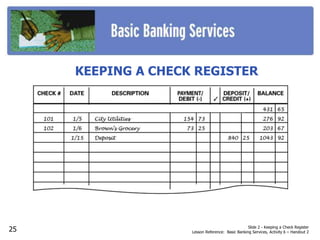
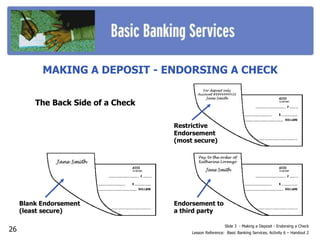
This document outlines 7 activities for teaching basic banking services: 1) why banks are needed and their services, 2) the various services banks provide, 3) checking accounts, 4) opening a checking account, 5) writing checks, 6) maintaining a checking account, and 7) savings accounts. Each activity contains slides on key topics like bank safety, electronic banking services, checking account terms, and opening and managing different types of bank accounts.