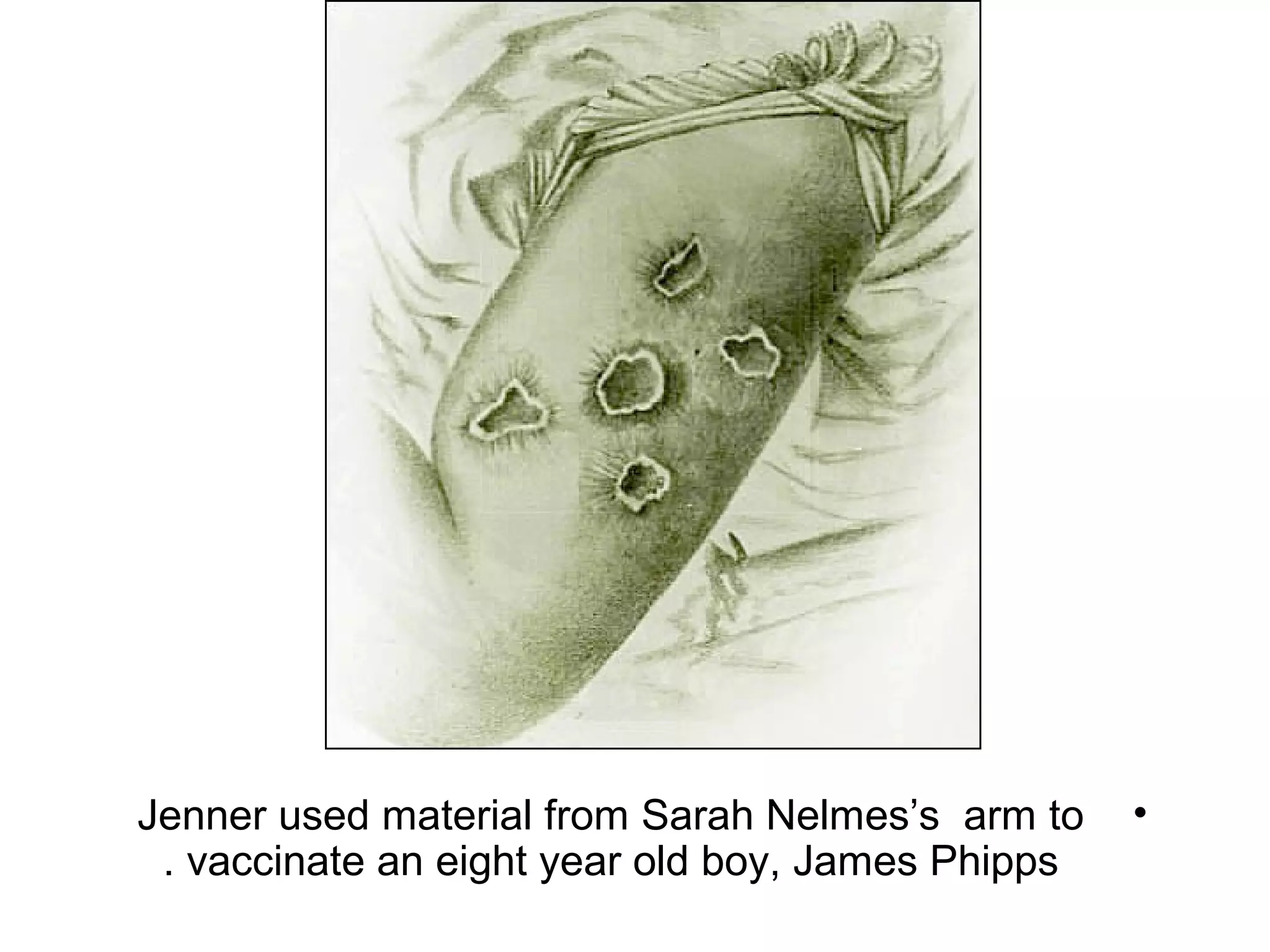
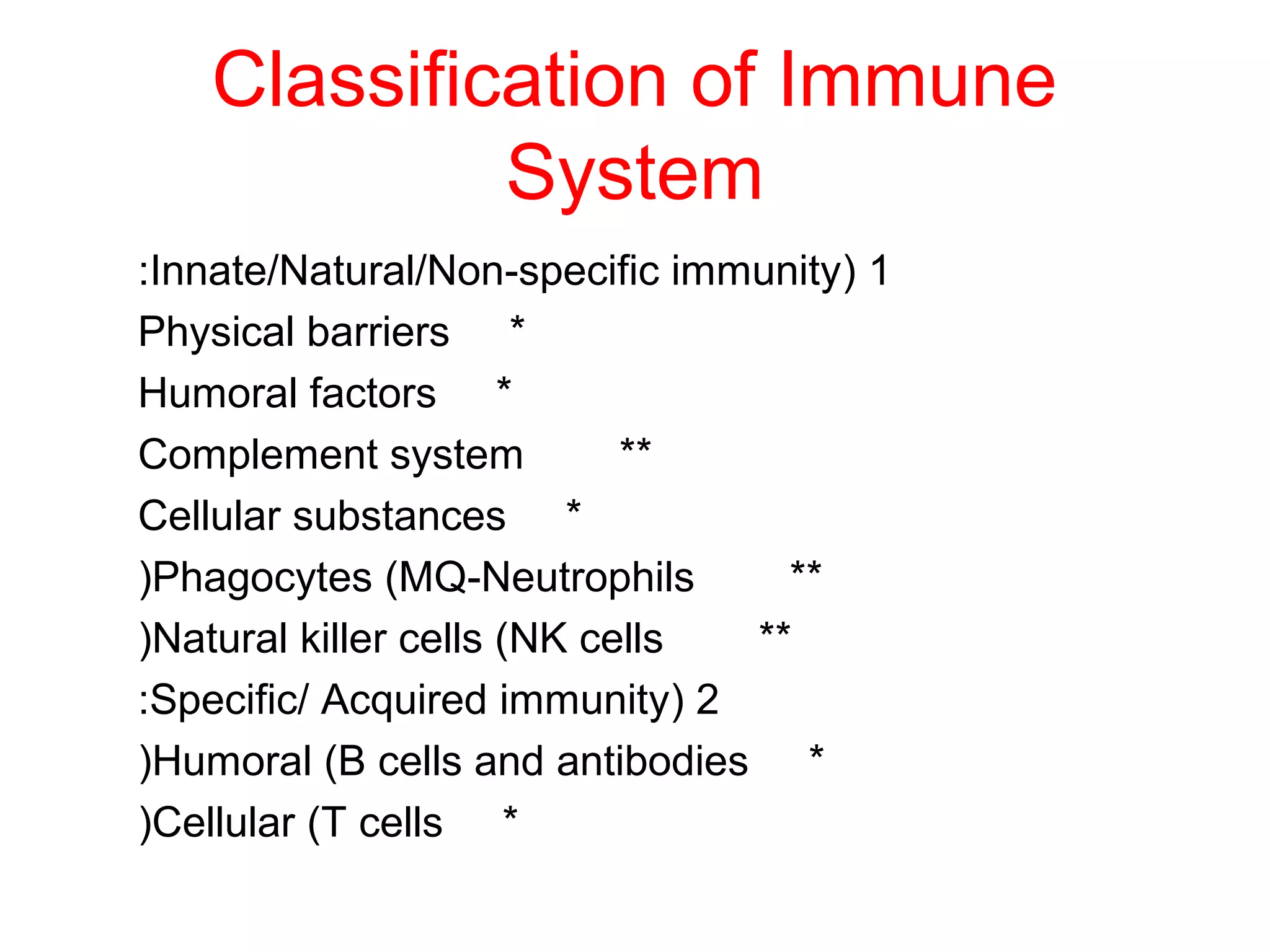
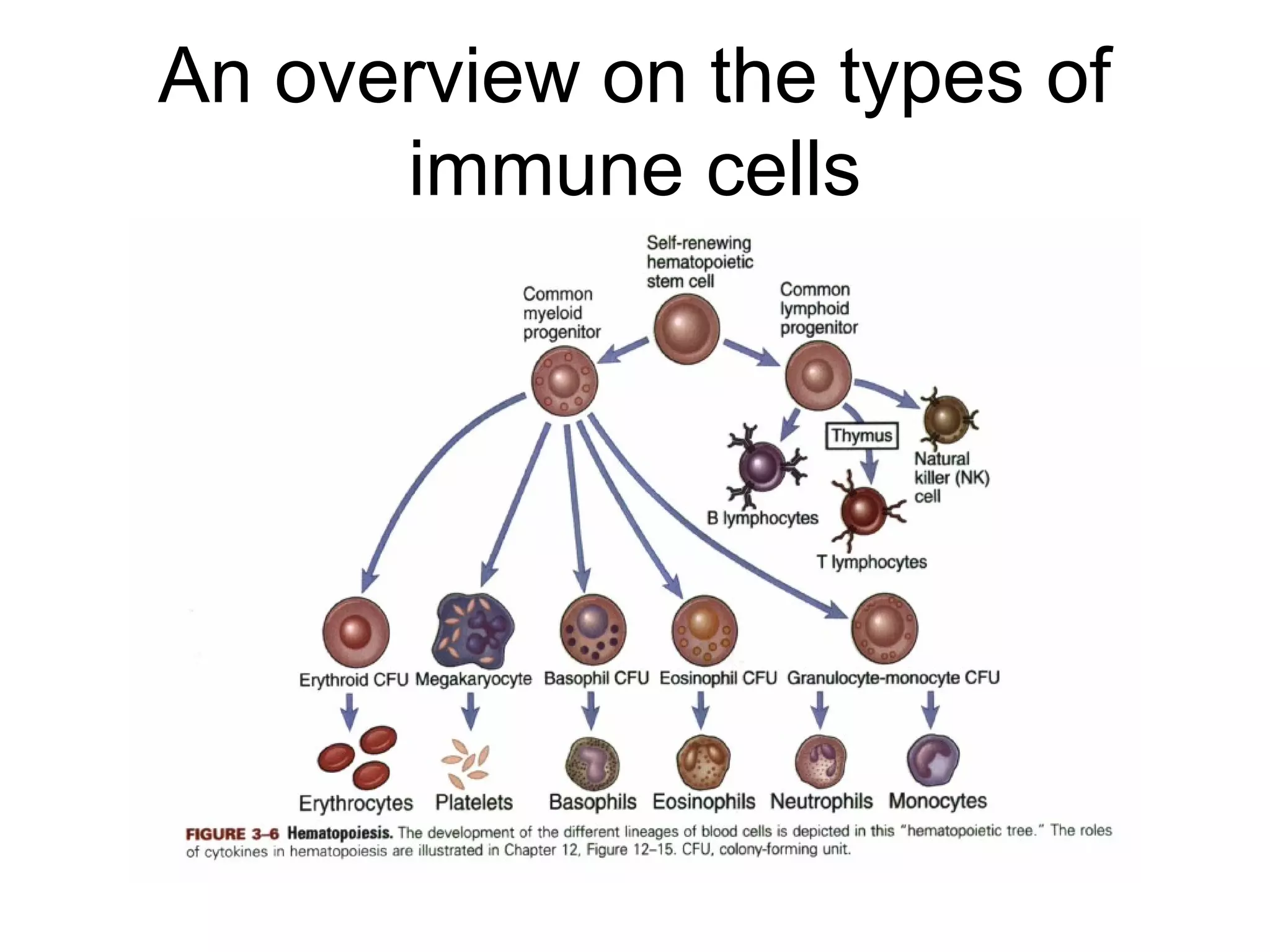
