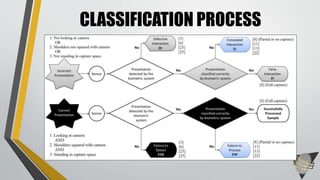
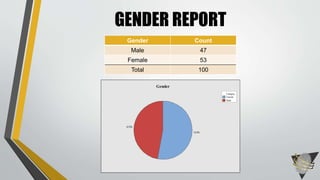
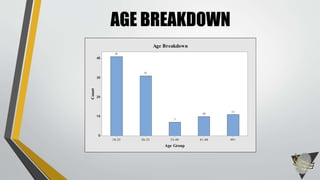
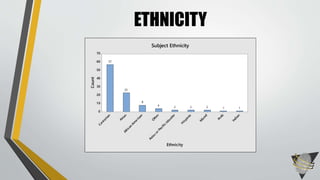
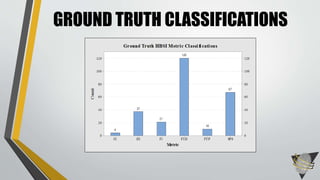
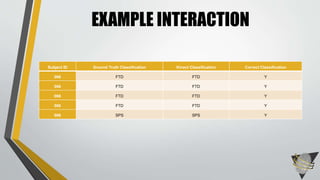
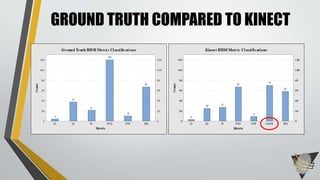
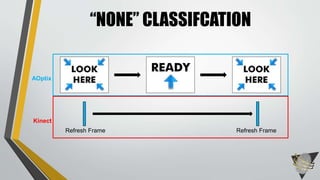
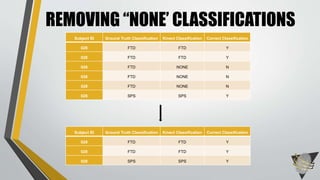
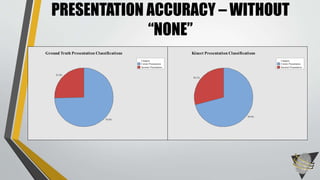
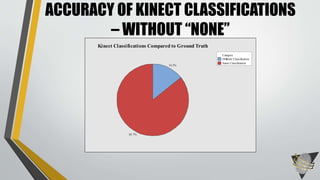
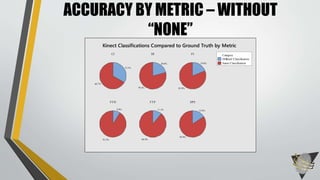
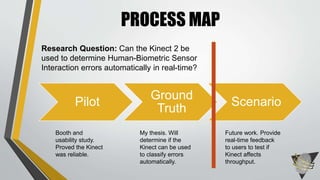
The document explores whether the Kinect 2 can automatically detect human-biometric sensor interaction errors in real-time, utilizing a structured methodology that includes programming, construction, and data collection phases. It presents findings that highlight the Kinect's reliability, while noting limitations related to its refresh rate which affects the classification accuracy of biometric interactions. Future work is proposed to enhance performance through increased refresh rates, real-time feedback, and adjusting classification thresholds.





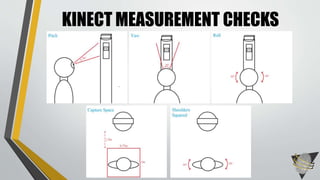
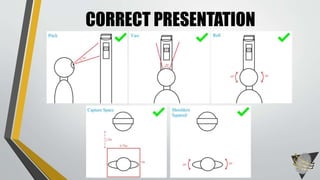
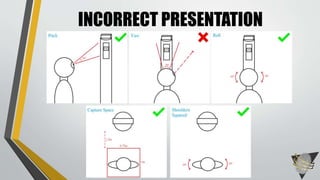
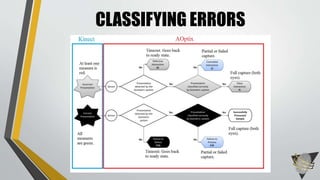




![AOPTIX STATES[1] [2] [3] [4] [5]
[6] [8] [11] [13] [15]
[21] [22] [23] [25]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/defense-slides-160211205016/85/HBSI-Automation-Using-the-Kinect-15-320.jpg)