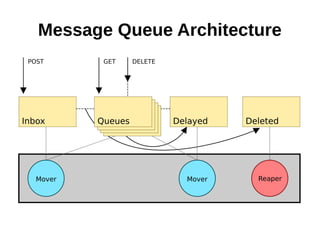
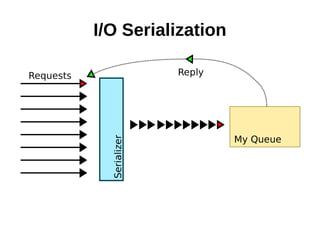
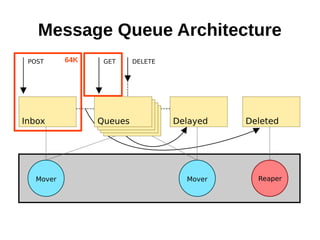
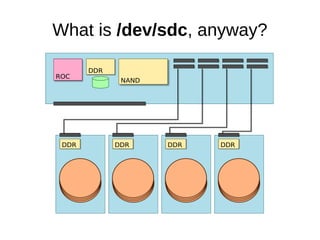
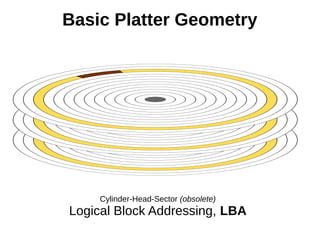
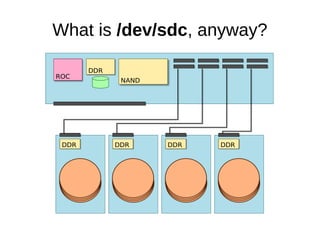
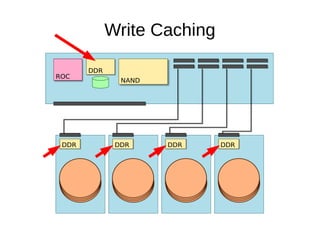
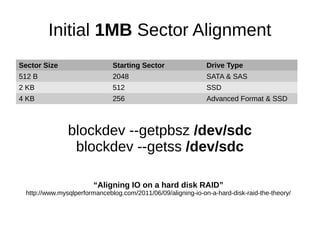
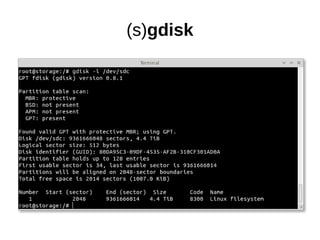
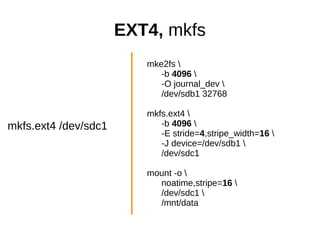
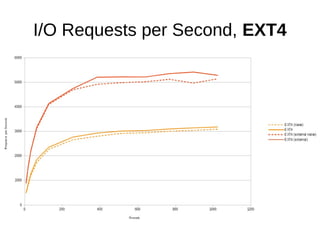
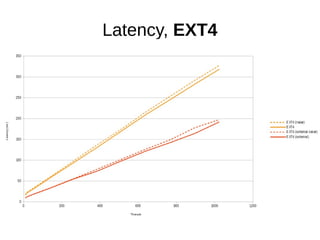
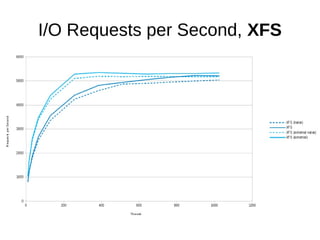
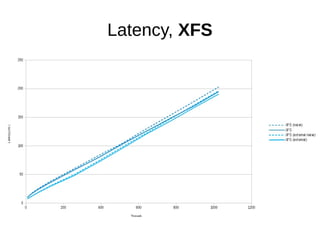
The document discusses optimizing file systems for efficient workflows, focusing on RAID configurations and file system choices like ext4 and XFS. It emphasizes the importance of cache management, benchmarking tools such as sysbench, and understanding I/O patterns for improved performance. Best practices for setup, configuration, and tuning are provided, along with references to further resources on file systems and MySQL performance.





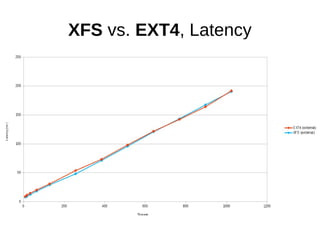
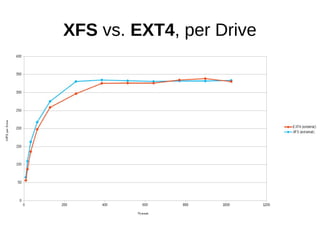
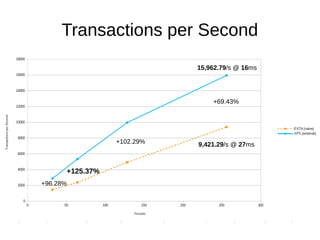
![sysbench, fileio
sysbench
--num-threads=[8-1024]
--test=fileio
--file-total-size=10G
--file-test-mode=rndwr
--file-fsync-all=on
--file-num=64
--file-block-size=16384
[prepare|run|cleanup]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/filesystems-130722163946-phpapp01/85/Exploiting-Your-File-System-to-Build-Robust-Efficient-Workflows-14-320.jpg)



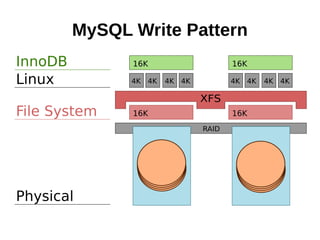
![sysbench, mysql
sysbench
--num-threads=[32|64|128|256]
--test=oltp
--oltp-test-mode=nontrx
--oltp-nontrx-mode=insert
--oltp-table-size=100000
--max-requests=10000000
[prepare|run|cleanup]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/filesystems-130722163946-phpapp01/85/Exploiting-Your-File-System-to-Build-Robust-Efficient-Workflows-27-320.jpg)
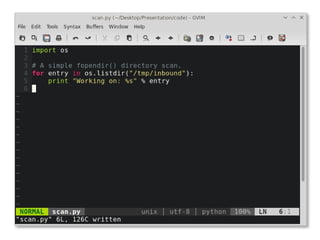
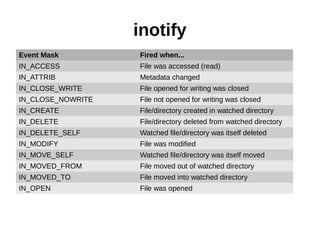
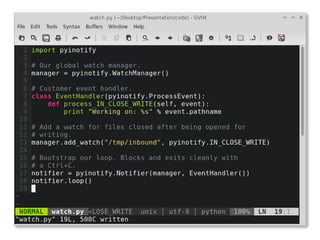
![inotify in [language]
Language Source
Python pip install pyinotify
PHP pecl install inotify
Go go's exp repository
Ruby gem install rb-inotify
C #include <sys/inotify.h>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/filesystems-130722163946-phpapp01/85/Exploiting-Your-File-System-to-Build-Robust-Efficient-Workflows-32-320.jpg)