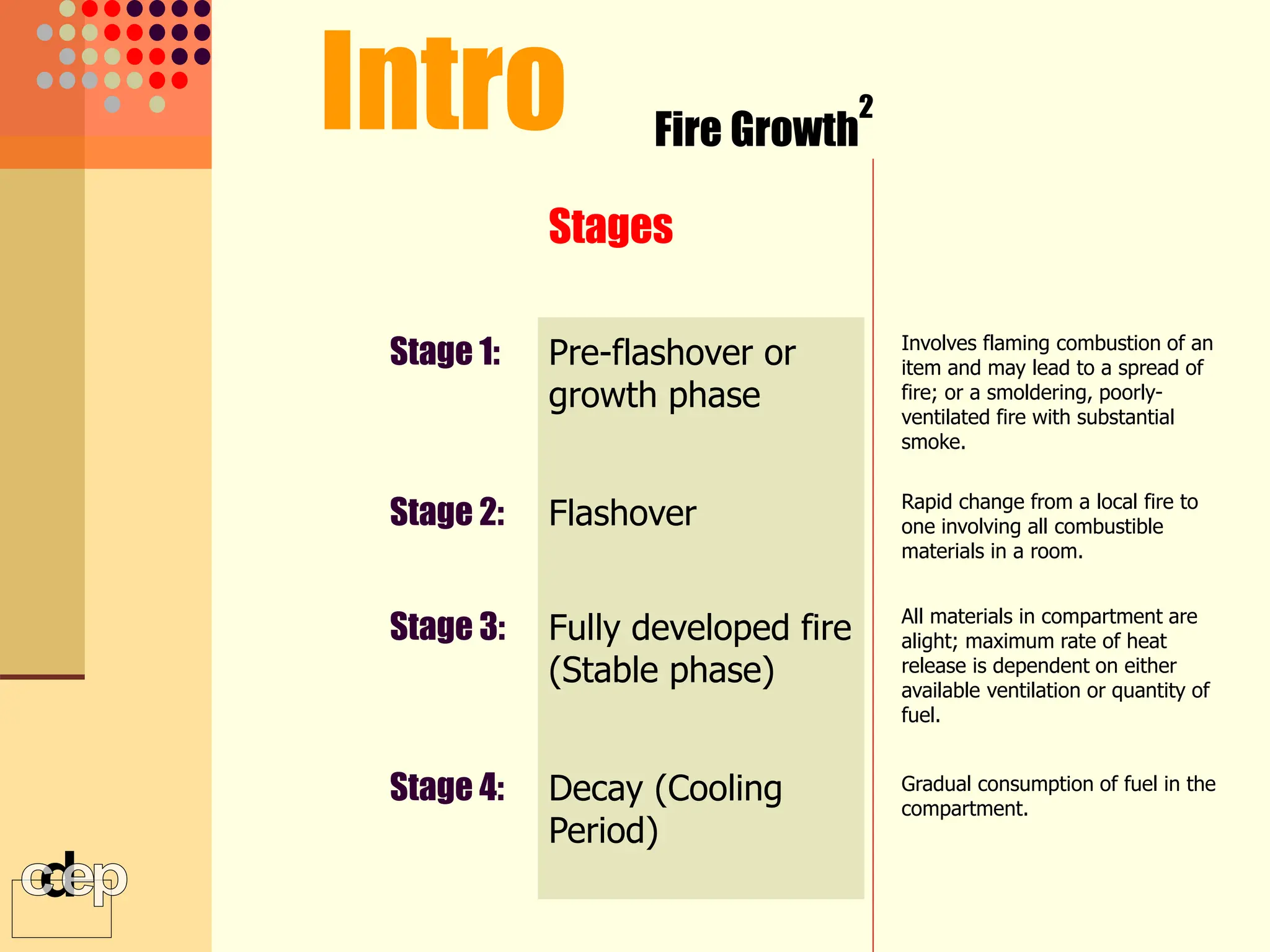
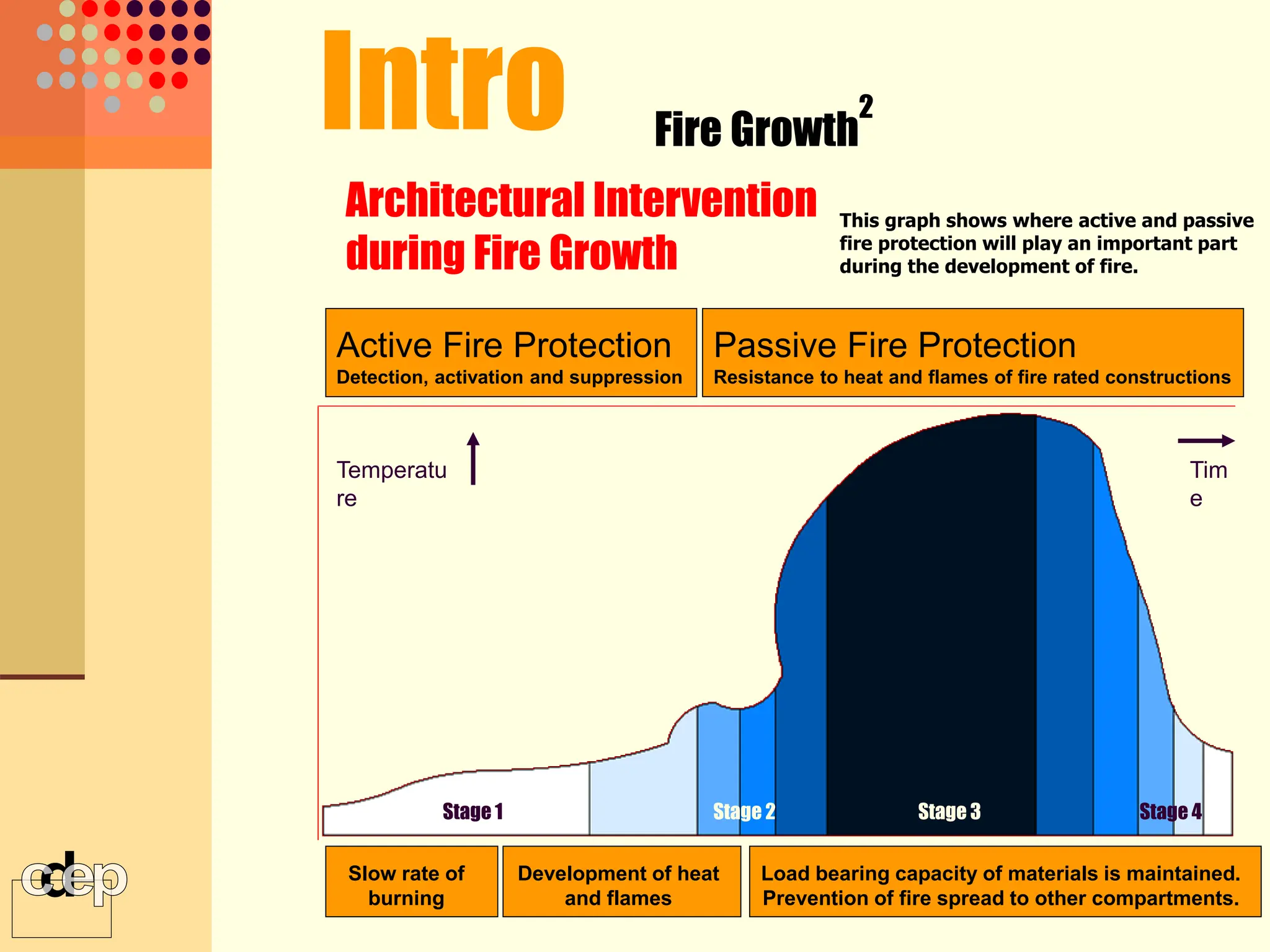
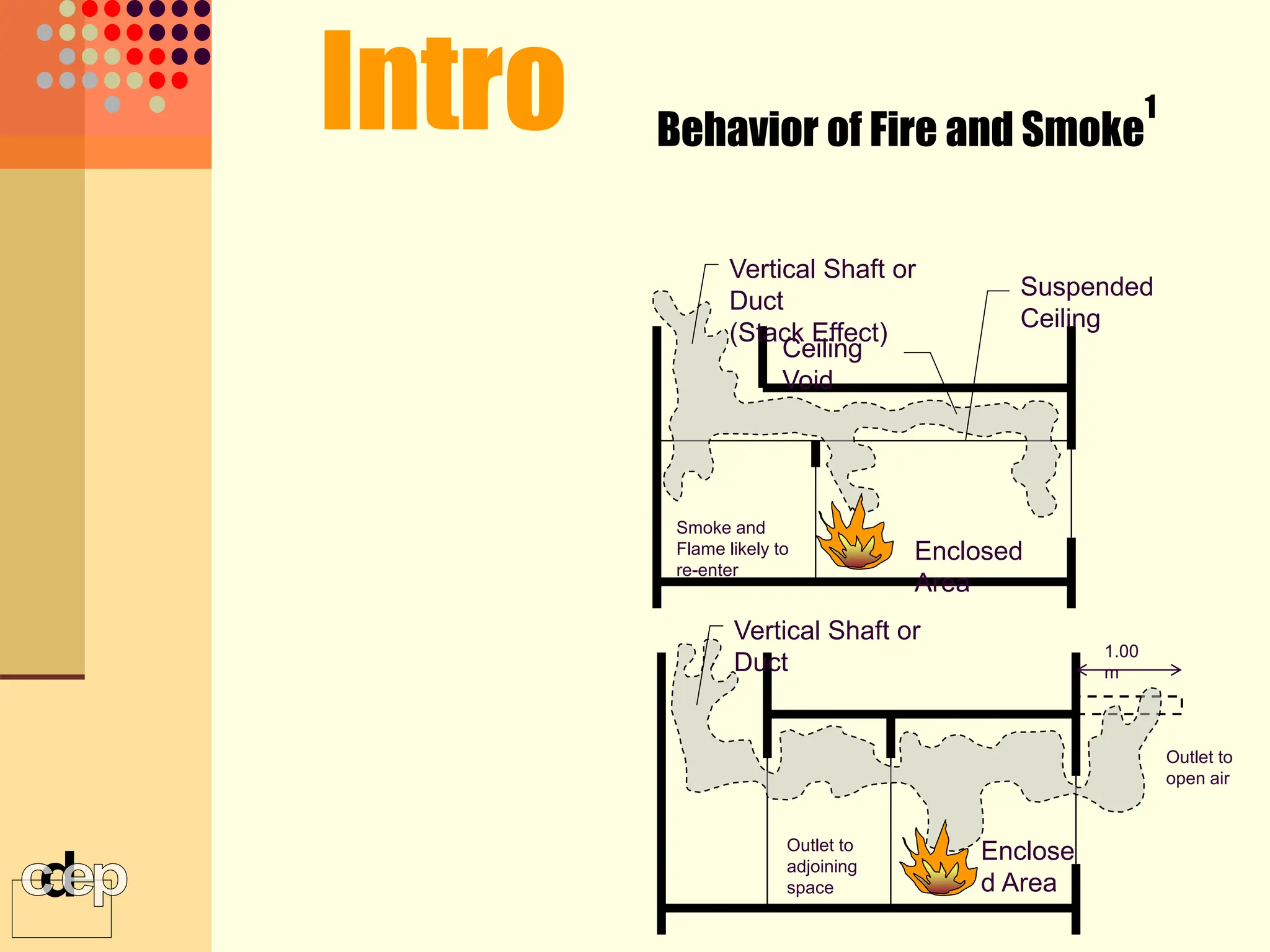
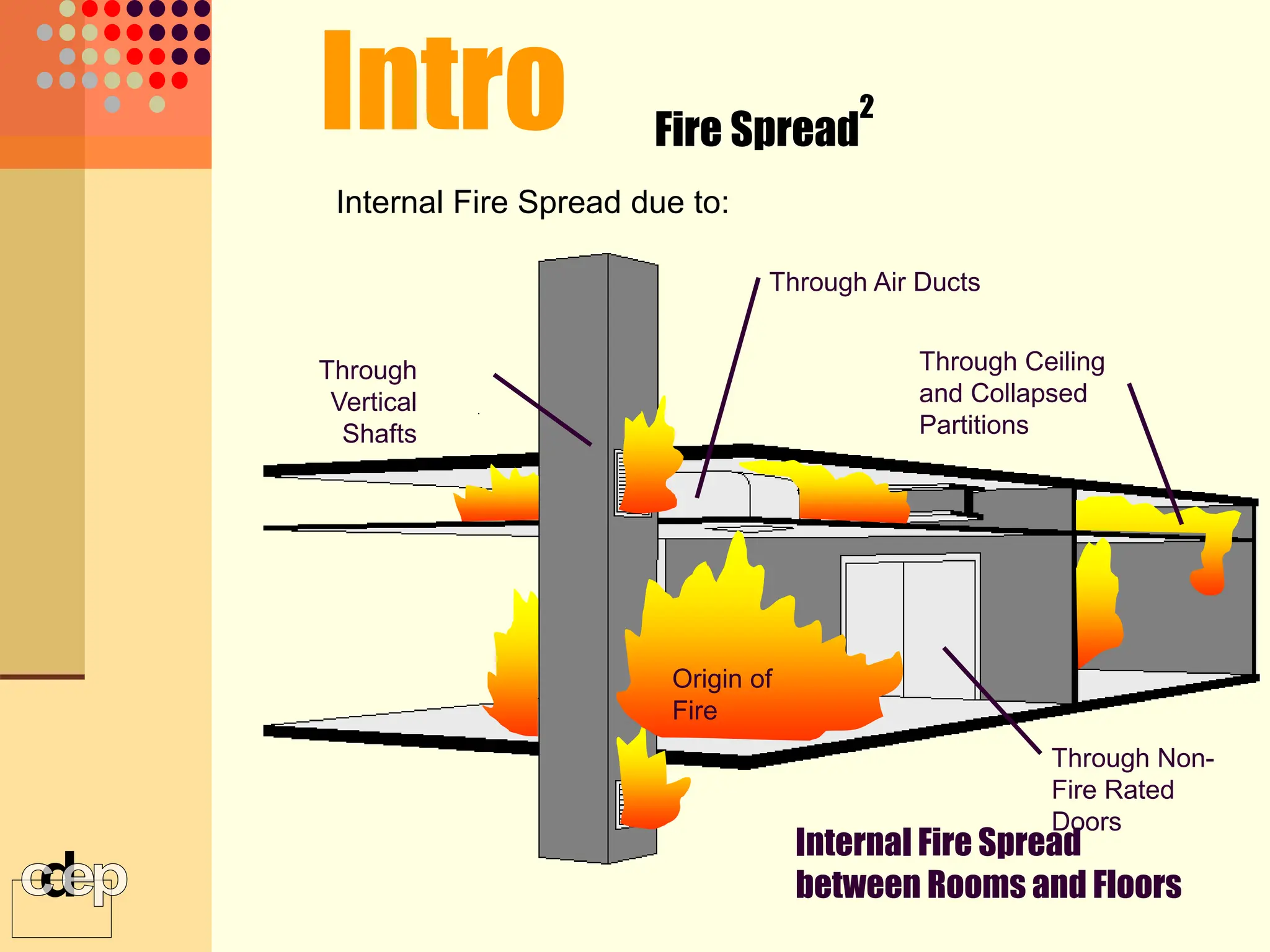
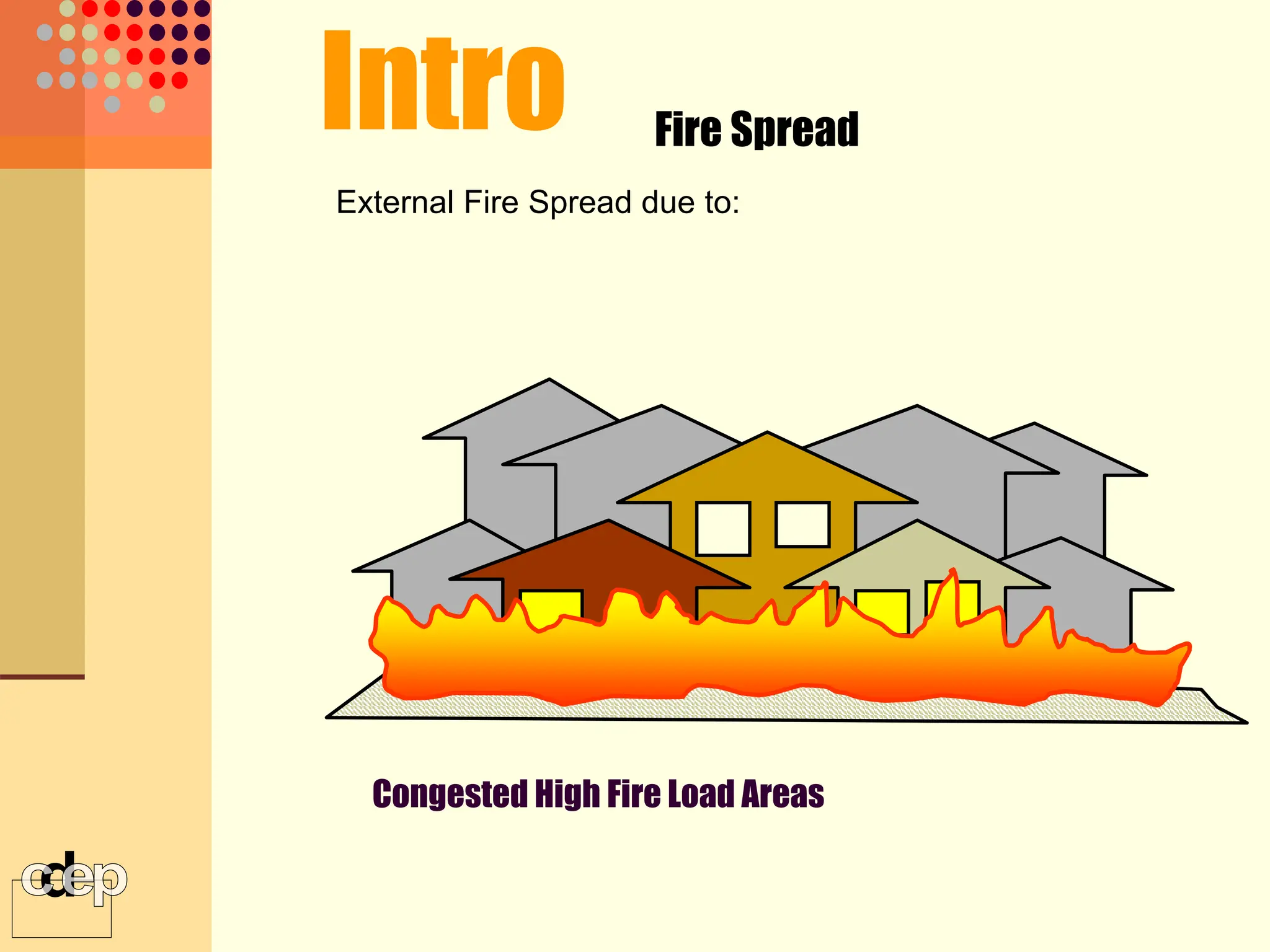