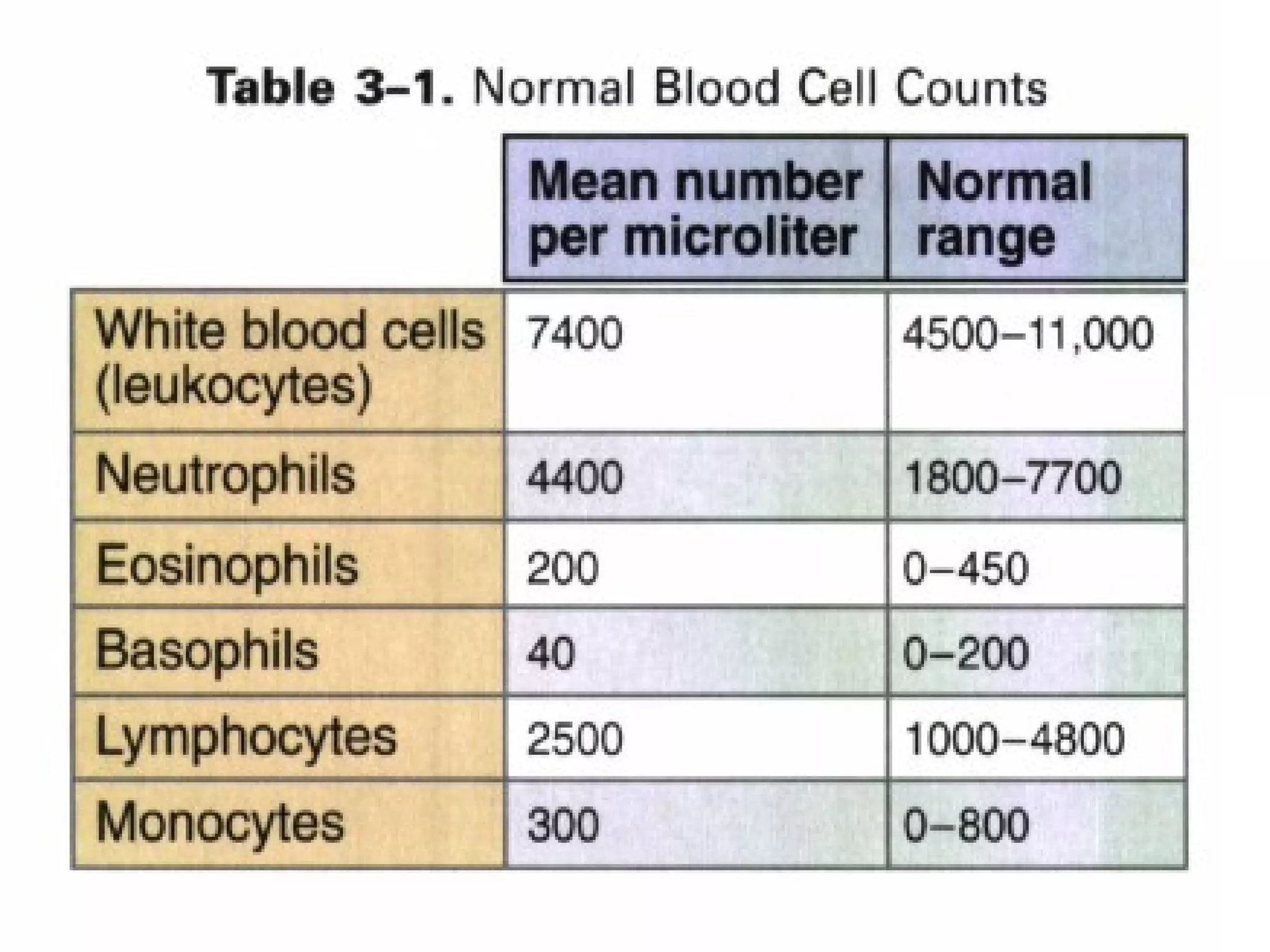
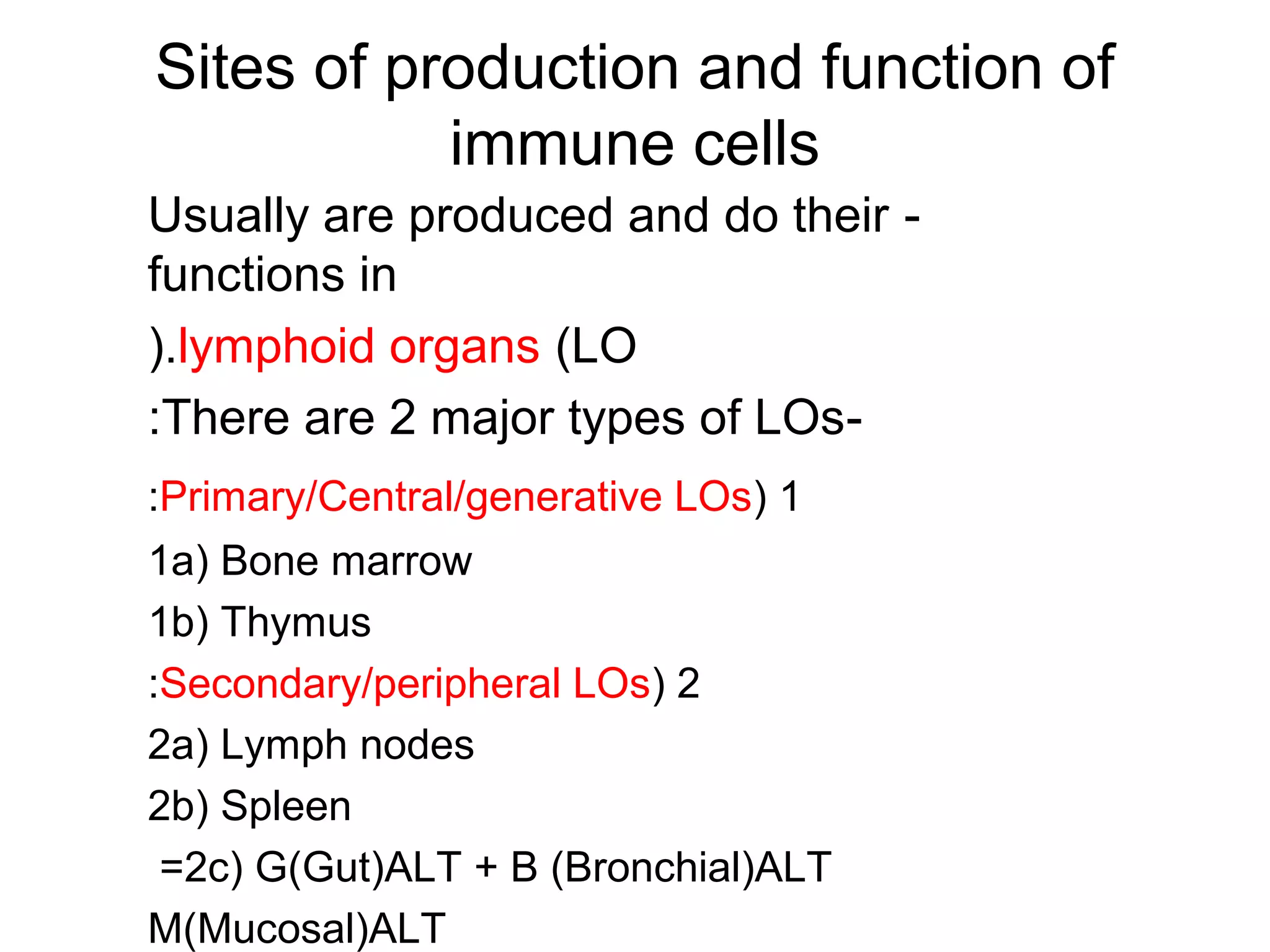
The document compares and contrasts specific and non-specific immunity. Both have similarities including self/non-self discrimination and homeostasis. Their differences are specificity and diversity and memory. Specific immunity can recognize pathogens it has previously encountered, while non-specific immunity cannot.