluation of potential abutment teeth considers factors like crown-root ratio, root configuration, bone support, and overall oral health to ensure the FPD can withstand functional forces.















![• Congenitally malformed teeth which do not
have adequate tooth structure[amelogenesis
imperfecta,dentinogenesis imperfecta]
• Medically compromised patients like
hypertension,bleeding disorders,leukemia etc,
• Mentally sensitive patients,very old patients.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fixedpartialdentures-copy-220319061814/85/FIXED-PARTIAL-DENTURES-Dr-PRASAD-ARAVIND-19-320.jpg)















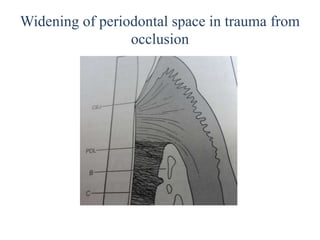
![• Width of periodontal ligament space[increased
in trauma from occlusion]
• Root stumps
• Impacted tooth
• Any other pathology like cysts
• Thickness of soft tissues](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fixedpartialdentures-copy-220319061814/85/FIXED-PARTIAL-DENTURES-Dr-PRASAD-ARAVIND-45-320.jpg)
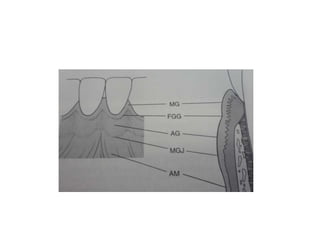







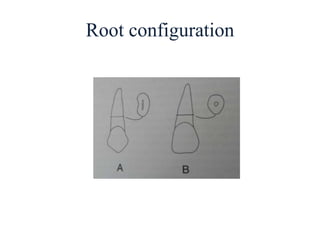
![Periodontal ligament area
• Antes law
• Any fpd with more than two teeth are high risk
• Possible to do fpd repacing more than two
teeth
• Teeth with low perio support can serve as
support in selected cases[splinting]
• Avoid herodontics
• Advice good post op recall and checkup](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fixedpartialdentures-copy-220319061814/85/FIXED-PARTIAL-DENTURES-Dr-PRASAD-ARAVIND-58-320.jpg)


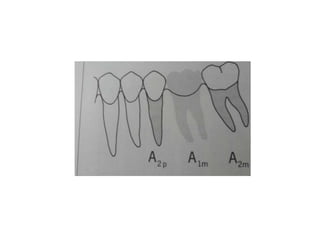
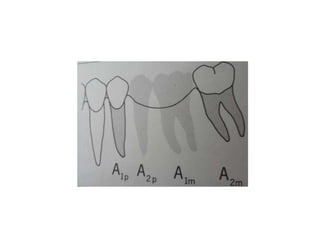
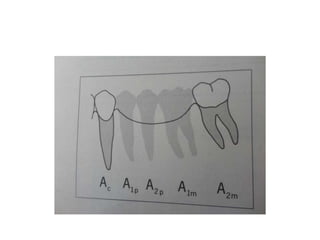












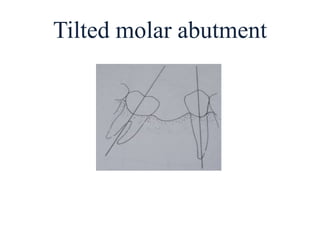
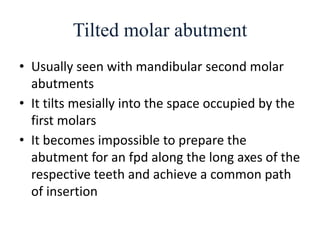
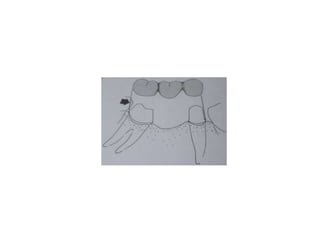

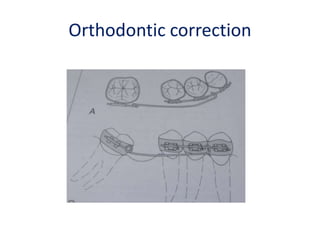



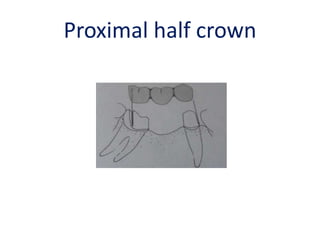




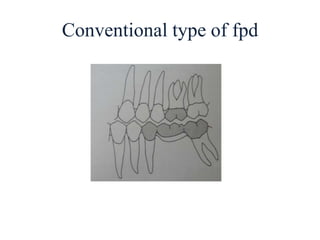
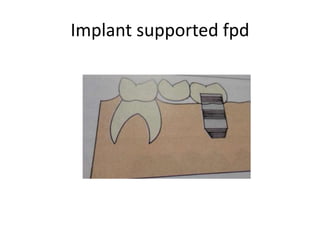