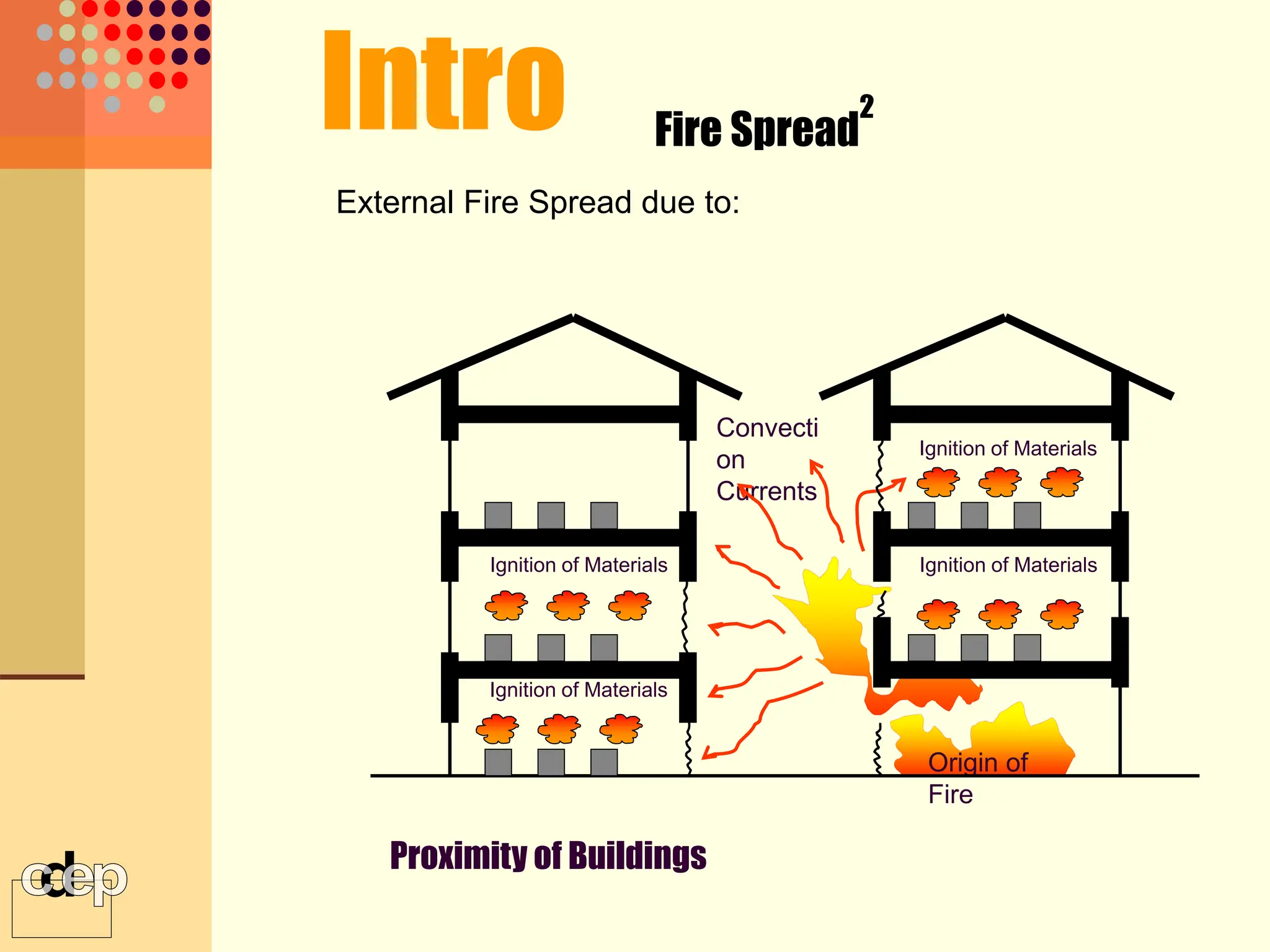
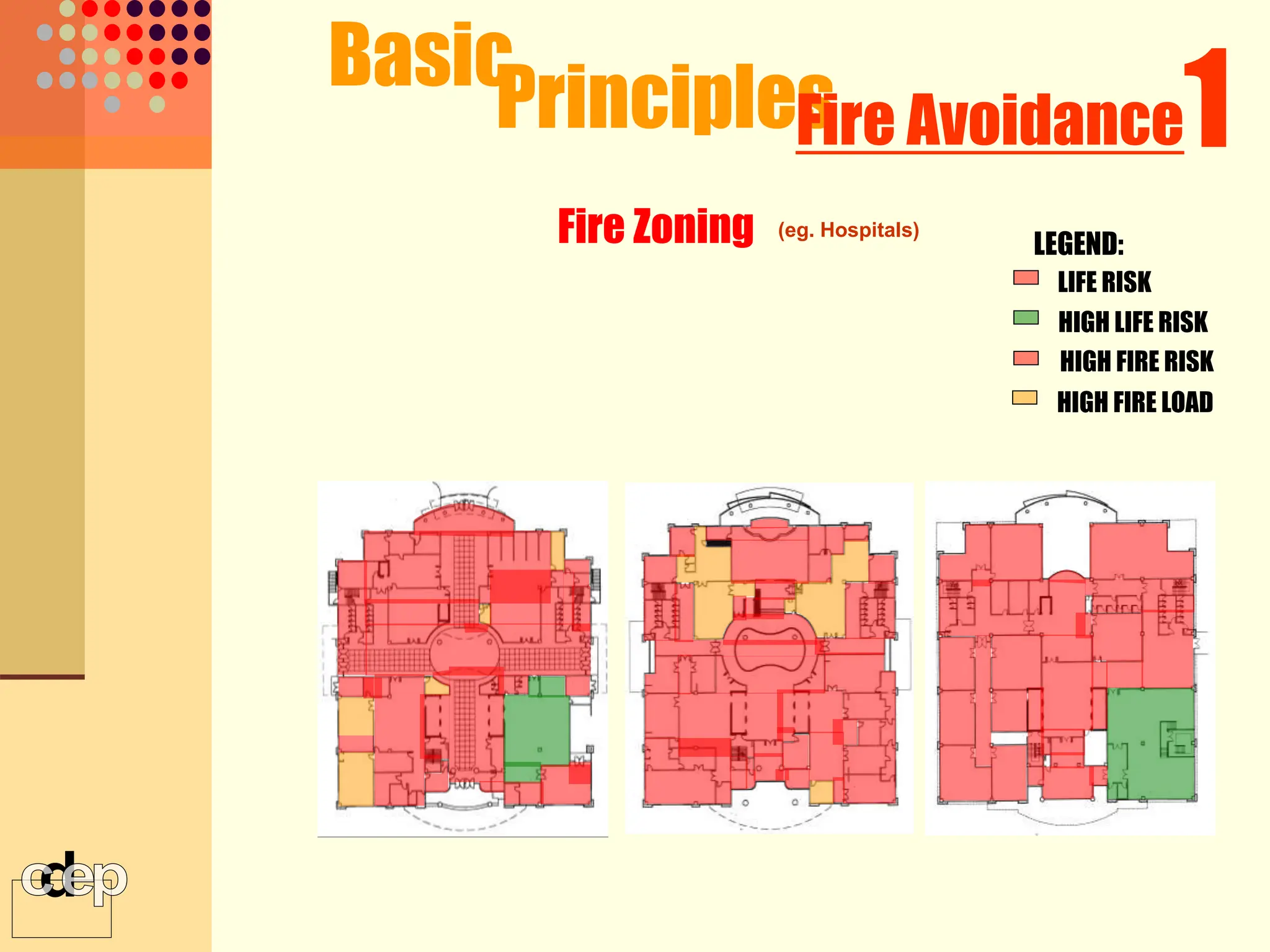
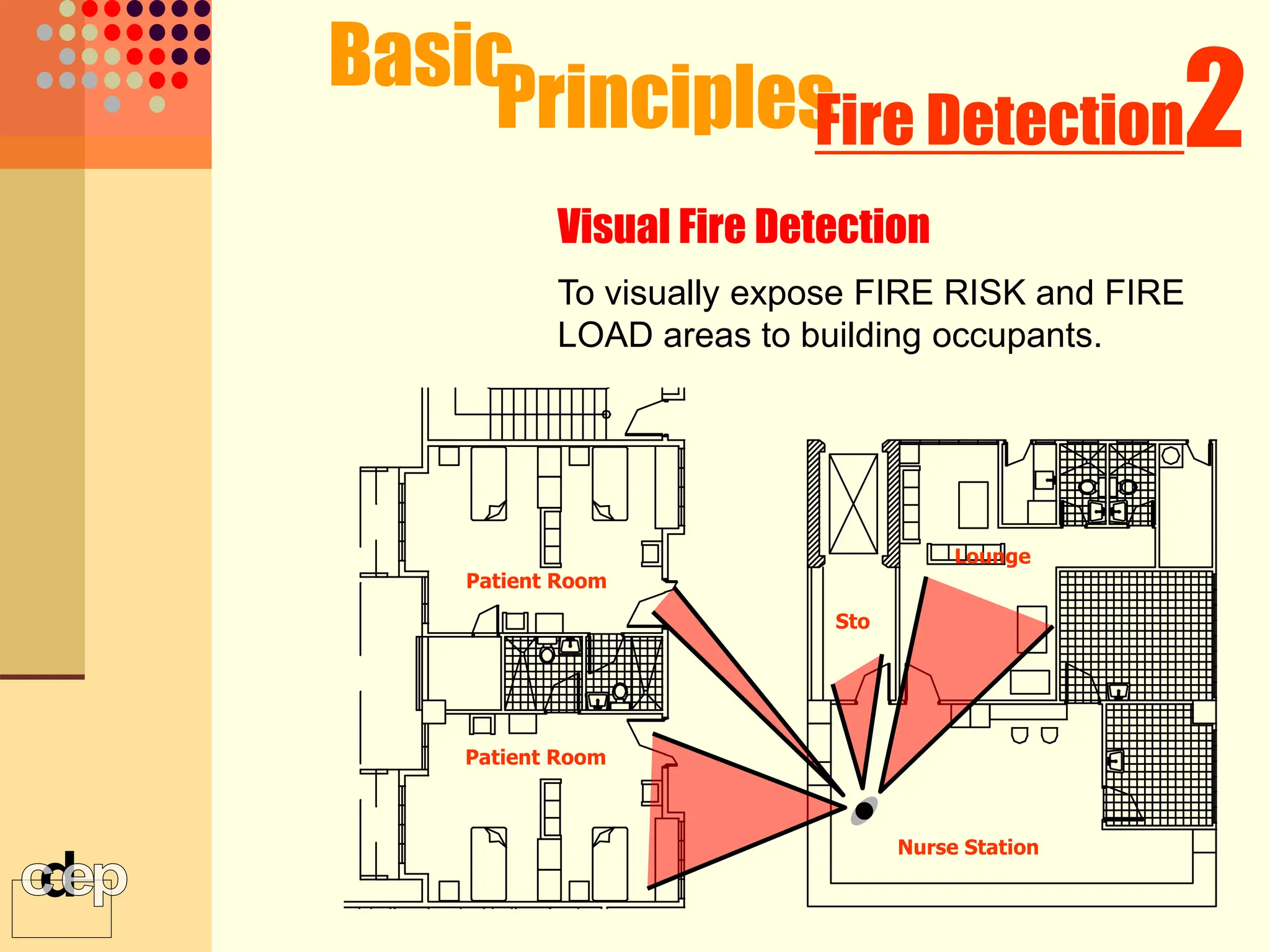
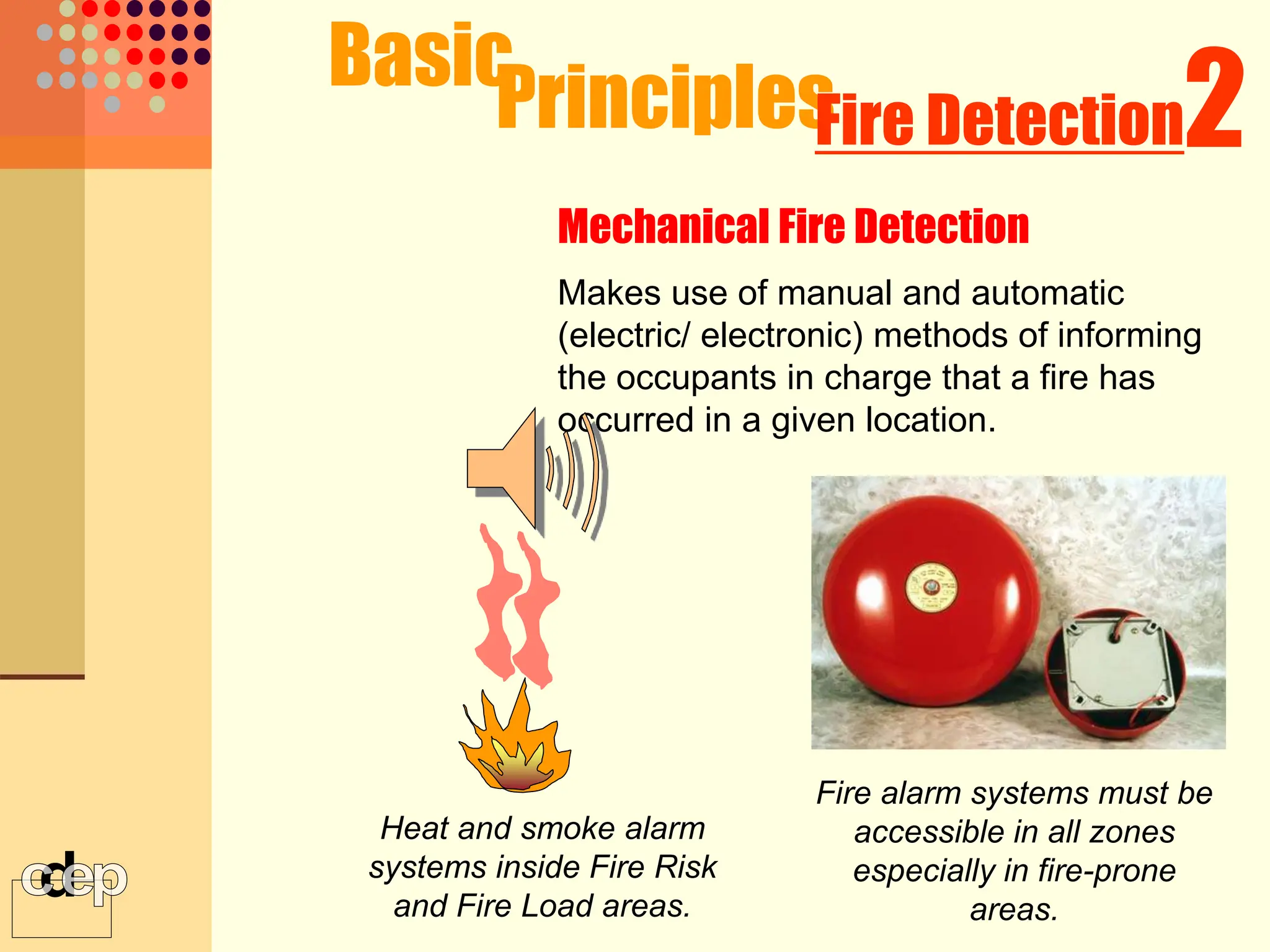
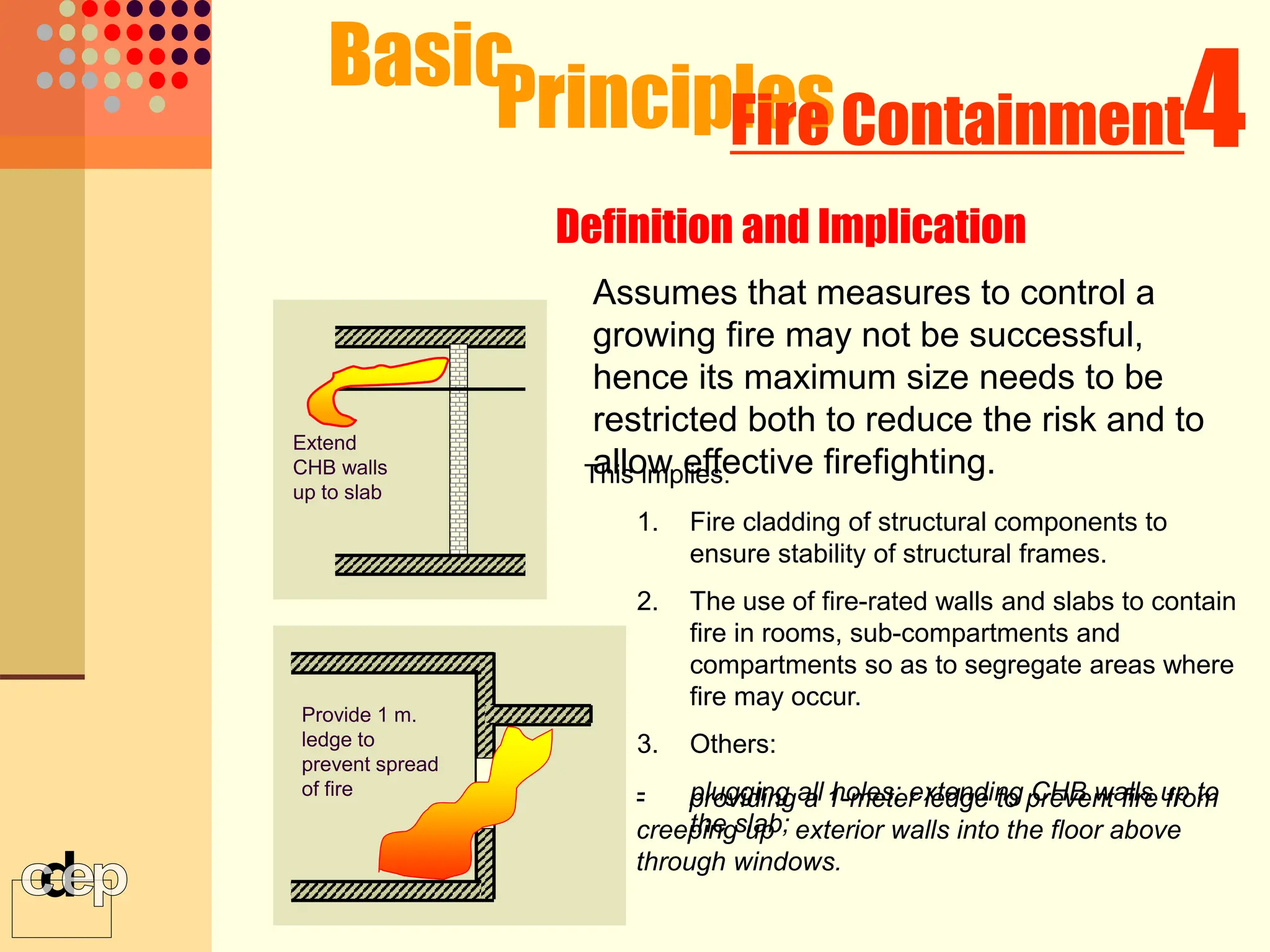
