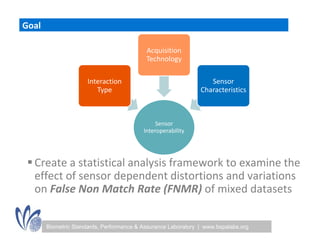
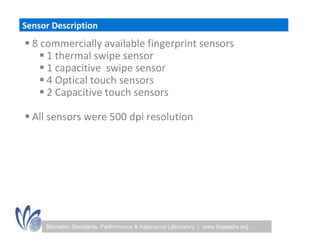
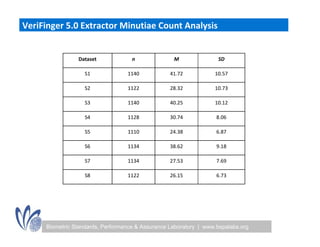
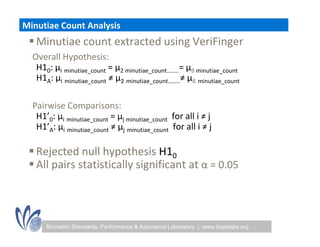
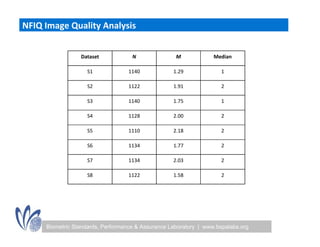
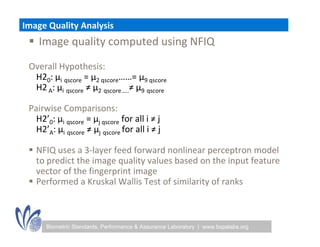
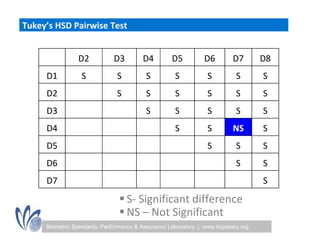
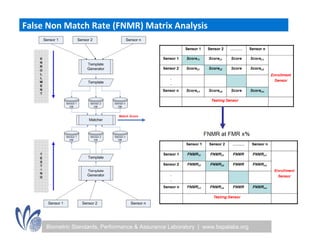
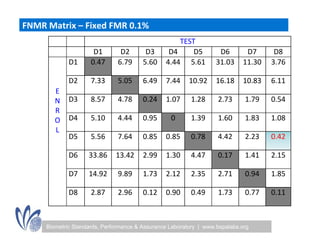
The seminar discussed the interoperability performance of various fingerprint sensors, focusing on the impact of sensor type on false match rates and the quality of collected images. Key findings indicated that while image quality adjustments could improve false non-match rates, they did not necessarily enhance the similarity of performance across diverse datasets. Future work will involve analyzing the effects of low quality images on false match rates and exploring further factors affecting biometric image quality.