This document provides an introduction to Firebase and some key concepts:
- It describes how to get SHA-1/SHA-256 fingerprints for authentication on Mac, Windows, and Linux.
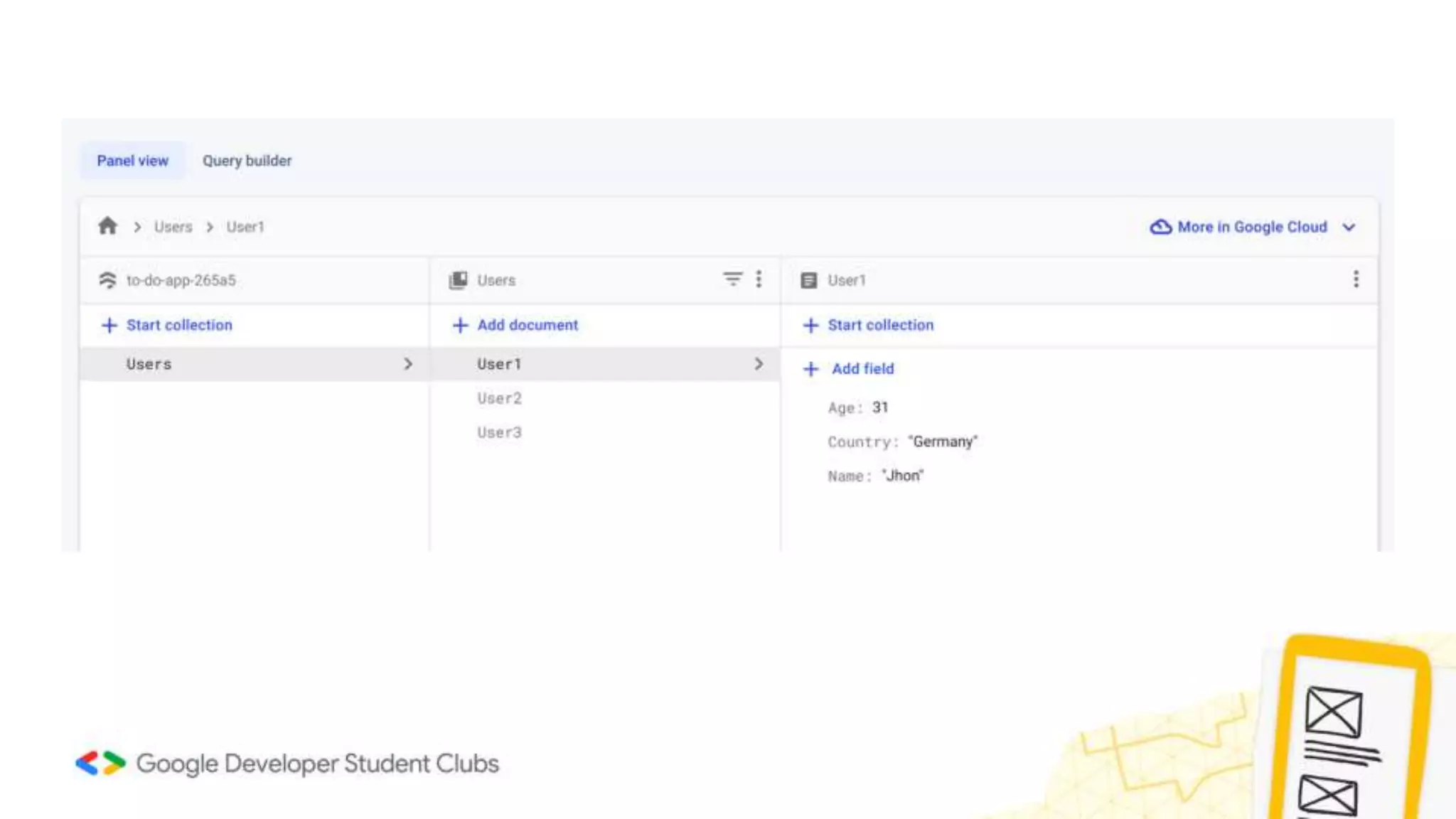
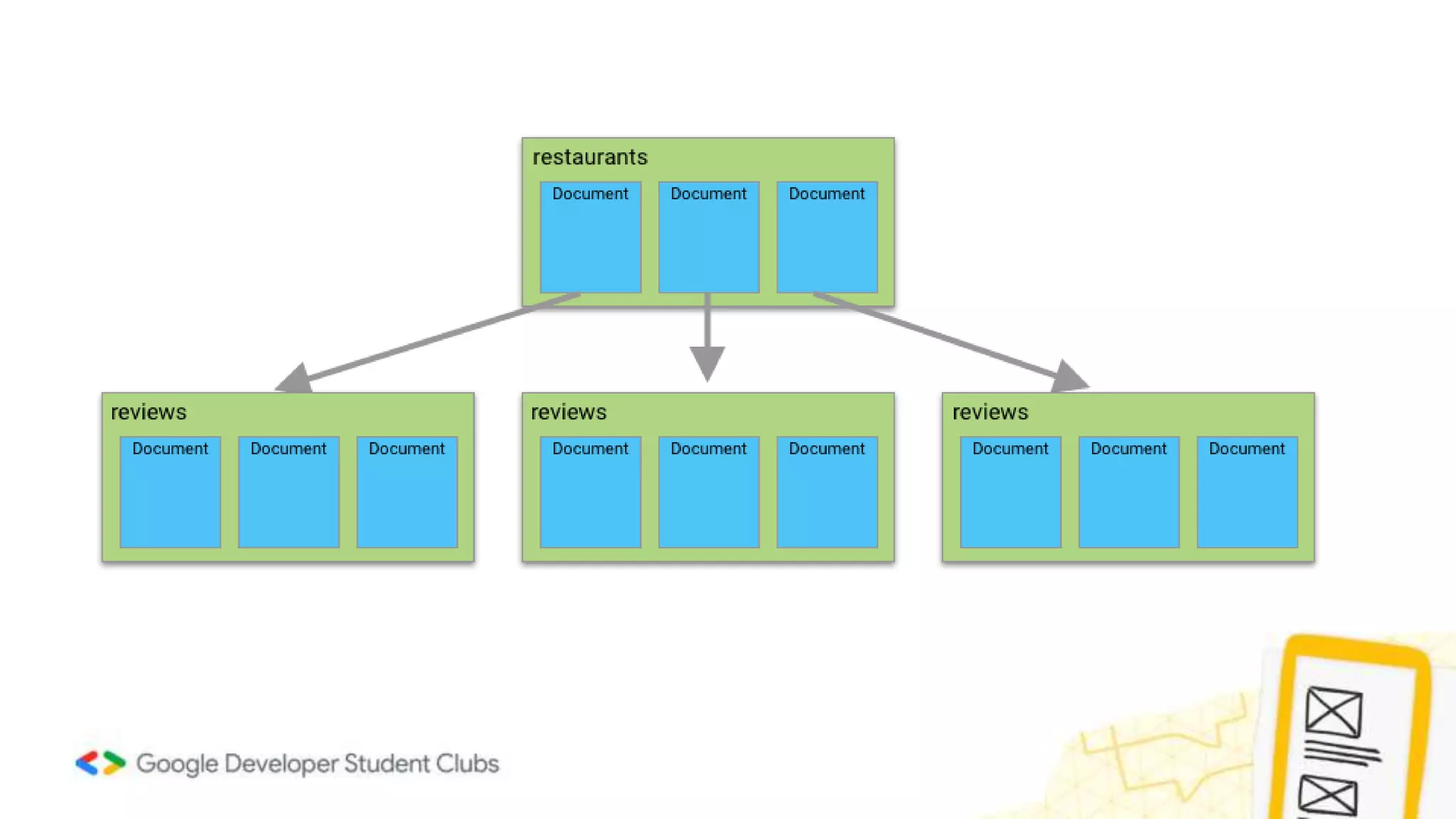
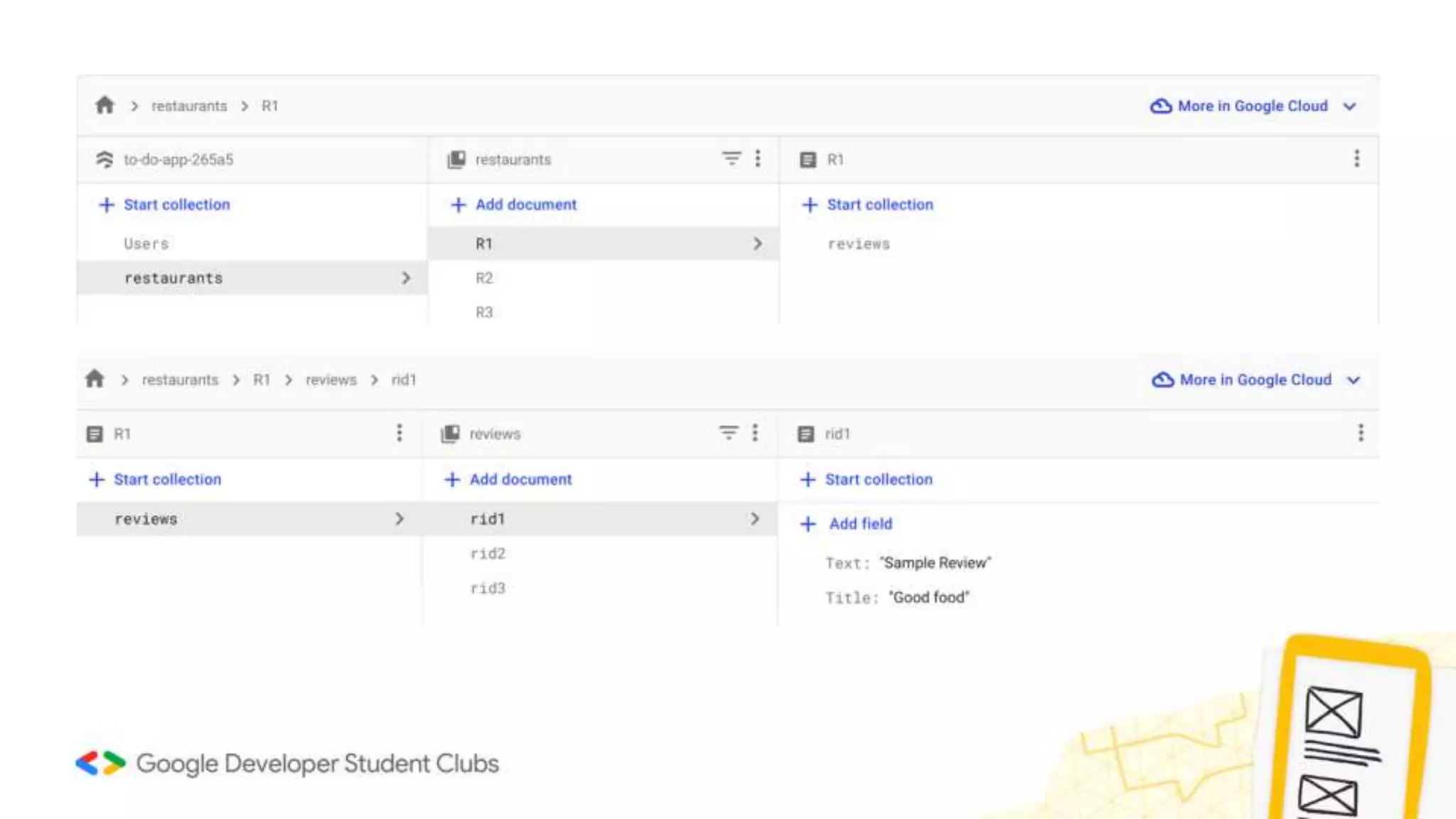
- It explains that Firebase Firestore is a NoSQL cloud database that stores data in documents within collections.
- It gives an overview of Firebase Firestore documents and nested collections.








![void main() {
List<String> ls = ["GDSC", "Flutter", "Forward"];
List<int> newls = [];
for(String s in ls) {
newls.add(s.length);
}
print(newls);
}
void main() {
List<String> ls = ["GDSC","Flutter","Forward"];
List<int> newls = ls.map((e)=>e.length).toList();
print(newls);
}
Output:
[4, 7, 7]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/firebaseintroduction-230416072045-64487284/75/Firebase-Introduction-pptx-12-2048.jpg)

