The internship summary involves the following:
1. The intern worked for the Solids Fertilizer Department at a fertilizer plant, updating process files and analyzing operating data.
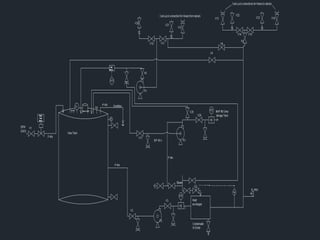
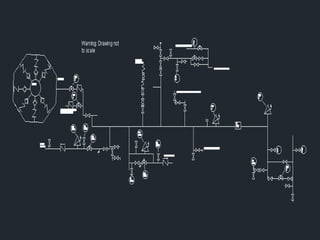
2. Projects included calculating ammonia inventories, developing piping and instrument diagrams, and investigating fertilizer size properties.
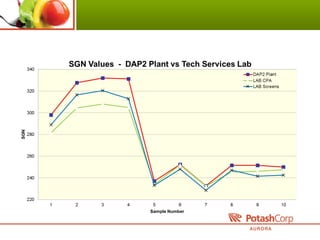
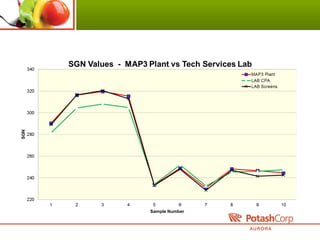
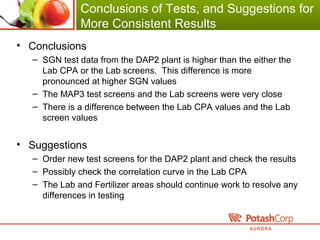
3. The intern analyzed historical operating and quality data, documented environmental limits, and identified differences in fertilizer testing methods.