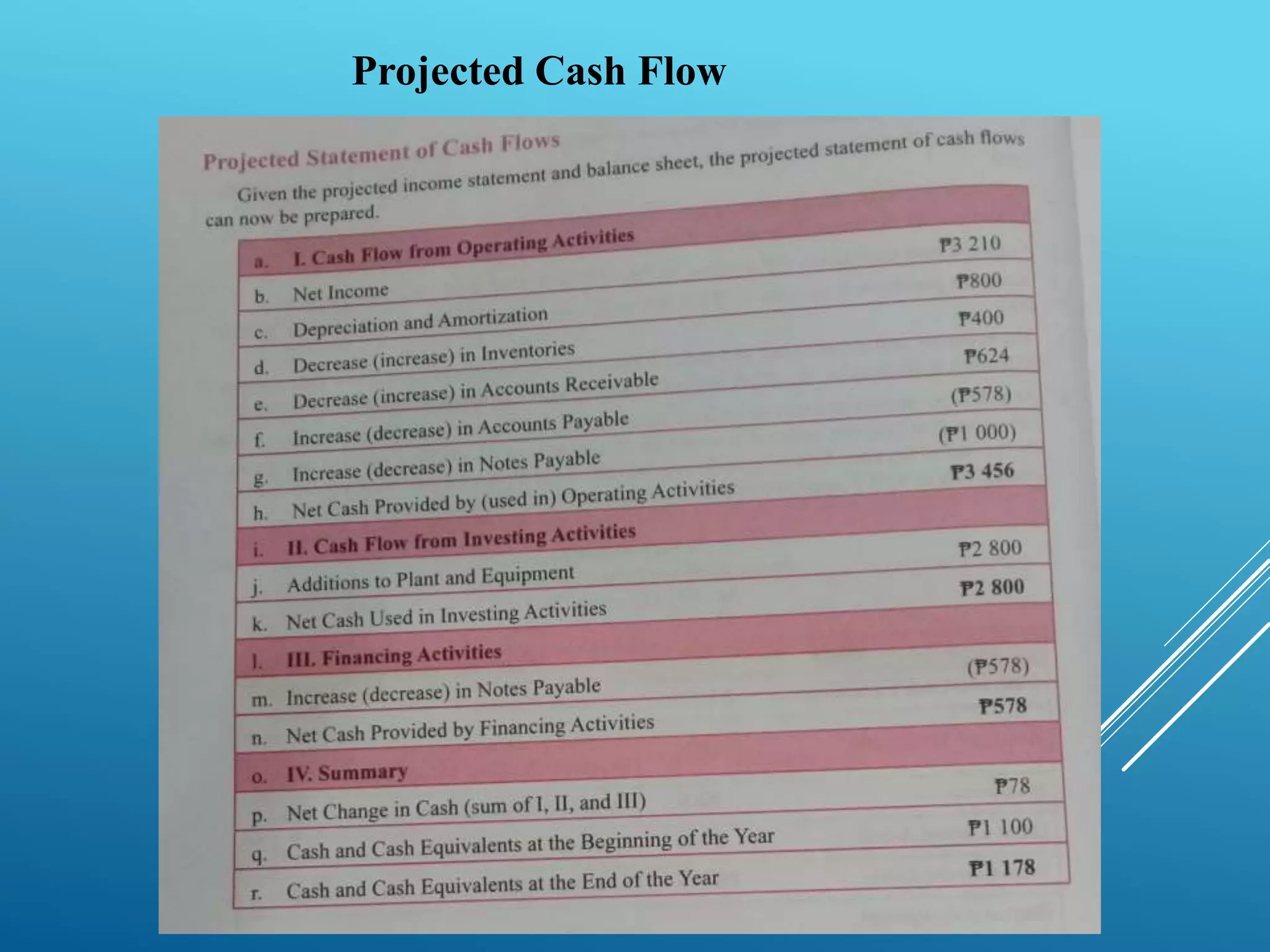
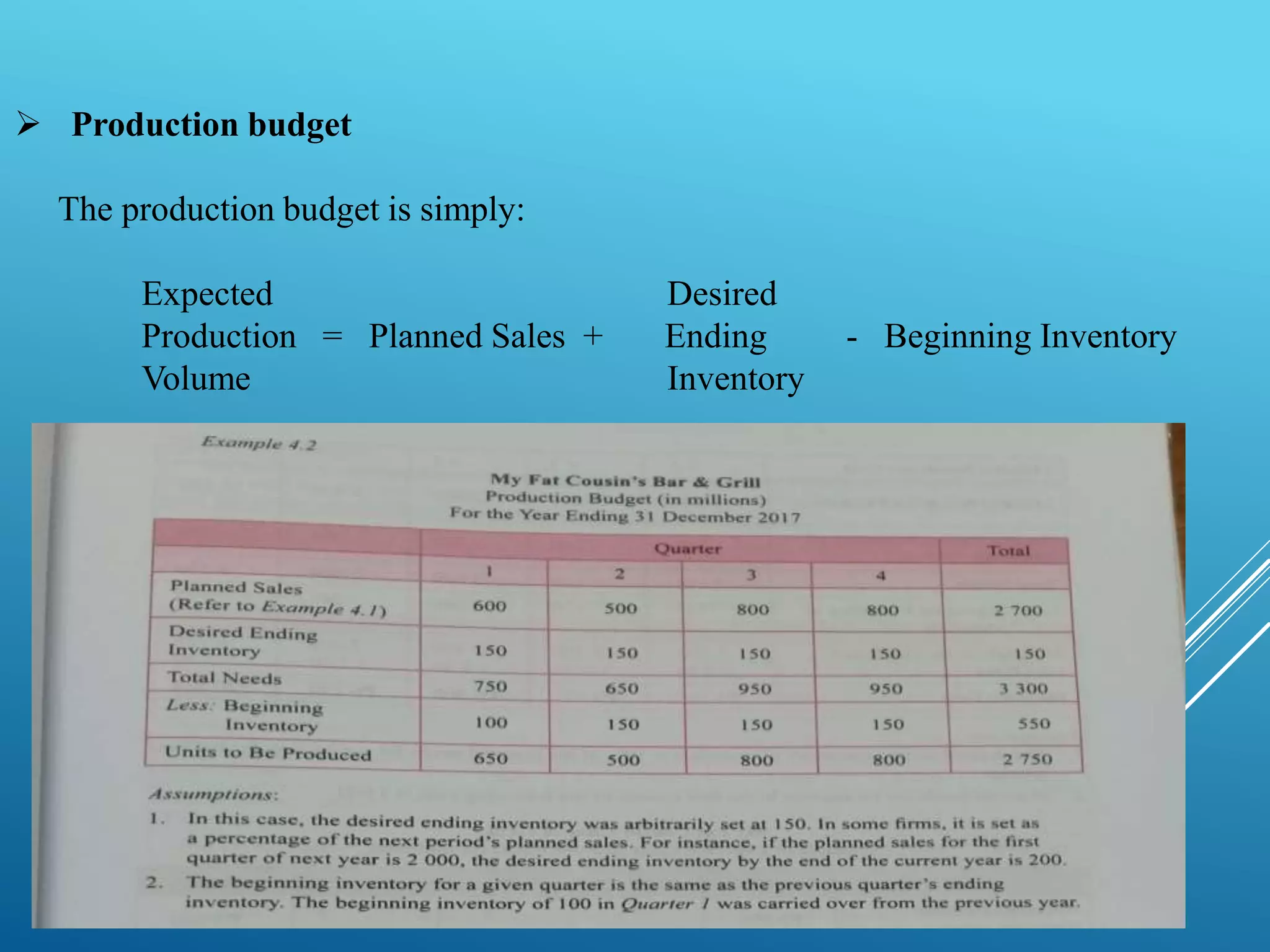
This document discusses strategic planning and financial projections and budgets. It defines key elements of a strategic plan like vision, mission, objectives and strategies. It also explains SWOT analysis and how managers can assess strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats. Additionally, it covers preparing projected financial statements like income statements, balance sheets and cash flows. Lastly, it defines budgets as financial plans and describes types of budgets like operating and financial budgets. It provides details on preparing individual budgets for sales, production, materials, labor, overhead, expenses and cash.