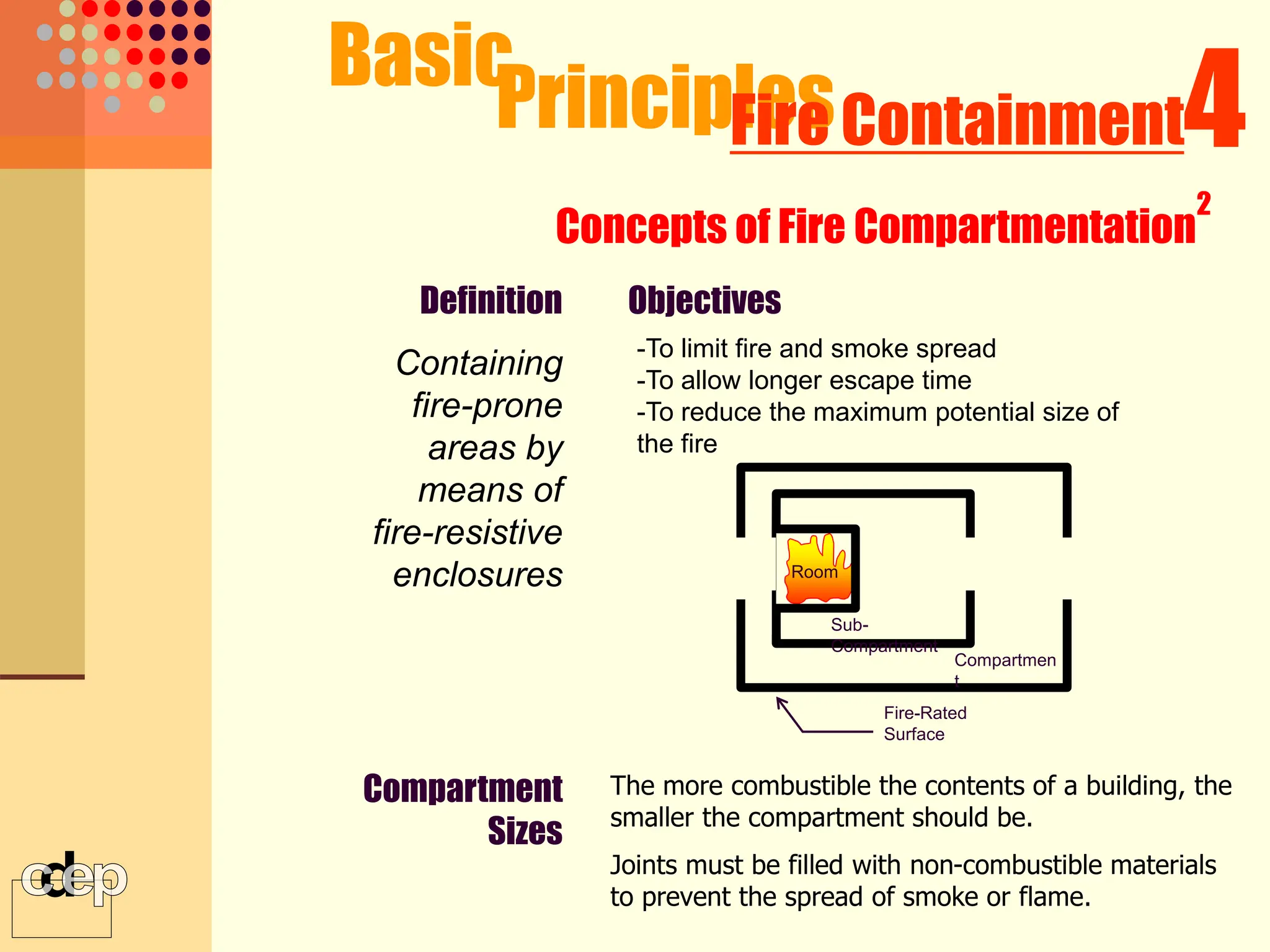
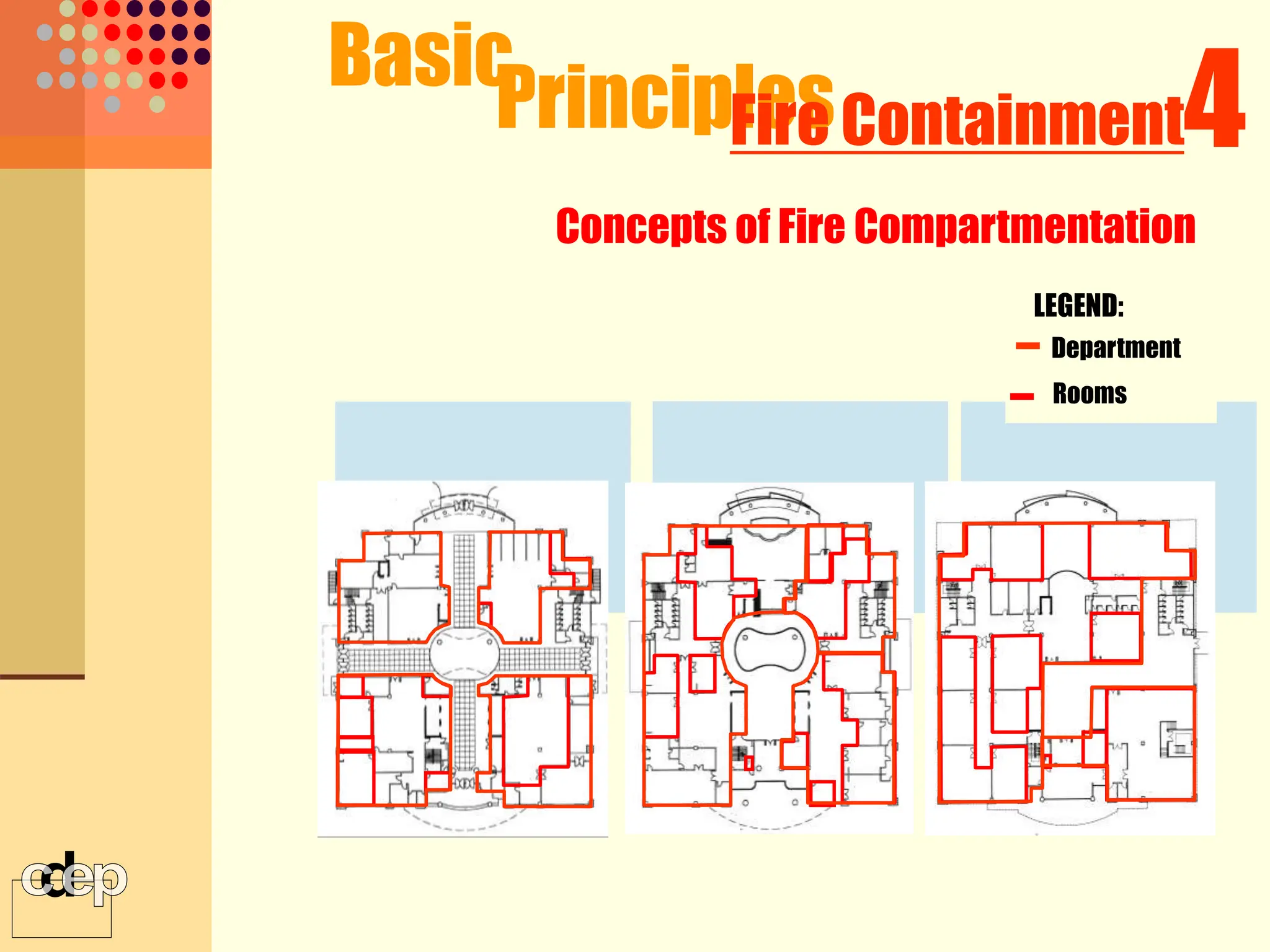
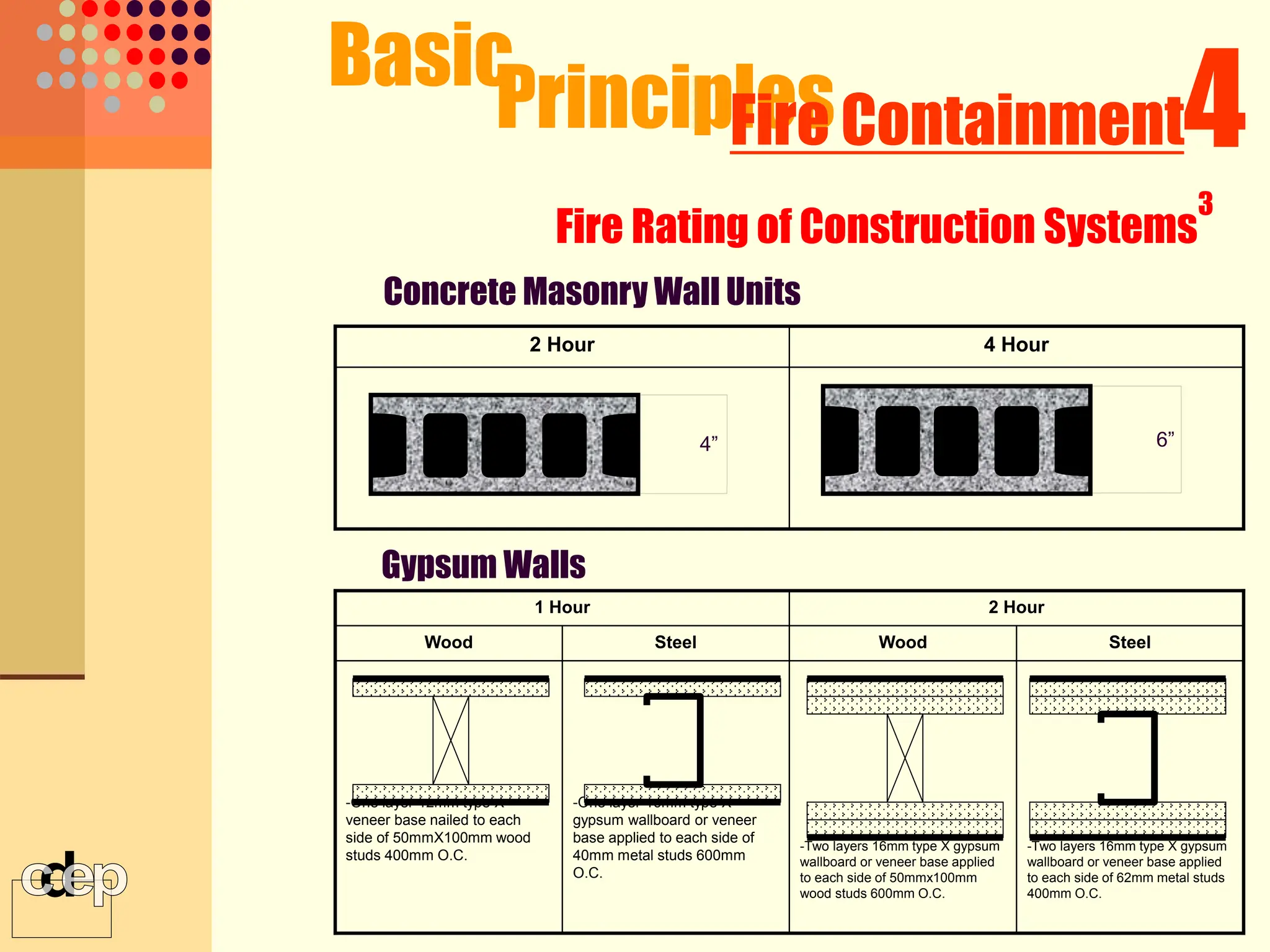
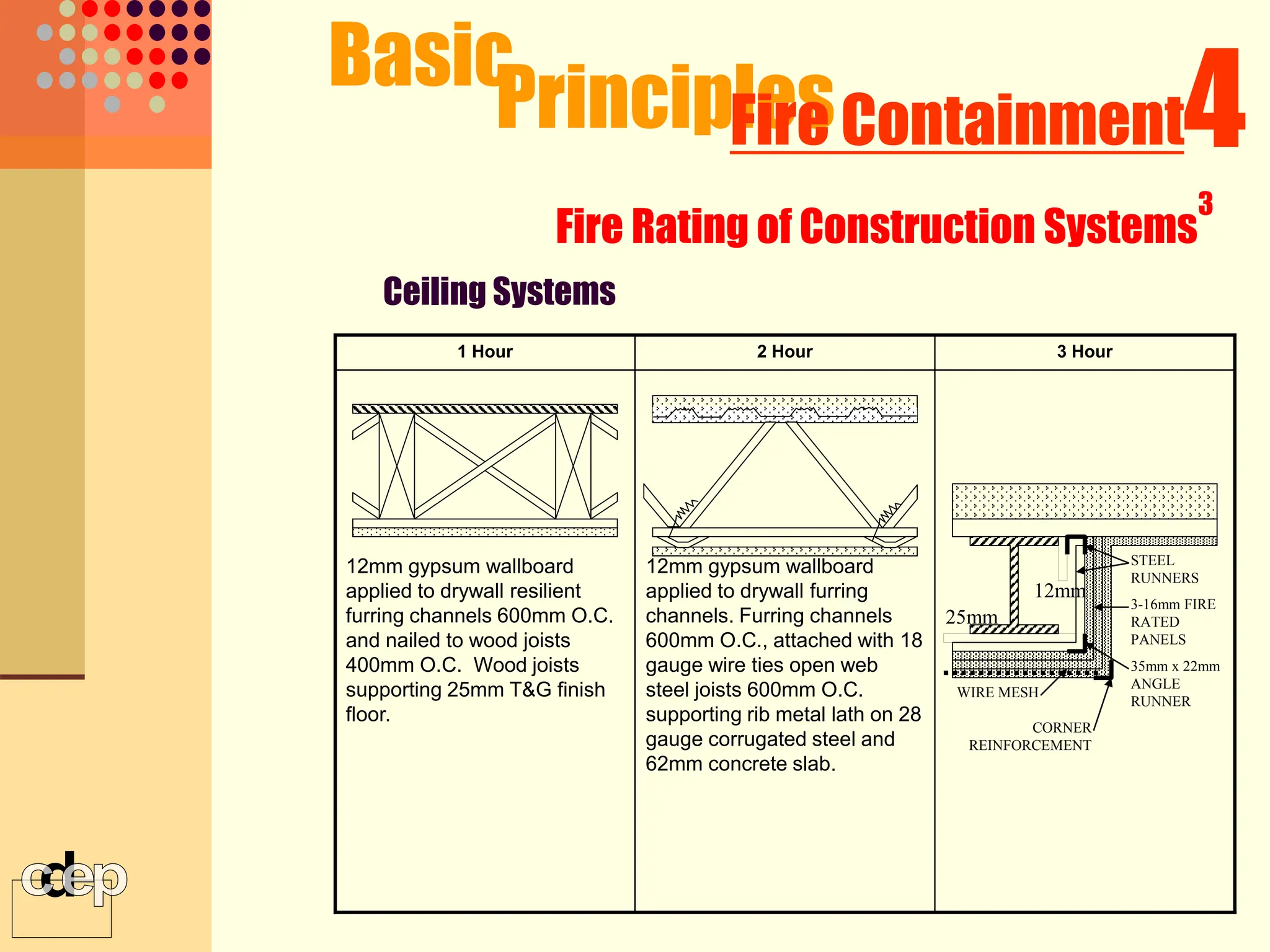
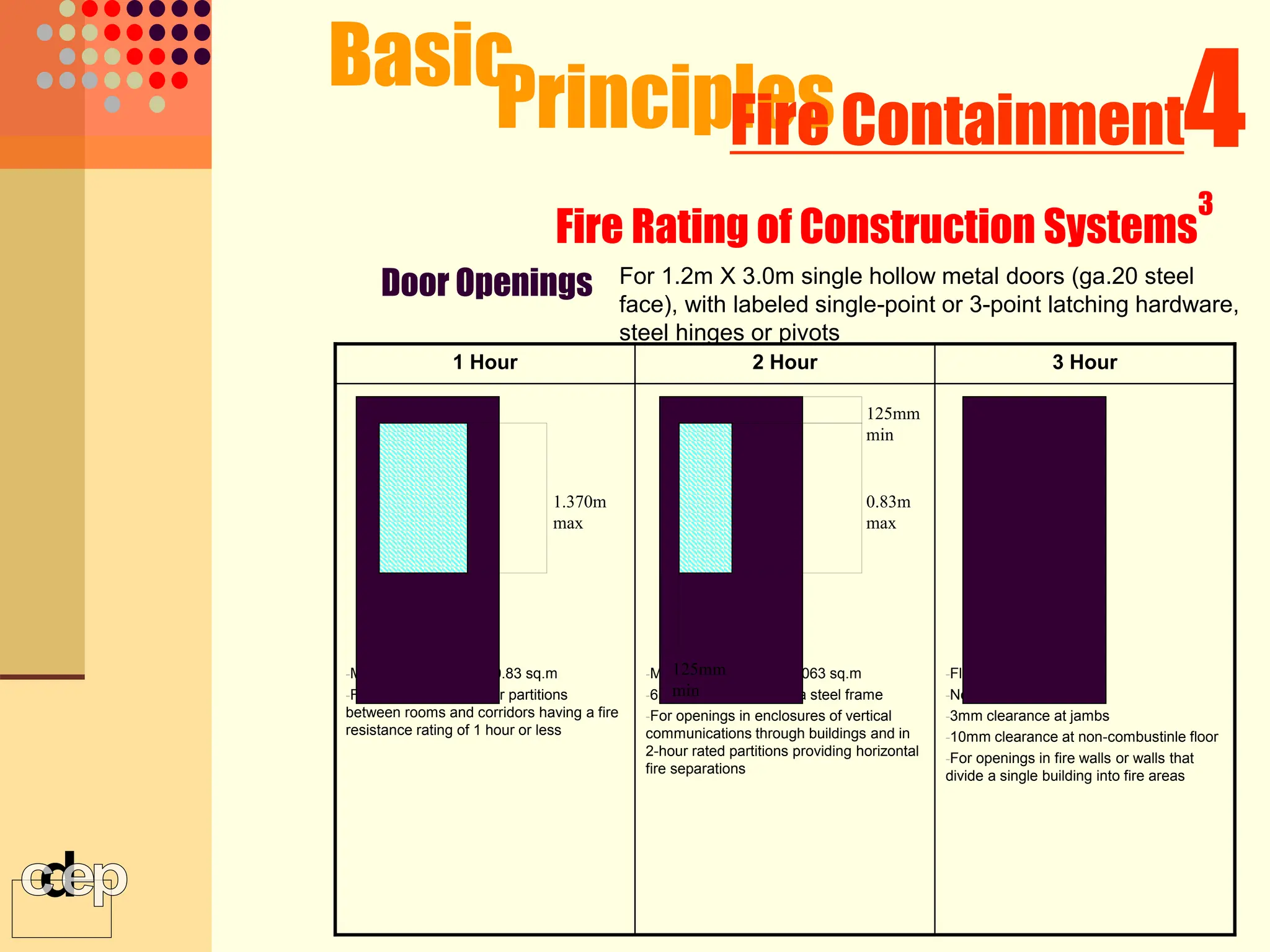
