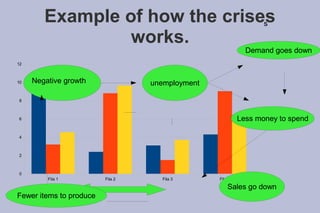
A financial crisis can have wide-ranging effects. It begins when the value of assets like stocks, housing, or currencies suddenly decreases. This can lead to a recession if economic activity declines. Financial crises occur for reasons like risky lending, herd behavior, and regulatory failures. They can cause unemployment to rise as demand falls, leading to less production and spending in a recessionary spiral.