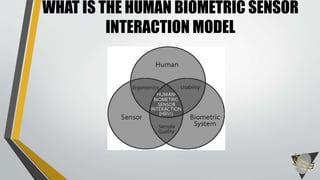
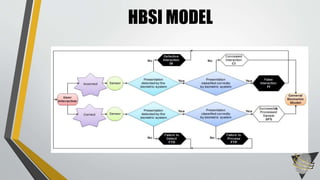
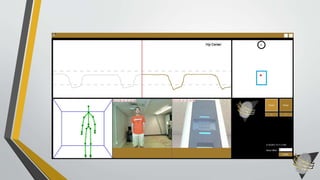
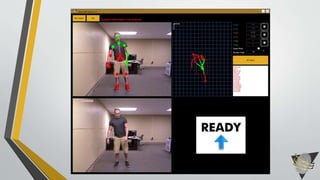
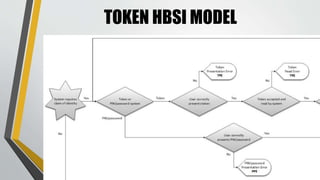
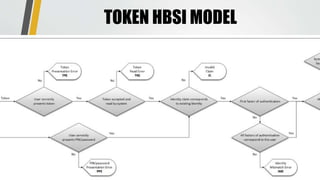
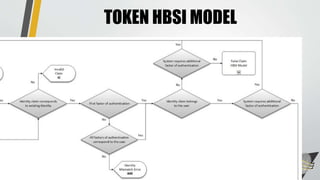
This document discusses advances in testing and evaluating human-biometric sensor interaction using a new model. It describes gaps in traditional biometric testing, such as how users interact with systems. A new Human Biometric Sensor Interaction model is presented and has been tested on iris and fingerprint biometrics. The model has been expanded to more complex systems like border gates. Testing looks at how users interact with biometric systems in different environments and factors like throughput. The goal is to better test and evaluate systems without overburdening test facilities.