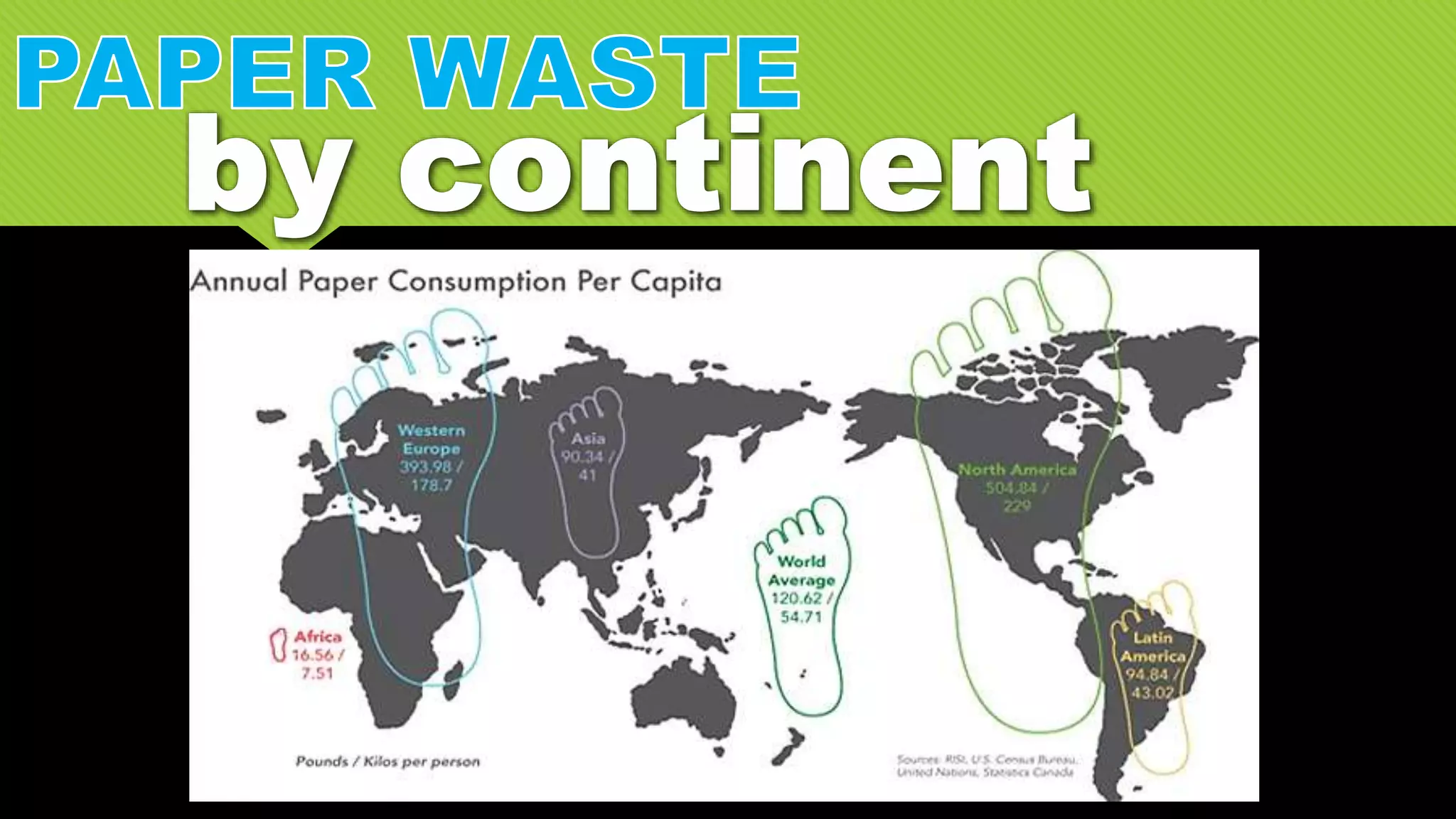
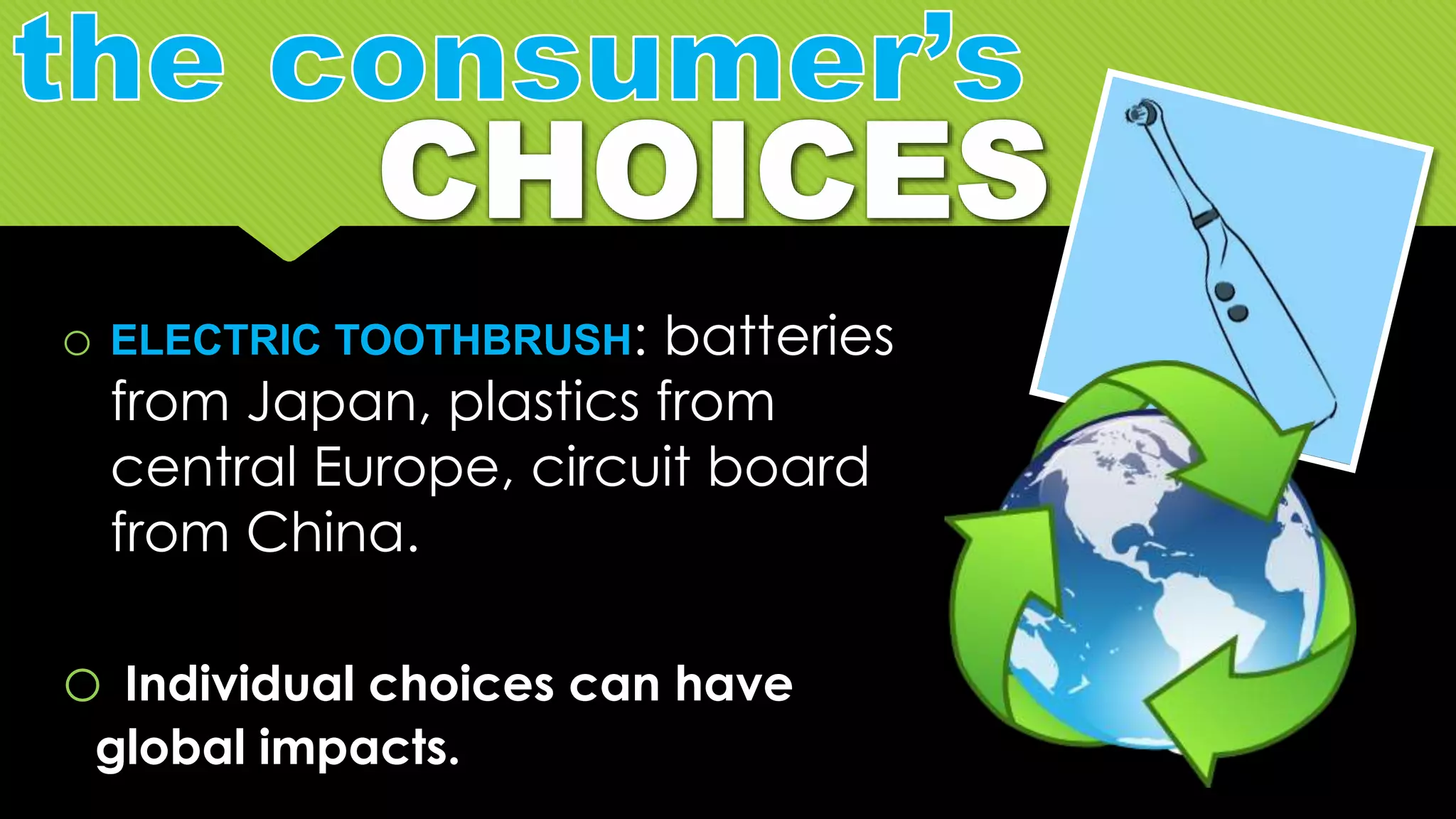
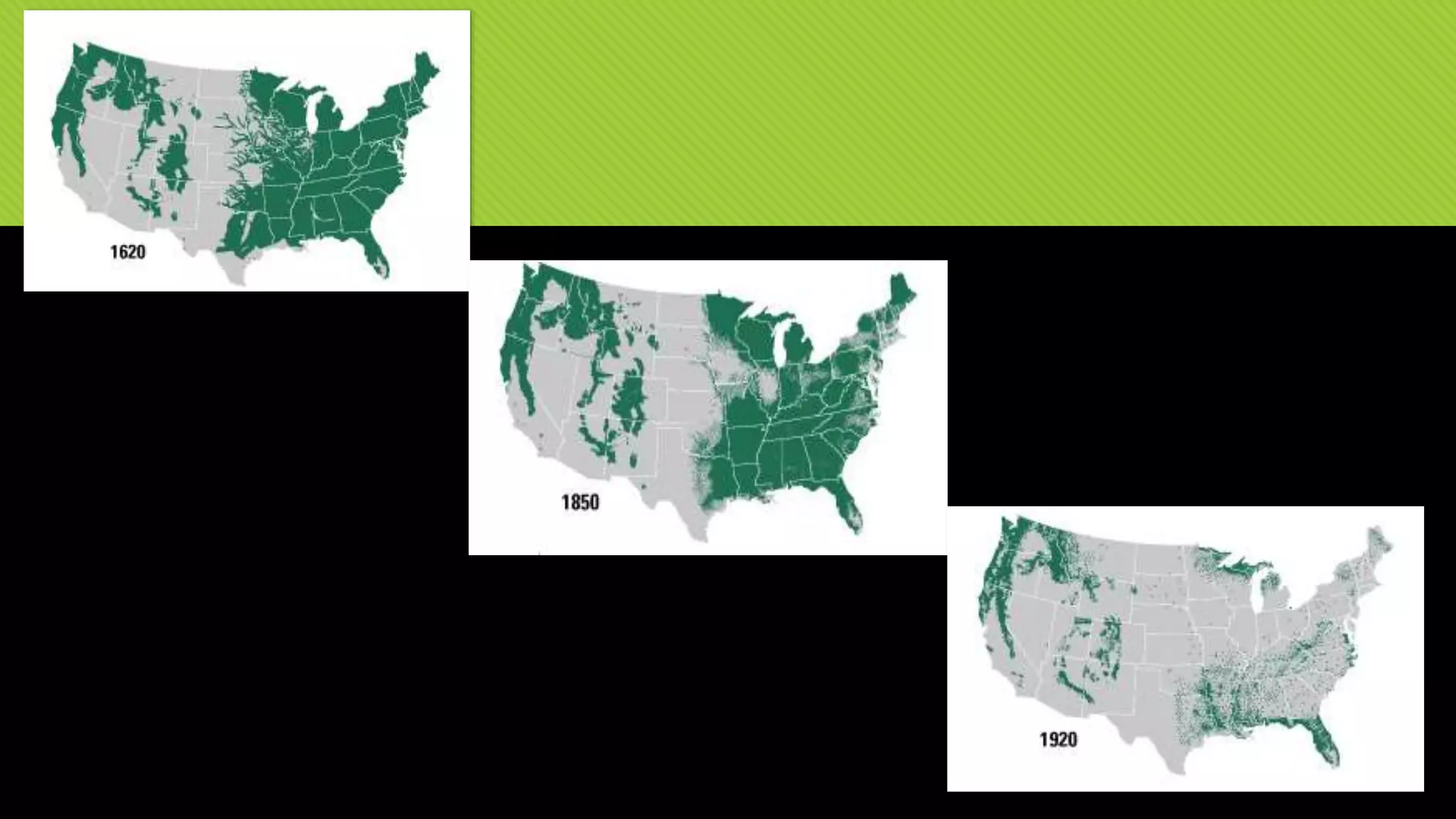