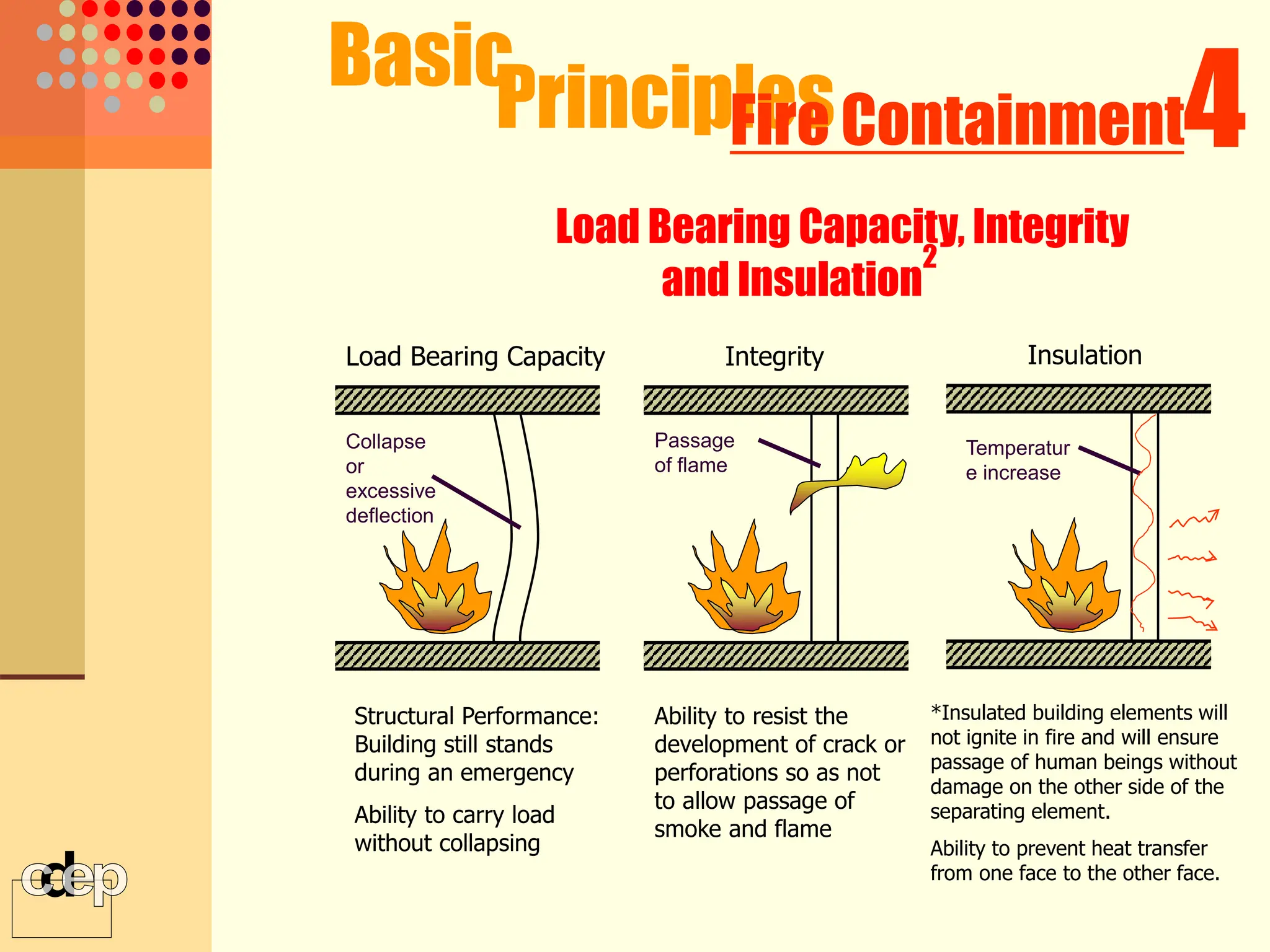
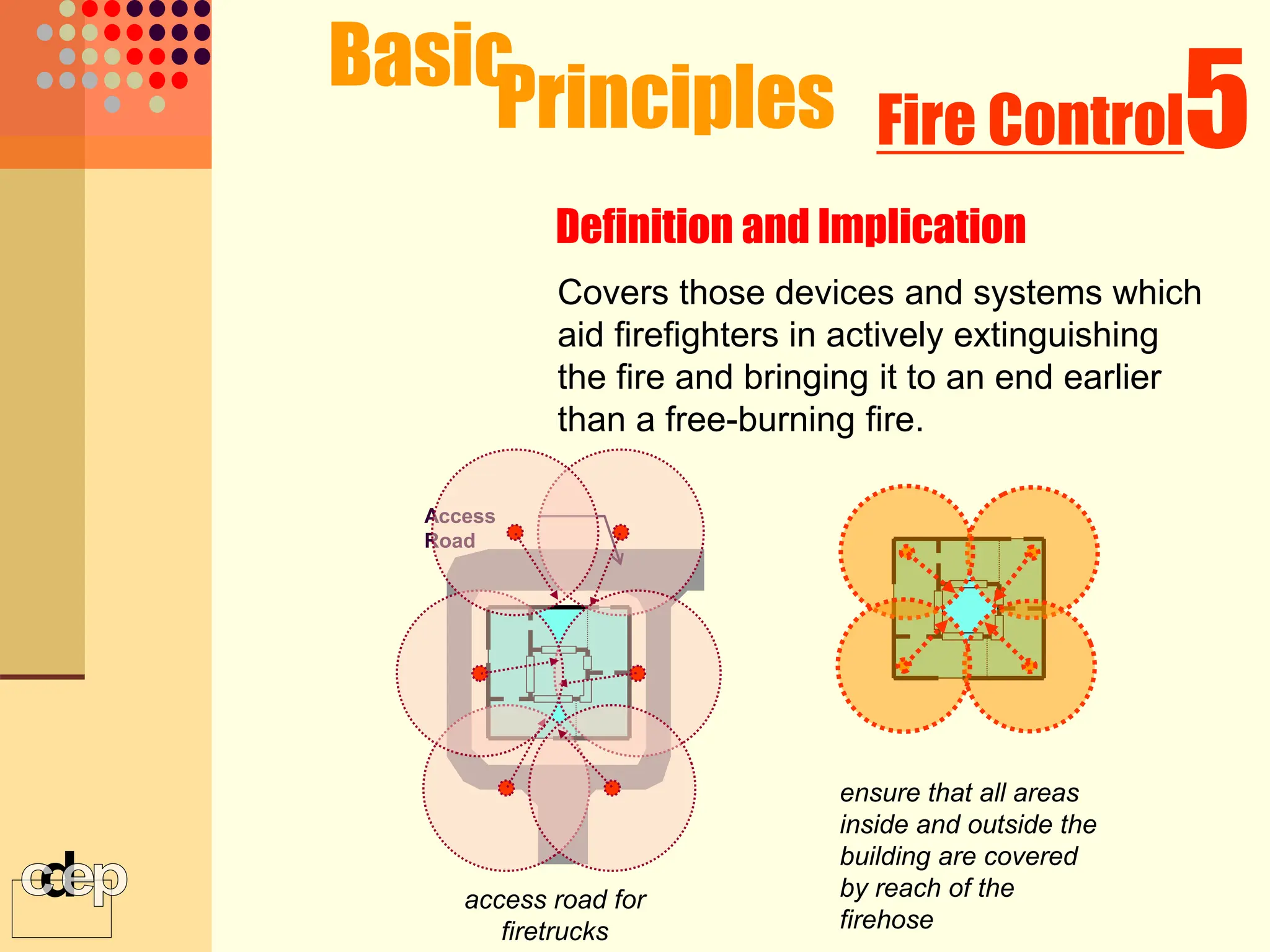
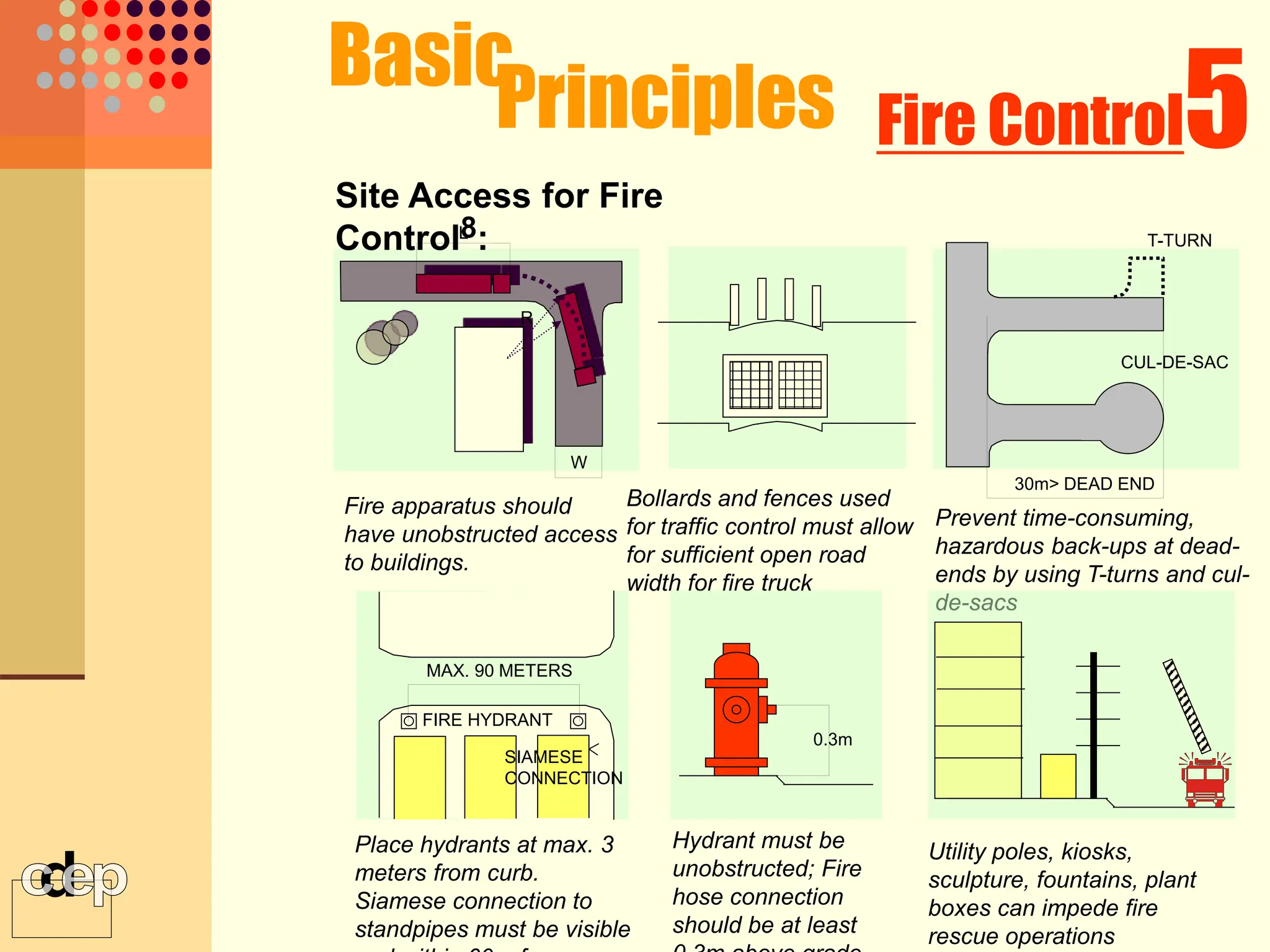
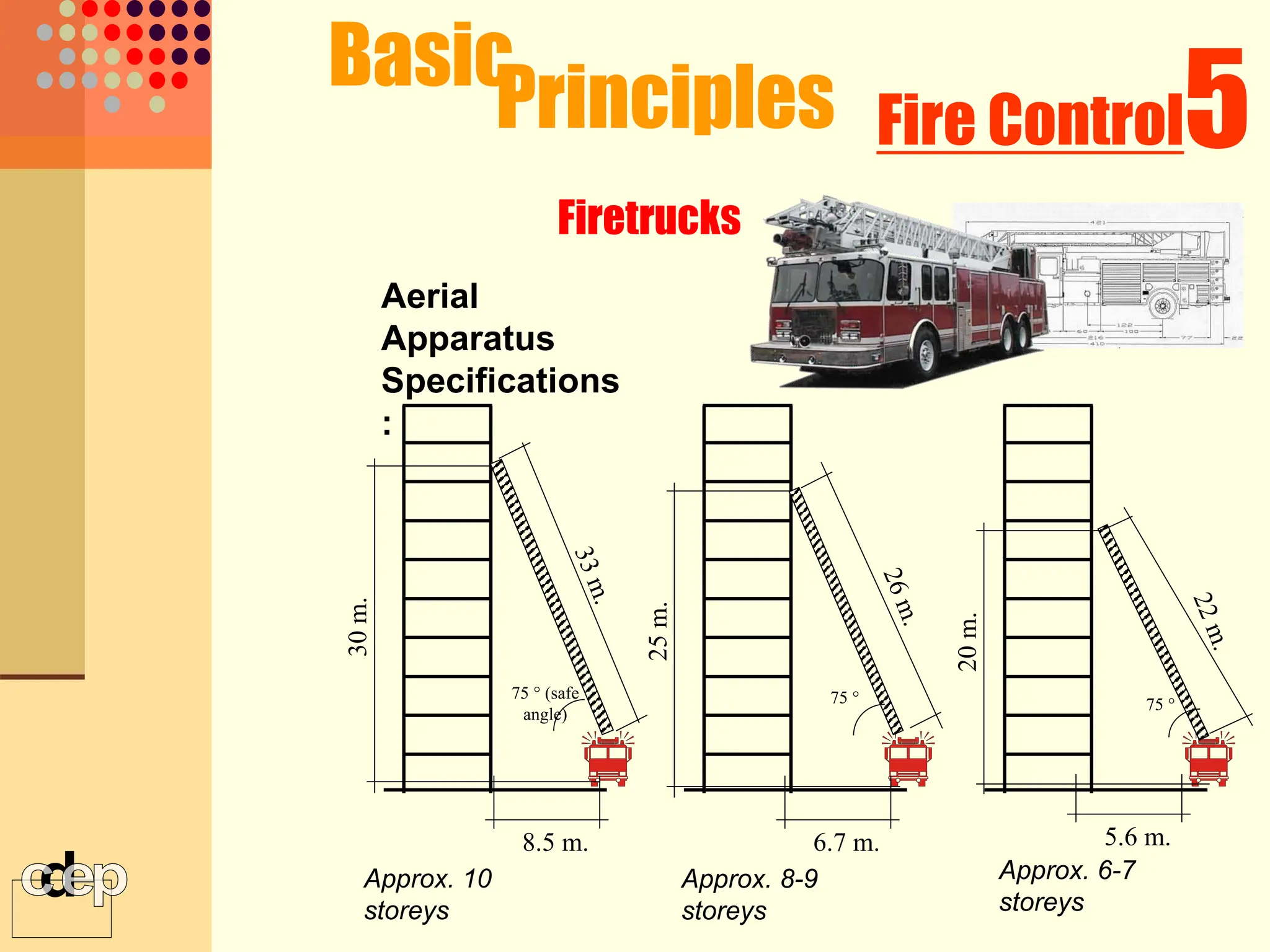
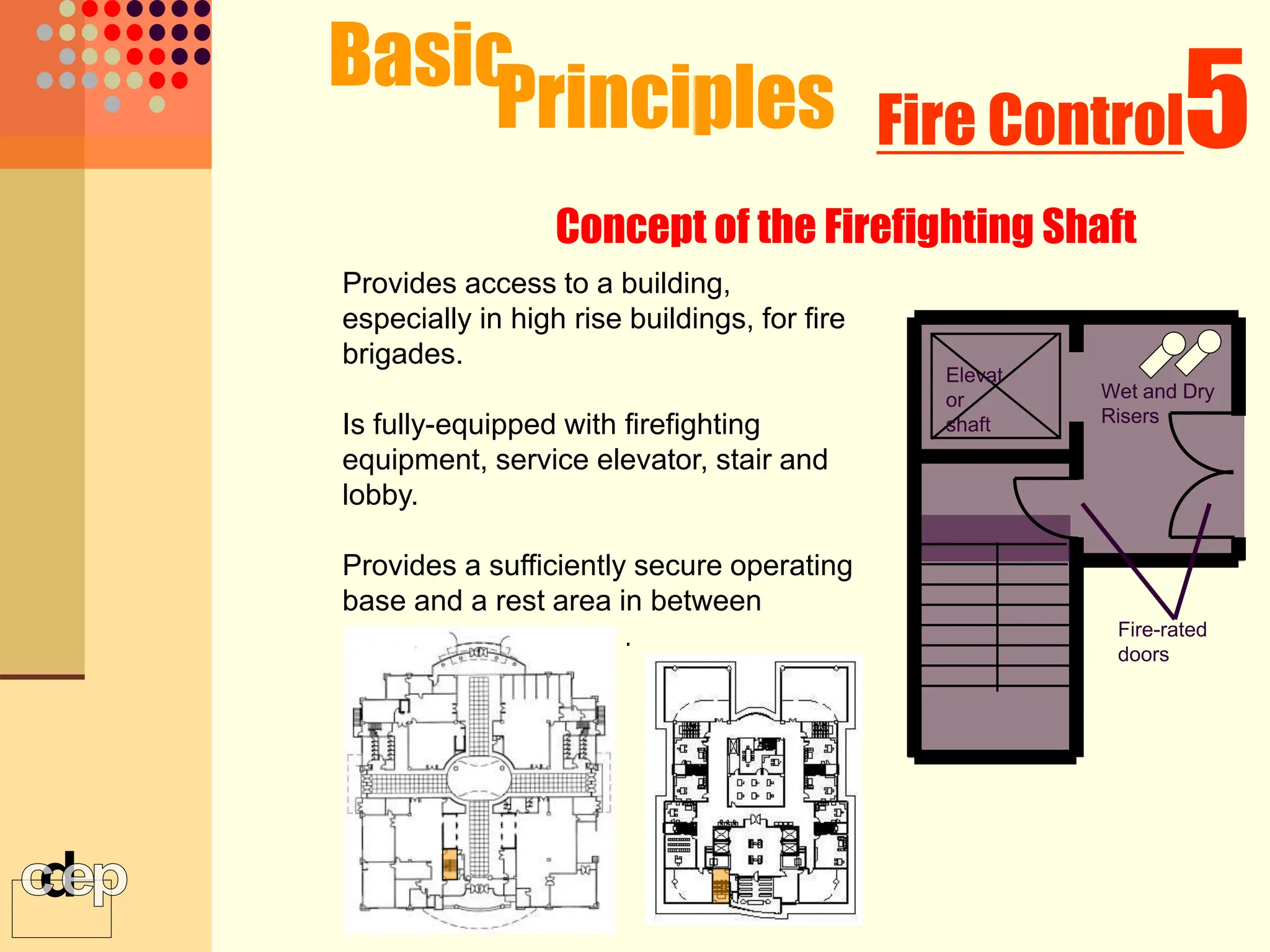
