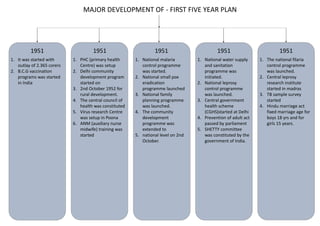
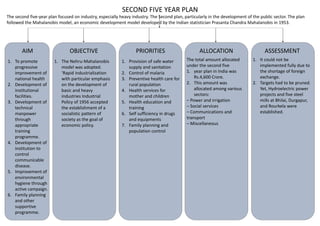
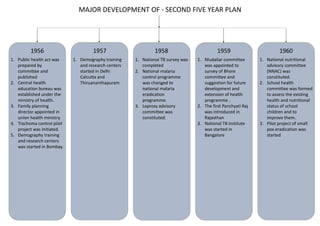
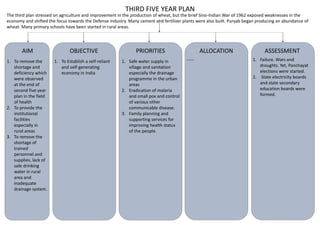
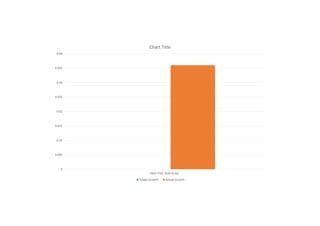
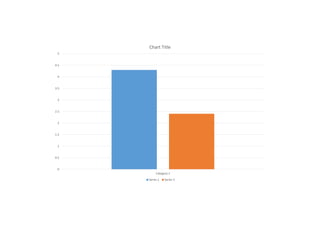
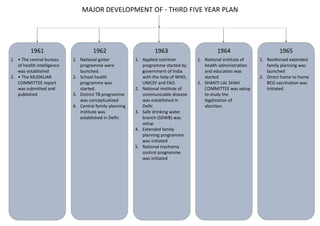
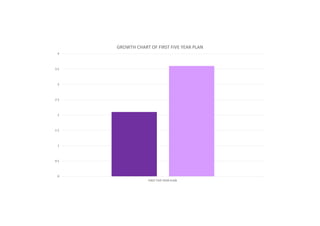
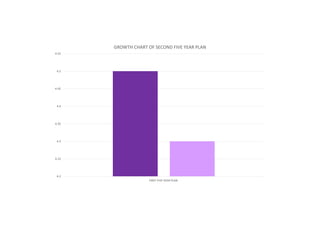
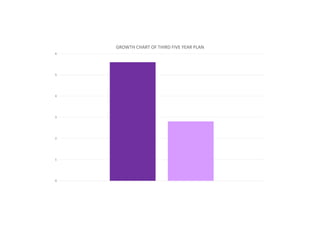
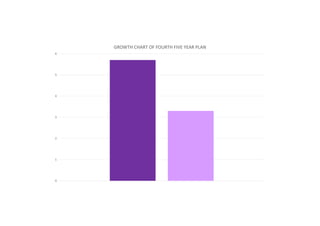
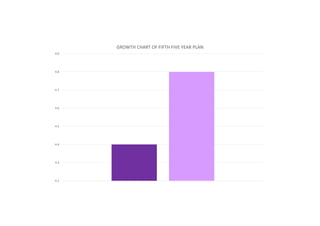
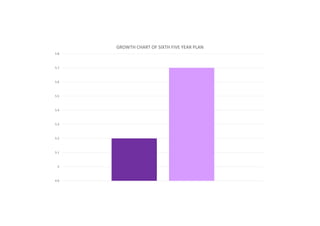
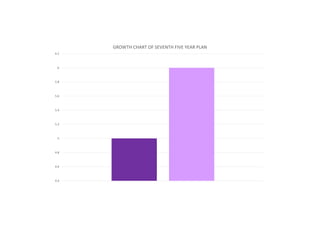
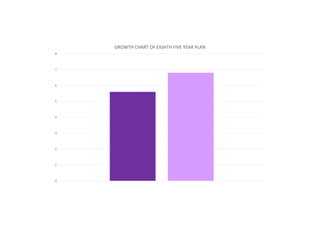
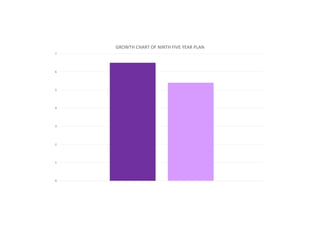
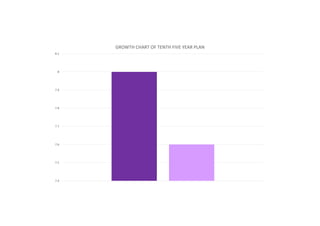
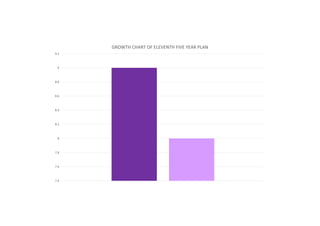
The first five-year plan in India aimed to improve public health, build rural health services, and enhance the general health status of the population. A total budget of Rs. 2,069 crore was allocated, with the largest shares going to irrigation/energy and transport/communications. In health, priorities included water/sanitation, malaria control, and health services for mothers and children. The plan achieved most of its targets through investments in agriculture, energy and infrastructure development.