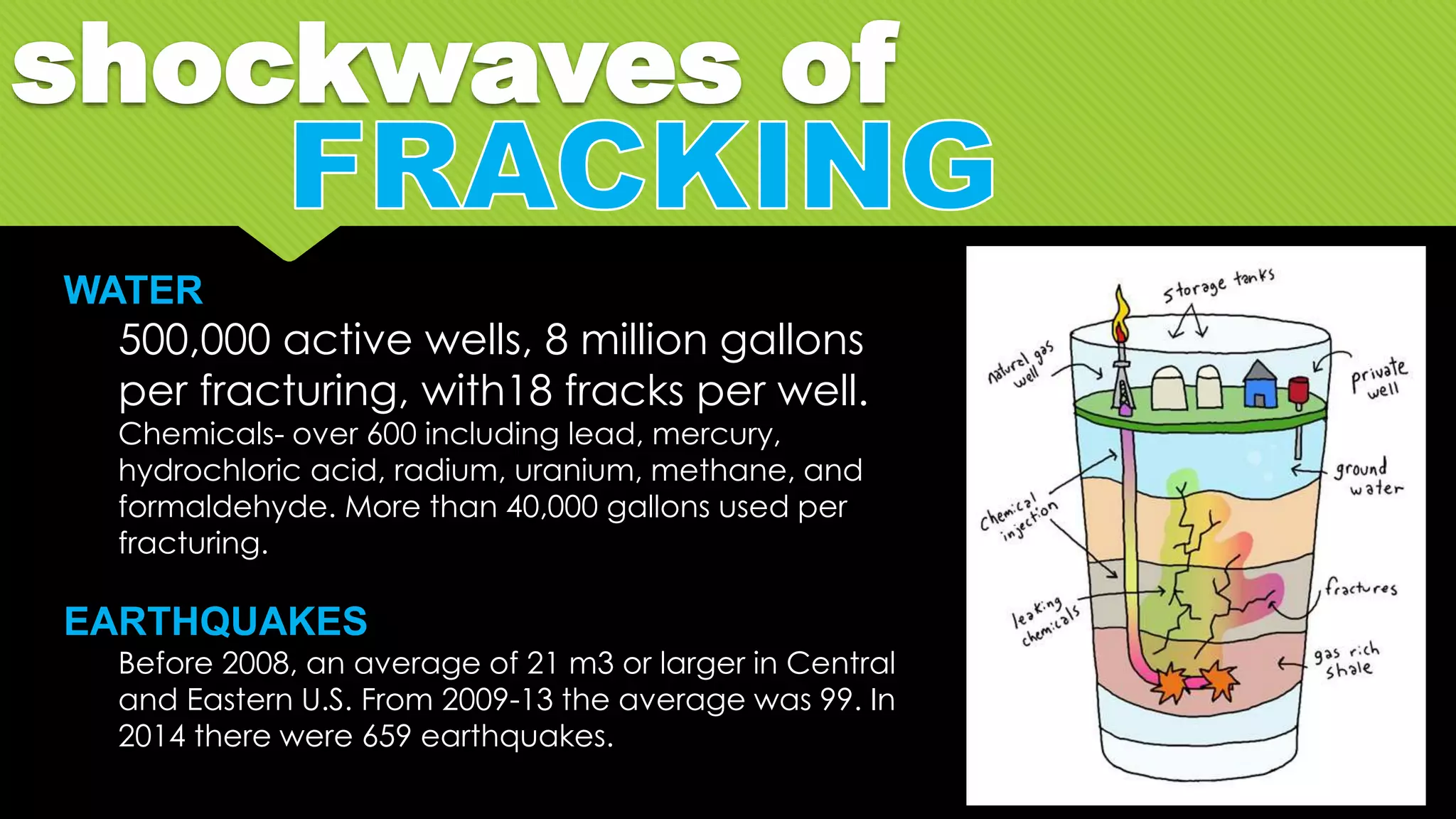
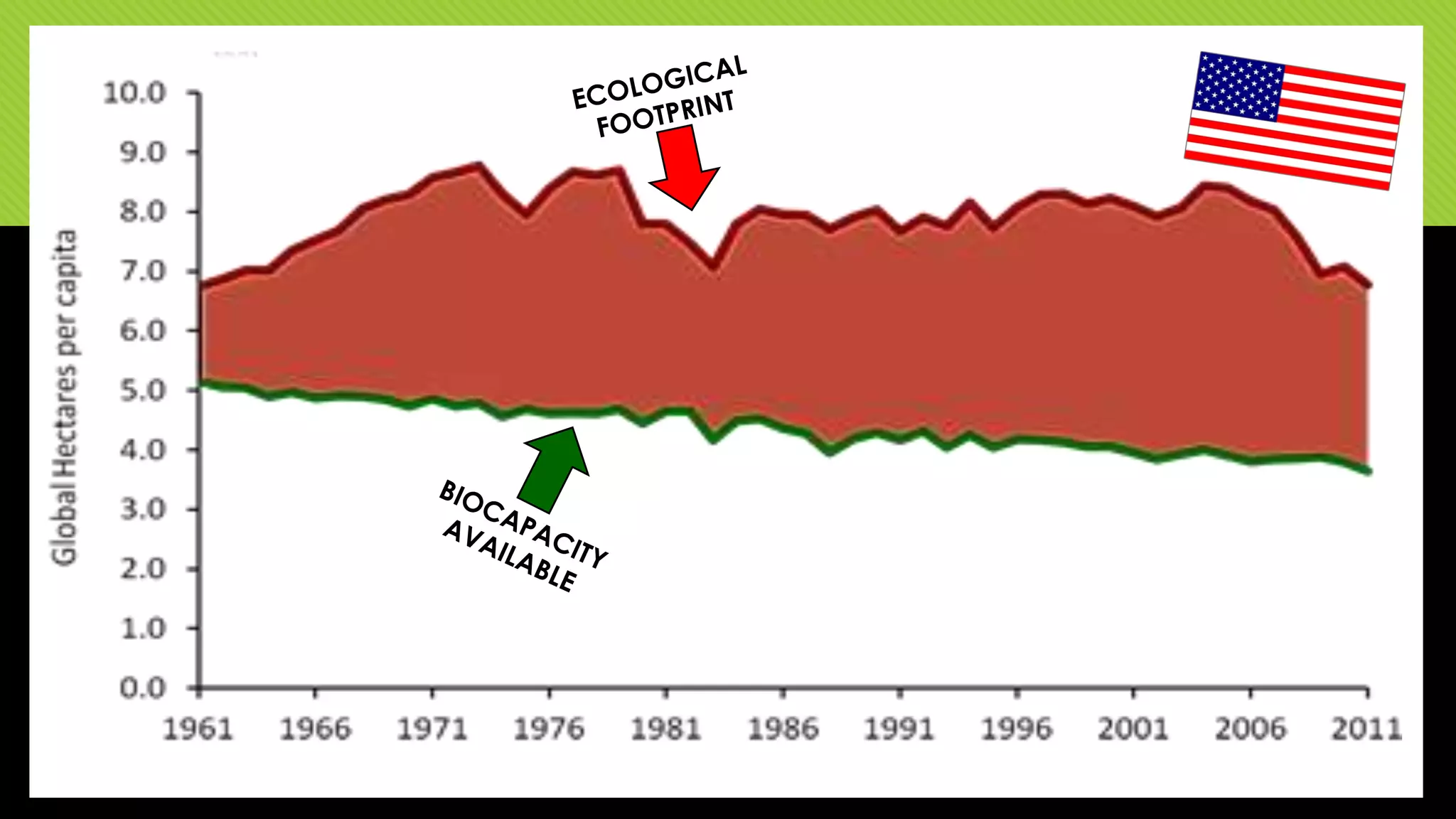