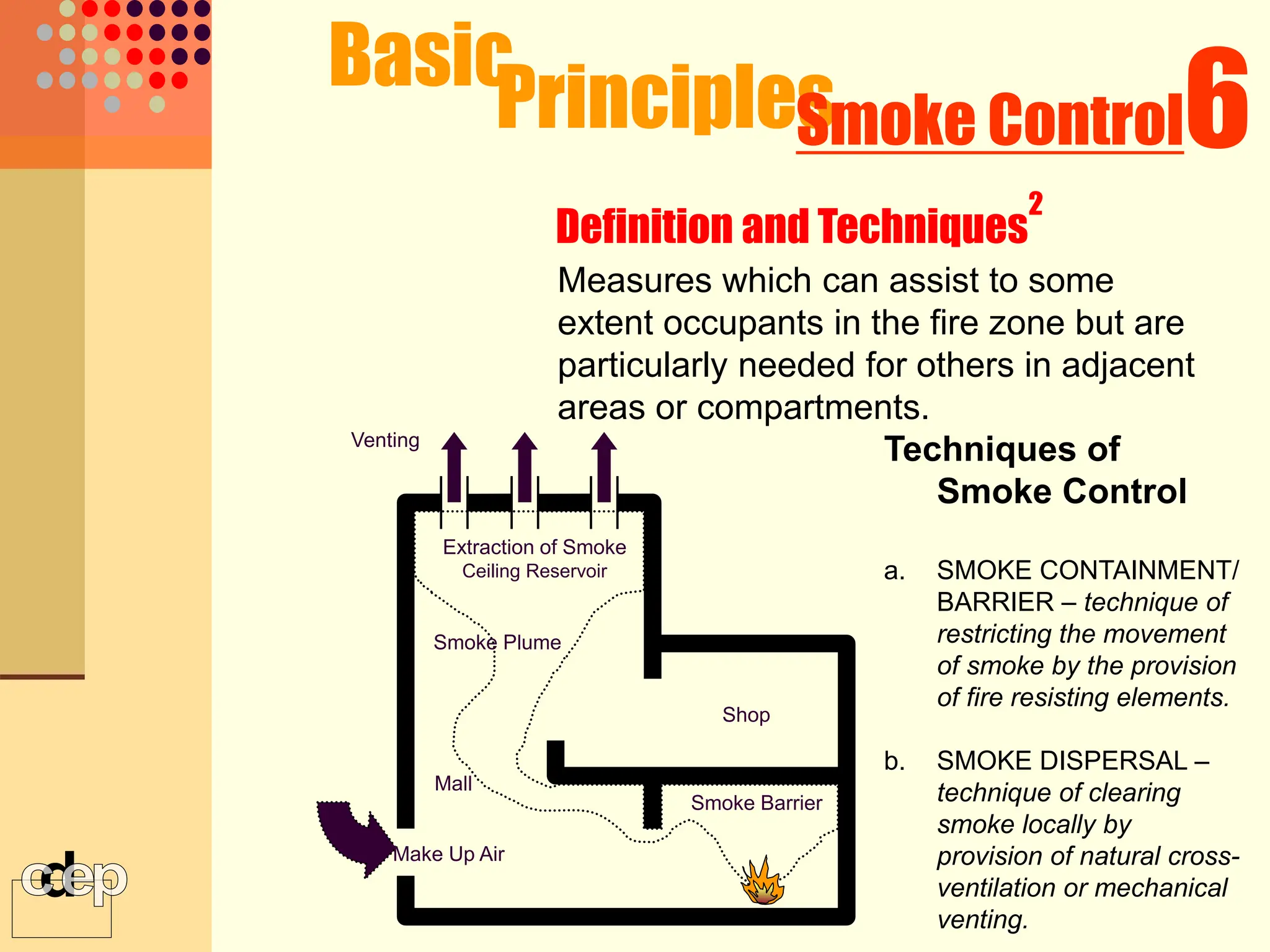
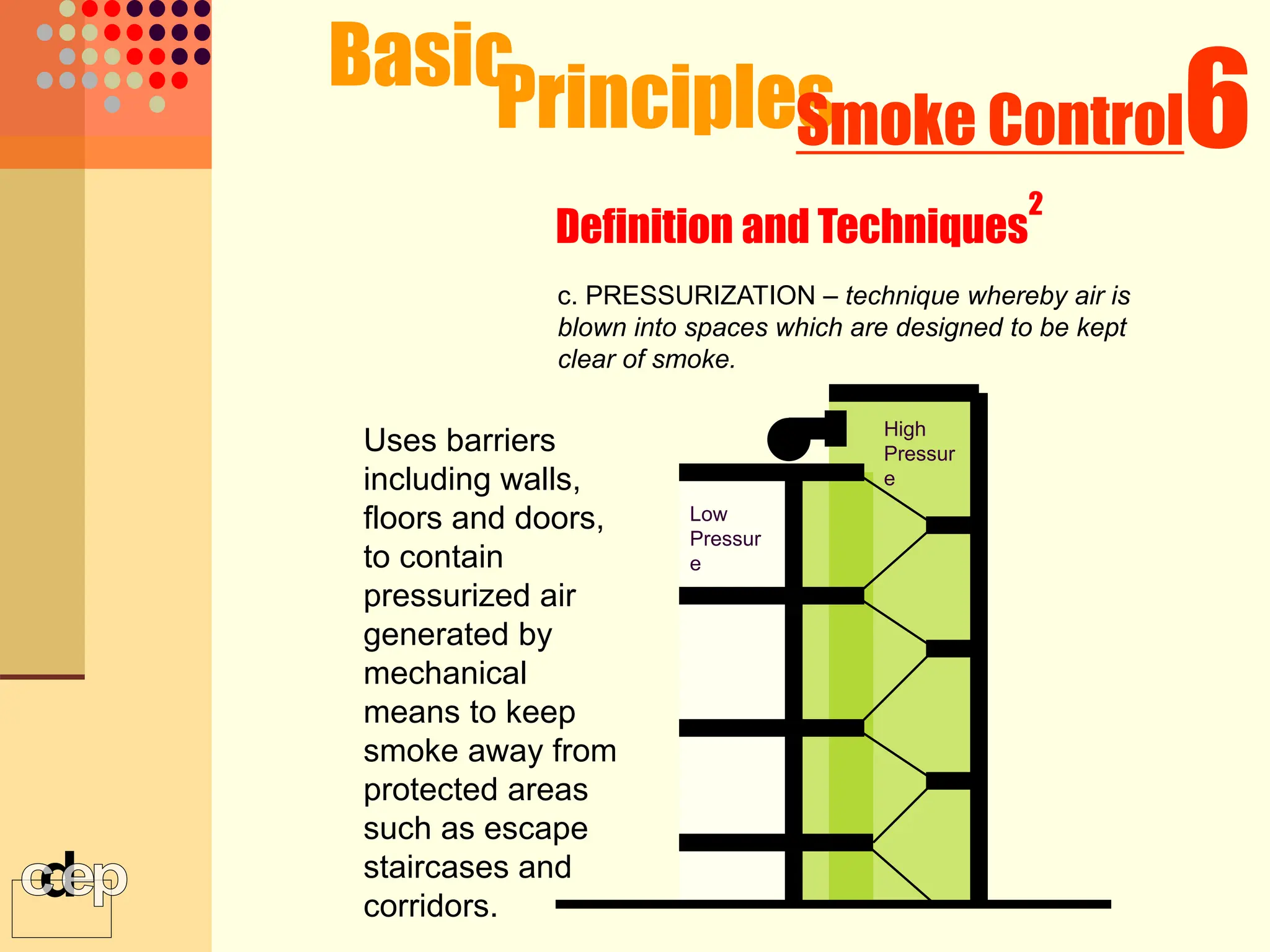
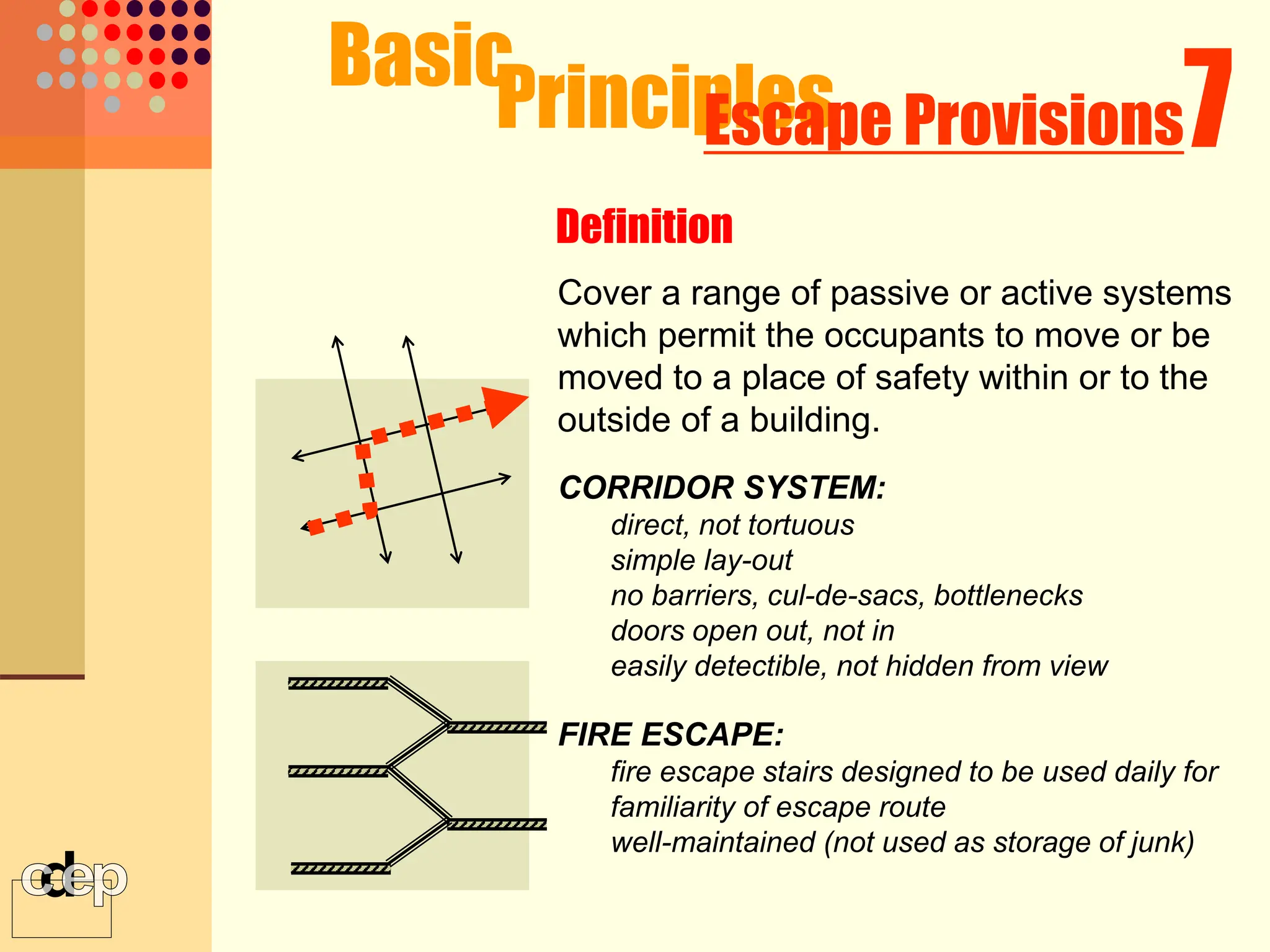
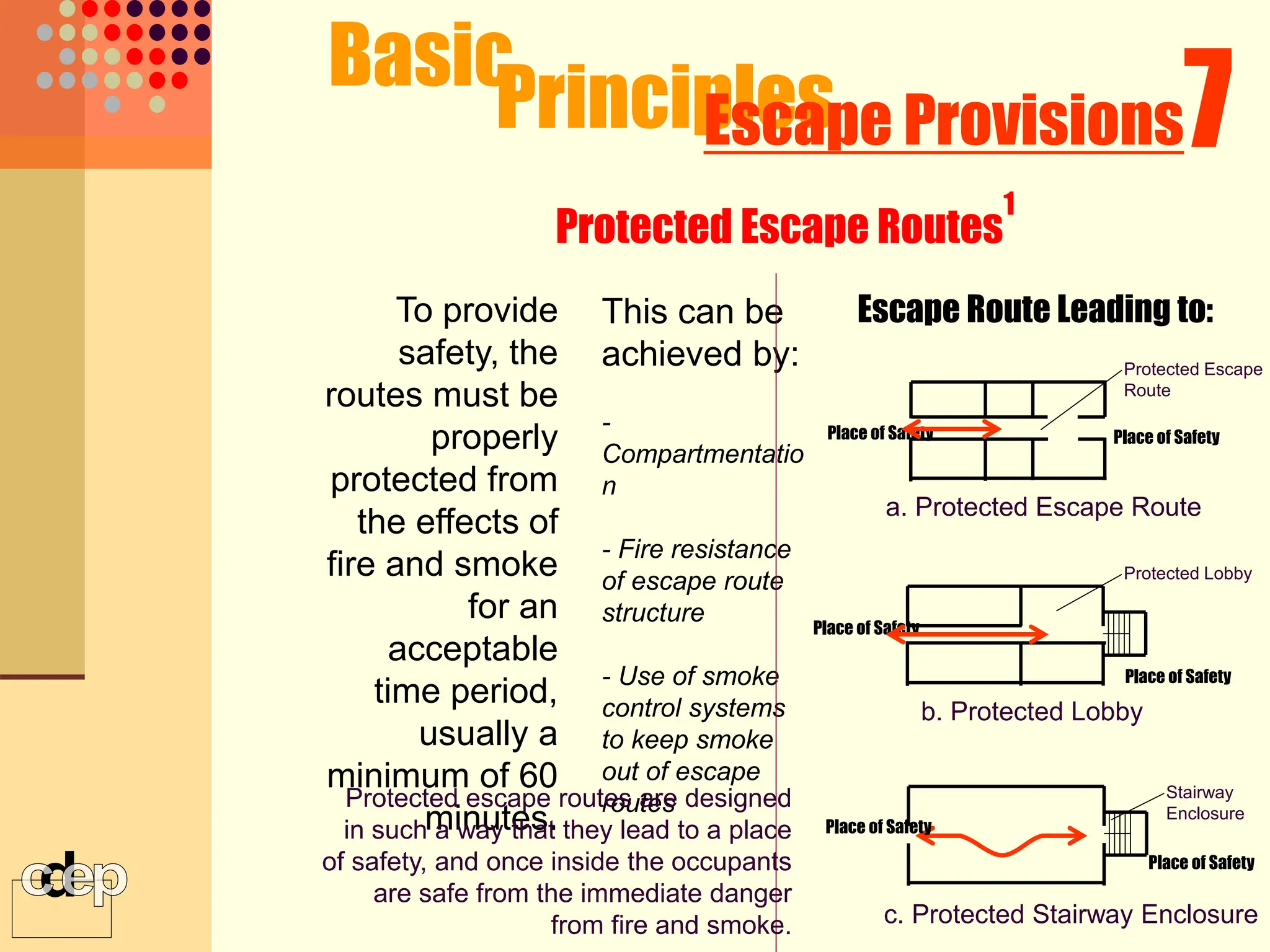
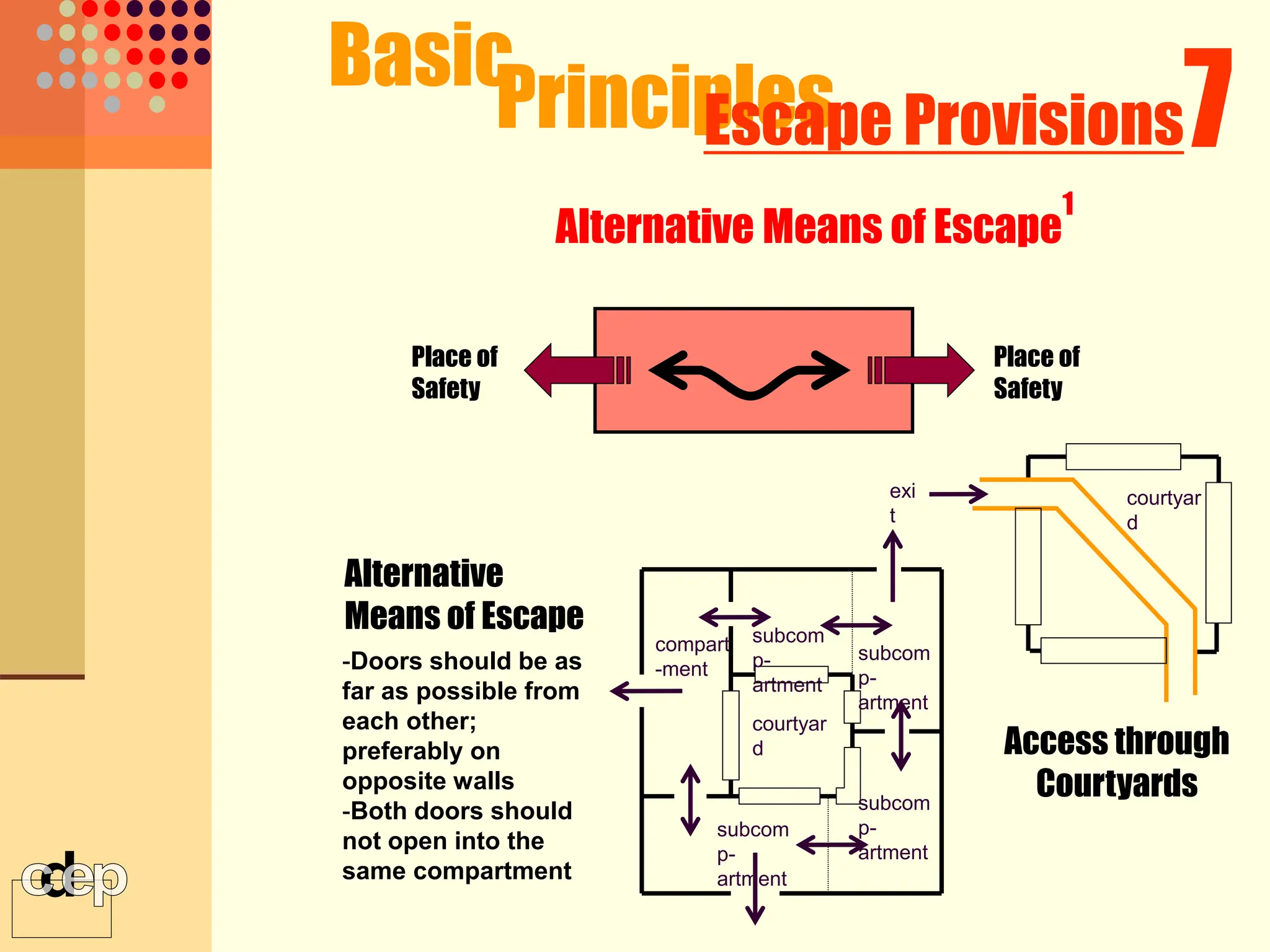
