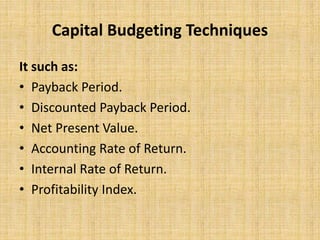
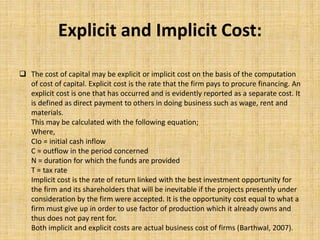
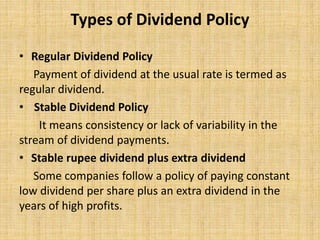
Financial management involves planning, organizing, and controlling financial resources to meet organizational goals. The key activities include investment decisions, financial decisions, and dividend decisions. Objectives include ensuring adequate and regular funding, adequate returns for shareholders, optimal fund utilization, and safety of investments. Functions include estimating capital needs, determining capital sources and structure, investing funds, and managing cash flows. Capital budgeting techniques for evaluating investments include payback period, net present value, internal rate of return, and profitability index. Cost of capital refers to the minimum return required by investors and is important for capital structure decisions and investment evaluations. Sources of capital include debt, preferred stock, common equity, and retained earnings.