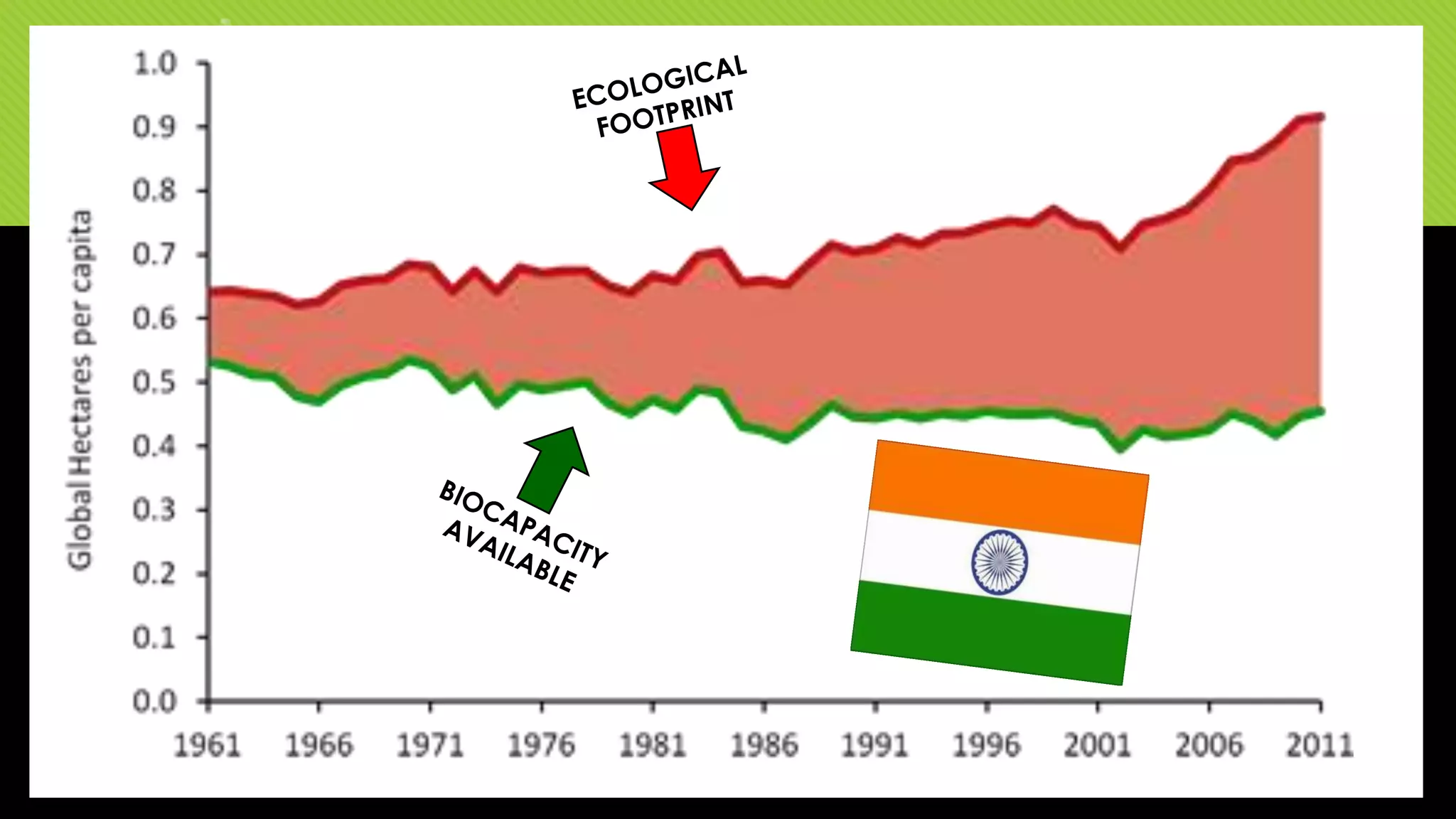
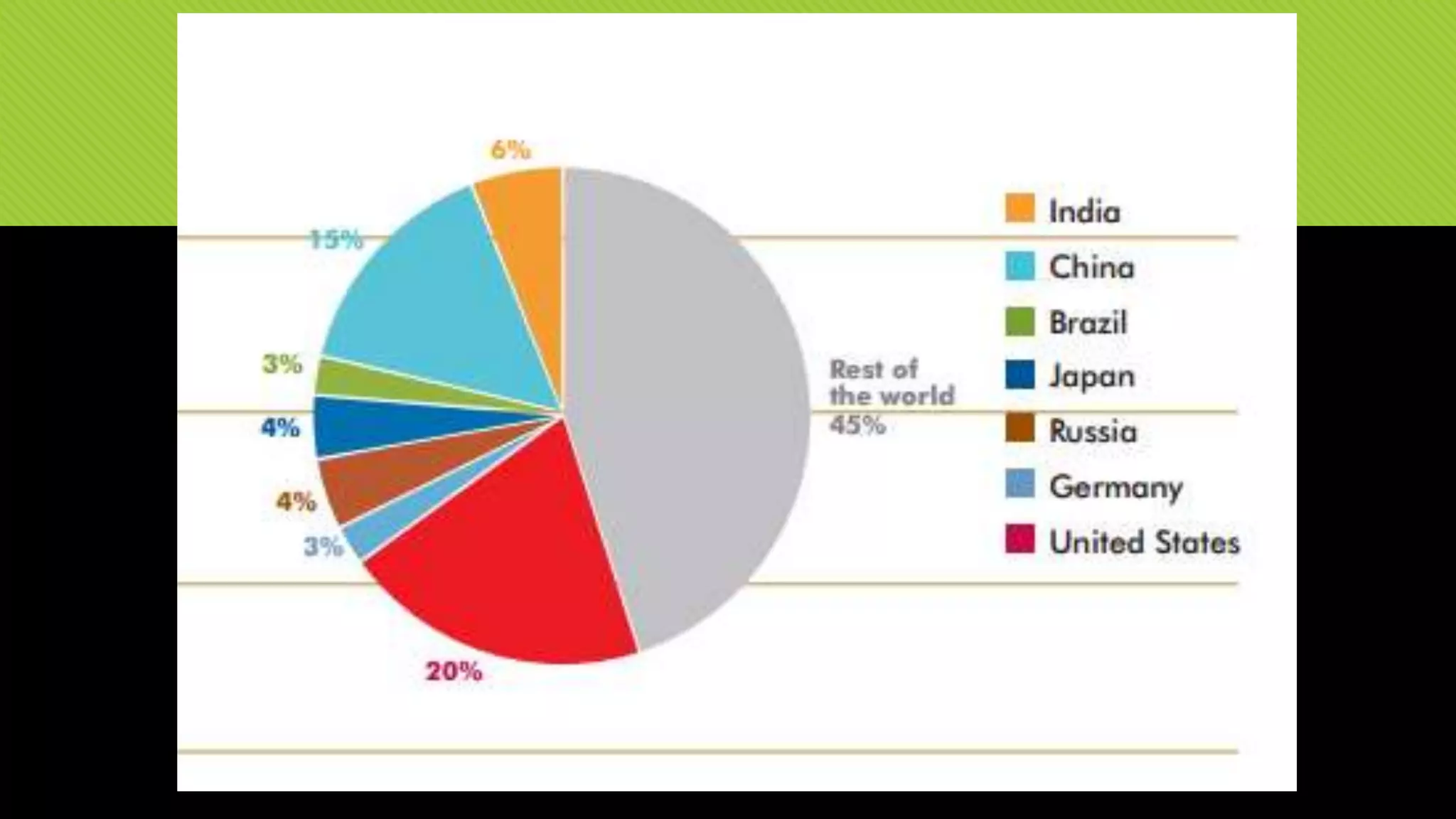
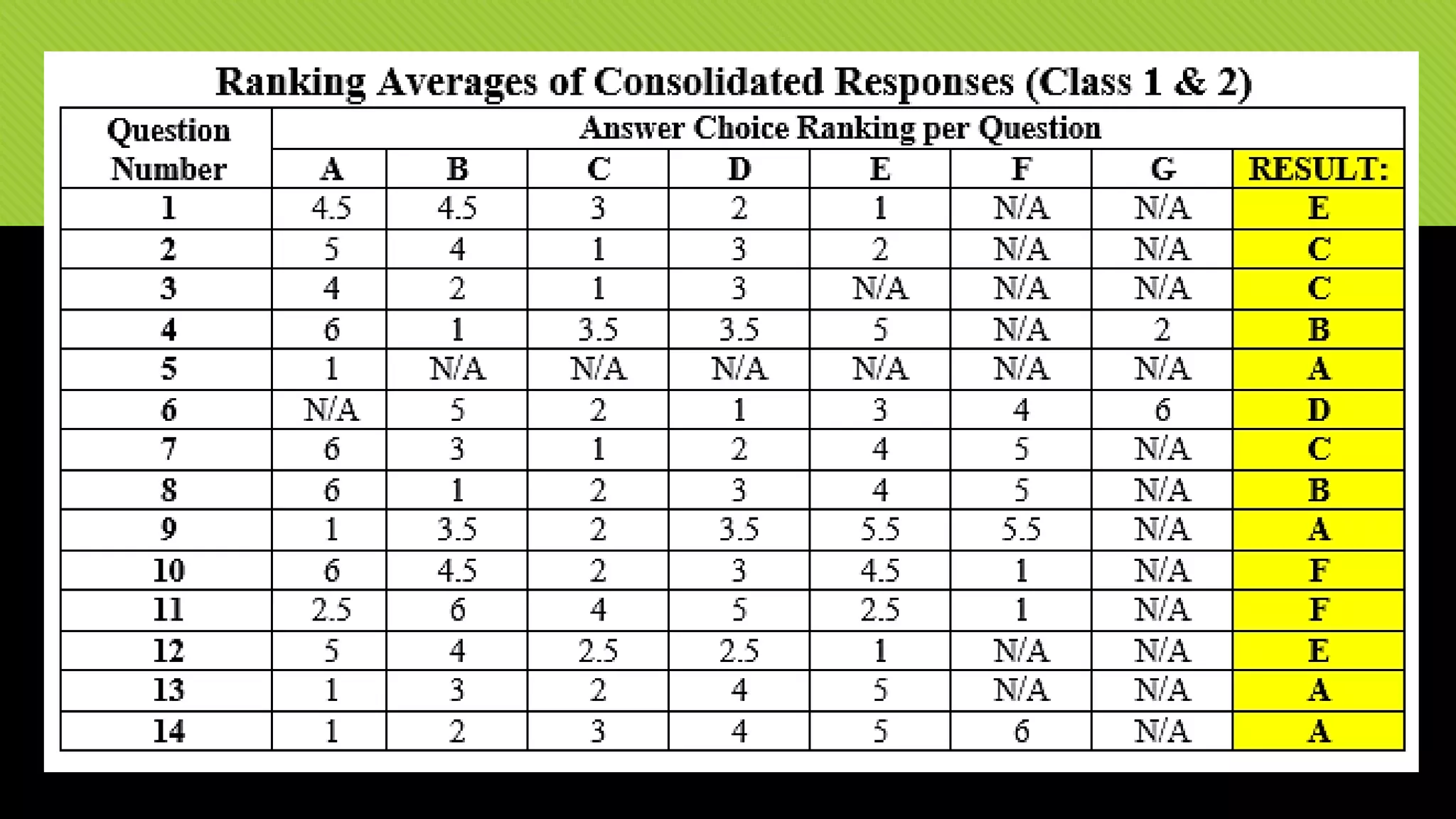