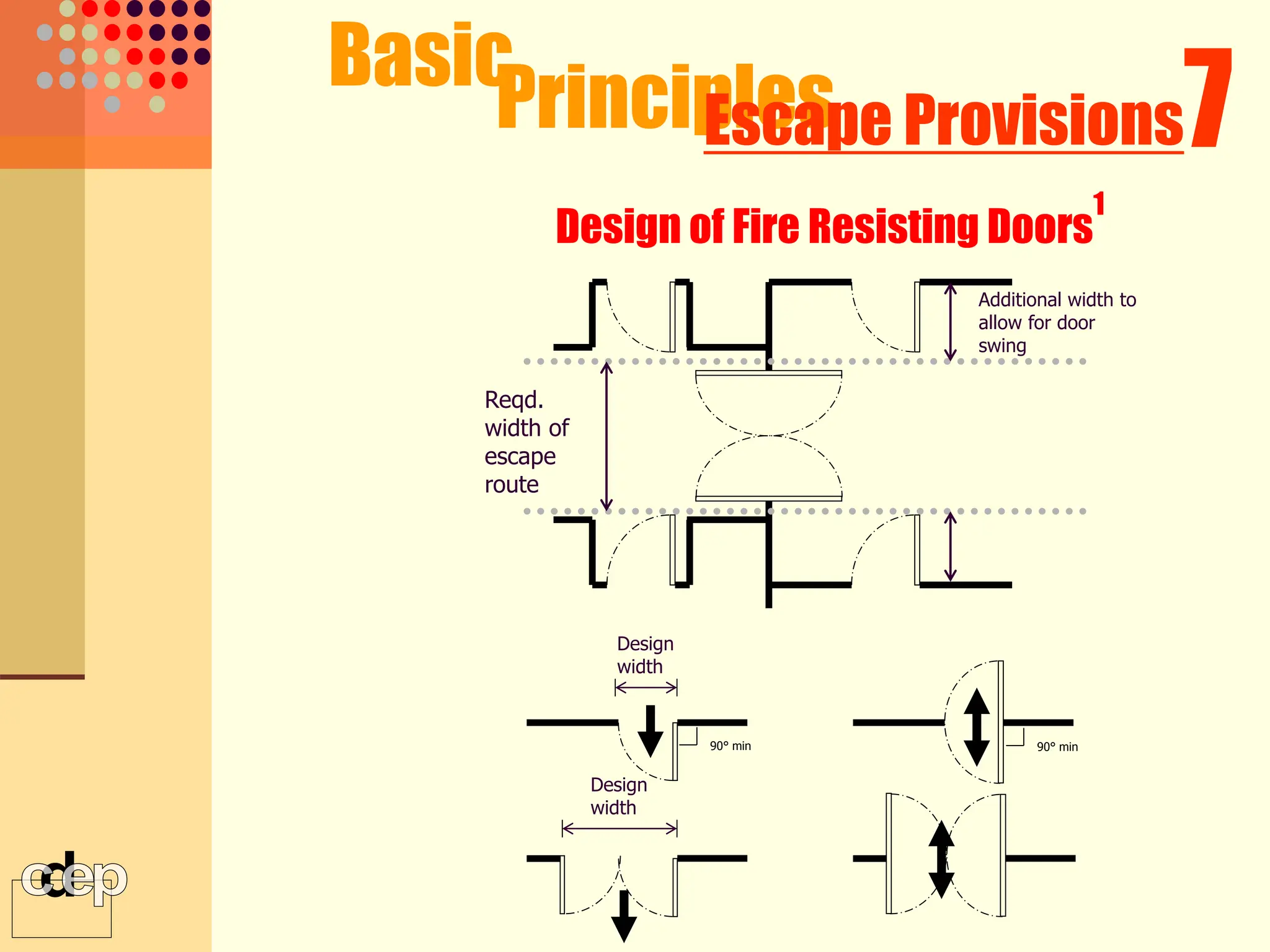
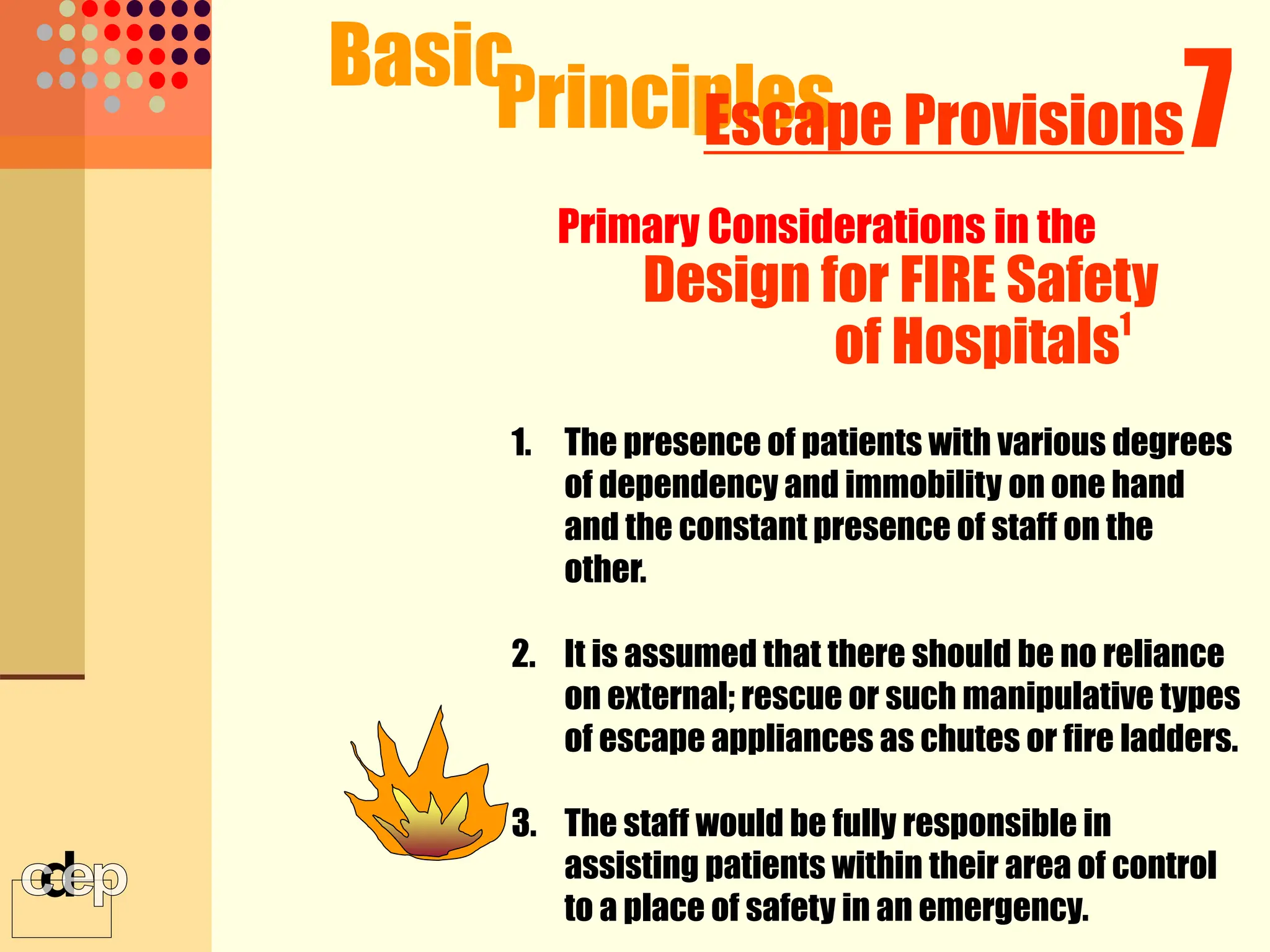
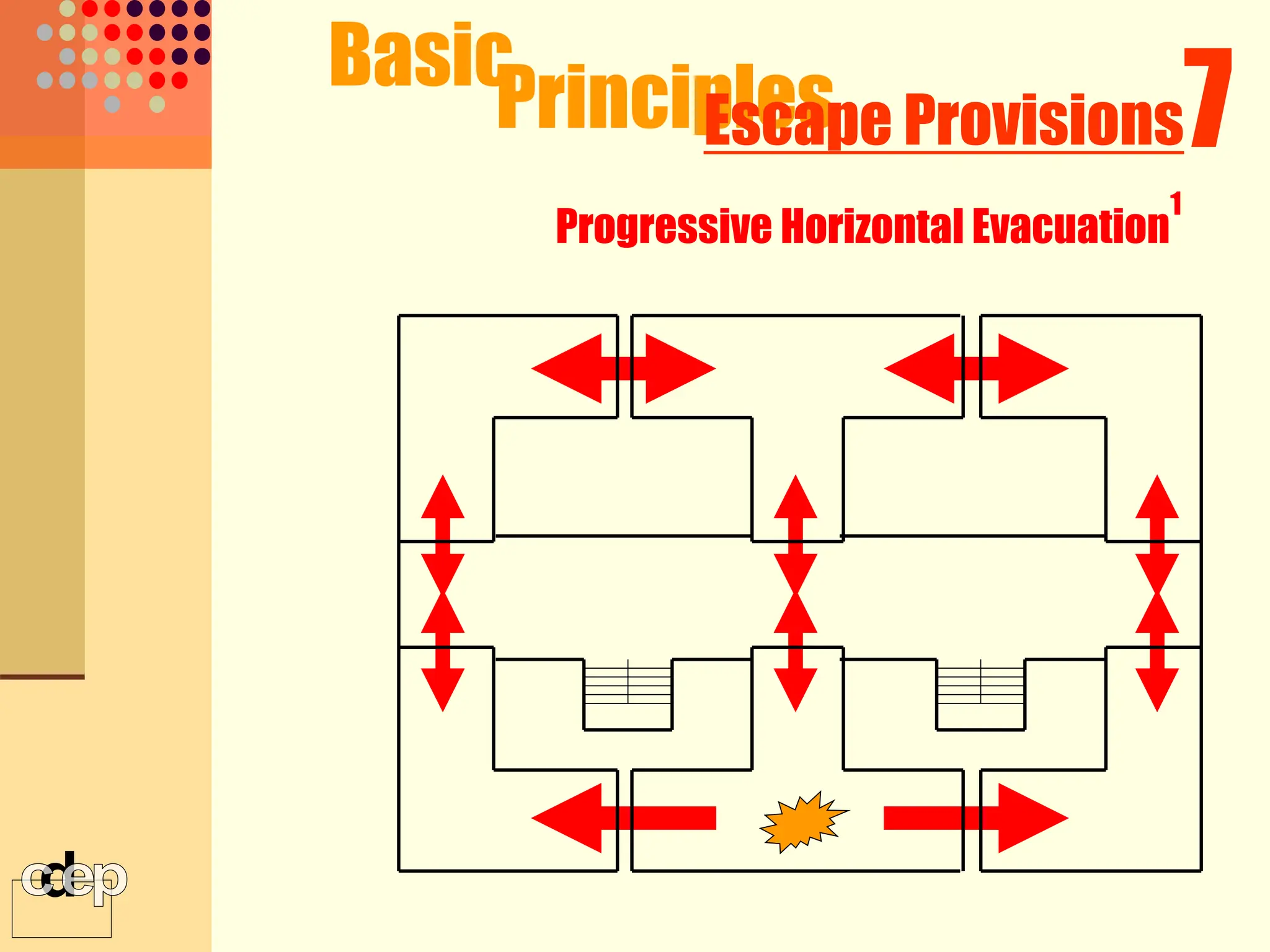
The document discusses principles of fire safety, including the fire triangle, classes of fire, fire growth stages, and architectural interventions during fire growth. It defines key concepts like fire containment, fire control, and smoke control. Various methods of fire detection, fire growth restriction, and fire ratings of construction systems are described. The goals of fire safety design are outlined as preventing fire, safeguarding lives, and reducing damage.