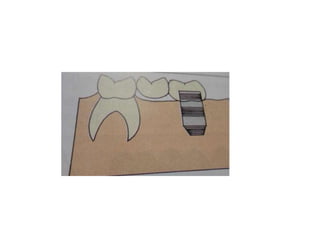


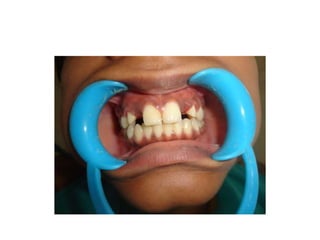
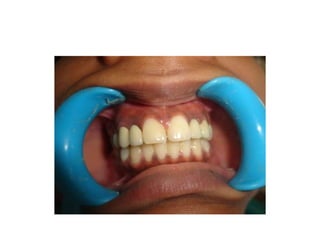
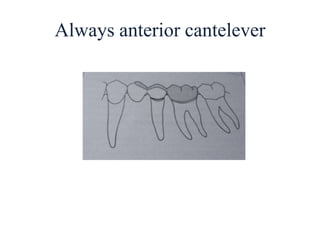


















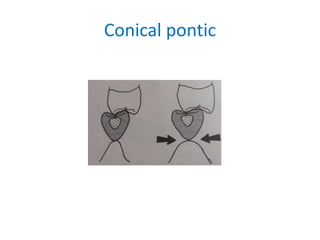
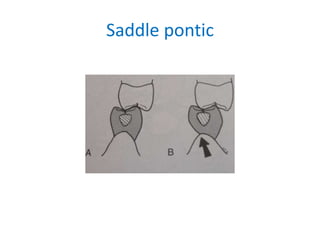
![• Portion of pontic touching the ridge should be
as convex as possible
• Tip of pontic should not extend past the
mucogingival junction[ulcer]
• There should not be a space between the
pontic and the ridge on the facial surface of
the ridge](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fixedpartialdentures-copy-220319061814/85/FIXED-PARTIAL-DENTURES-Dr-PRASAD-ARAVIND-137-320.jpg)









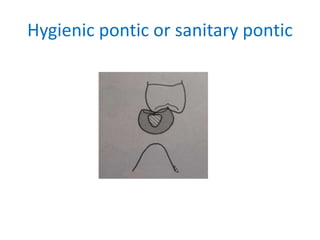
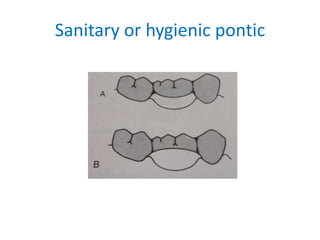
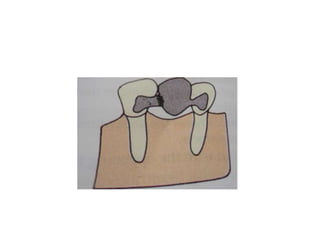
![• Pontic has no contact with the ridge
• Used in nonappearance zone[mandibular 1st
molars]
• It restores occlusal function and stabilizes
adjacent and opposing teeth
• If esthetics is not required it can be made of
metal](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fixedpartialdentures-copy-220319061814/85/FIXED-PARTIAL-DENTURES-Dr-PRASAD-ARAVIND-152-320.jpg)
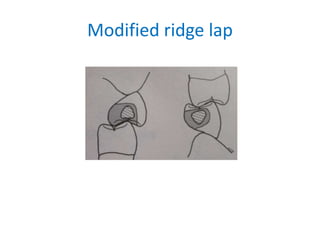
![• Occlusogingival thickness of the pontic should
be no less than 3mm
• Adequate space under the pontic to help easy
cleaning
• All convex design both faciolingually and
mesiodistally[conventional fish belly
appearance]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fixedpartialdentures-copy-220319061814/85/FIXED-PARTIAL-DENTURES-Dr-PRASAD-ARAVIND-153-320.jpg)