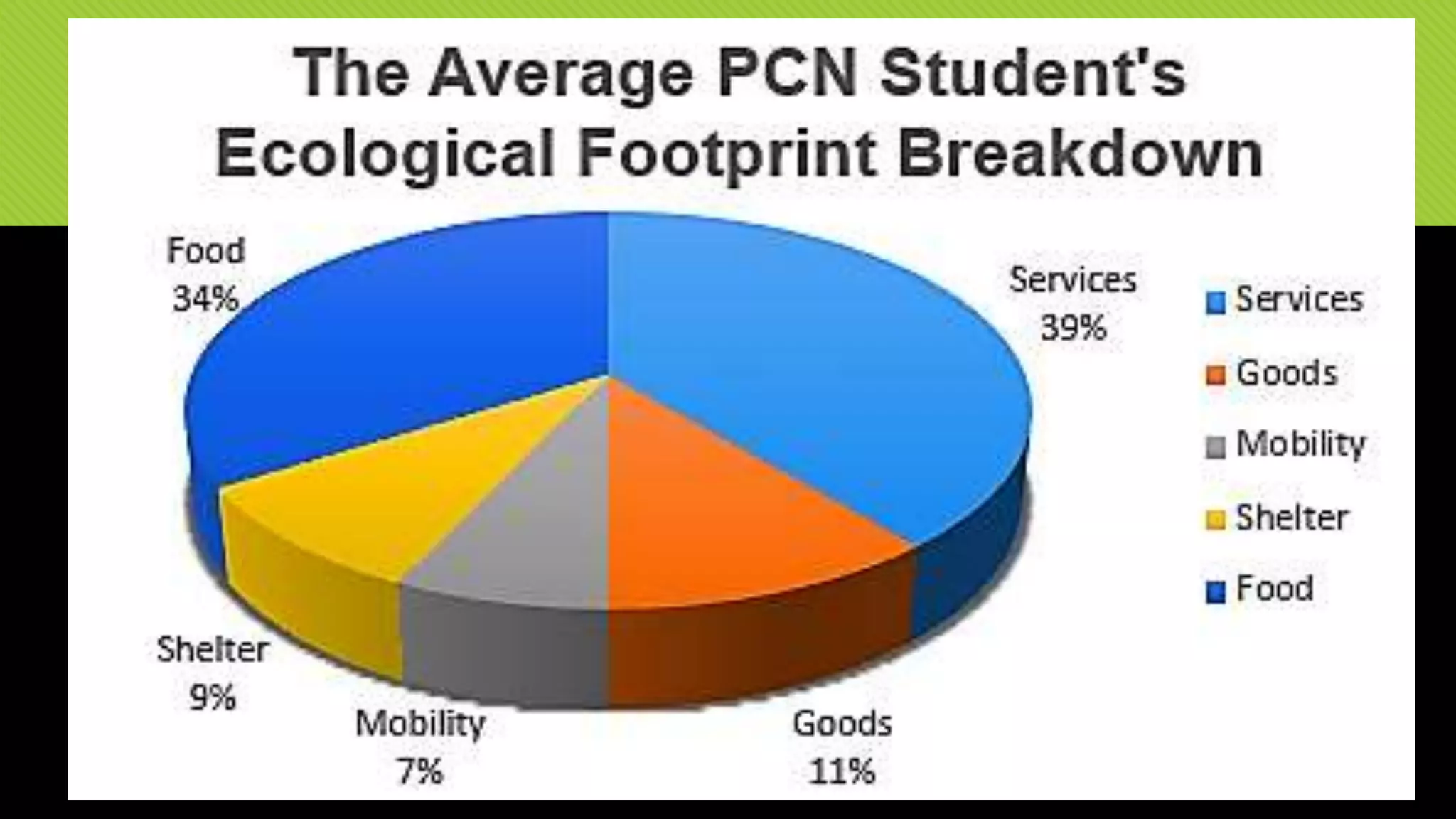
The document discusses whether Earth can sustain the resource demands of humanity, specifically the demands of a U.S. lifestyle. It finds that Earth cannot support a U.S. lifestyle for all people due to high consumption rates of fossil fuels, meat, paper and other resources. The U.S. uses disproportionately more resources than other countries despite having only 5% of the global population. Adopting more sustainable consumption patterns would reduce humanity's ecological footprint.